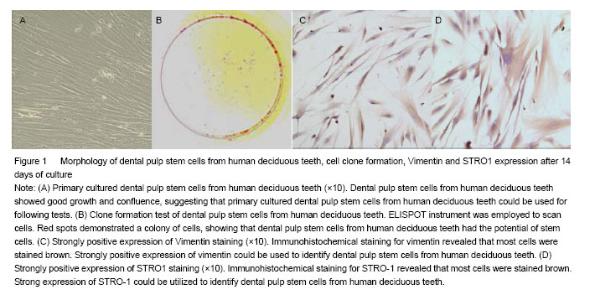
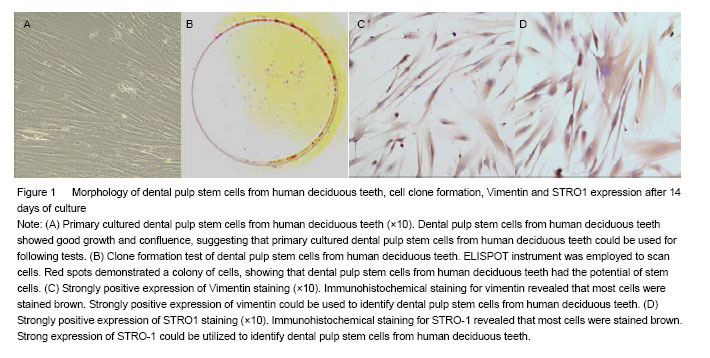
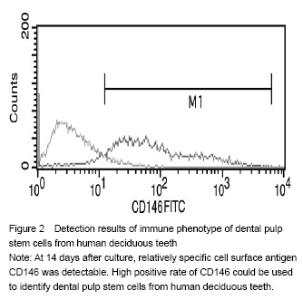
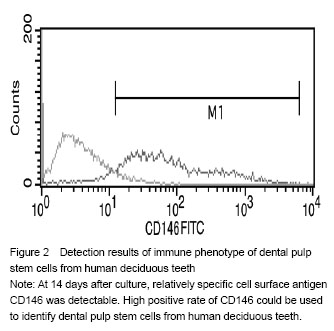
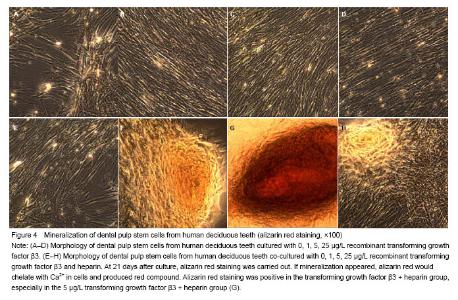
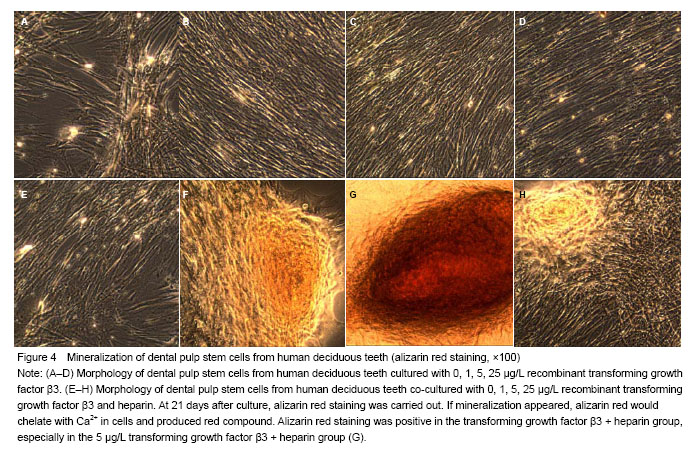
| [1]Miura M, Gronthos S, zhao M, et al. SHED: stem cells from human exfoliated deci- duous teeth. Cell Biol. 2003;100(10): 5807-5812.
[2]Hansen G, McIntire JJ, Yeung VP, et al. CD4(+)T helper cells engineered to produce latent TGF-beta1 reverse allergen-induced airway hyperreactivity and inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2000;105(1):61-70.
[3]Neurath MF, Finotto S, Glimcher LH. The role of Th1/Th2 polarization in mucosal immunity. Nat Med. 2002;8(6): 567-573.
[4]Sakai VT, Zhang Z, Dong Z, et al. SHED differentiate into functional odontoblasts and endothelium. J Dent Res. 2010; 89(8):791-796.
[5]Casagrande L, Demarco FF, Zhang Z, et al. Dentin -derived BMP-2 and odontoblast differentiation. J Dent Res. 2010; 89(6):603-608.
[6]Paula-Silva FW, Ghosh A, Silva LA, et al. TNF -alpha promotes an odontoblastic phenotype in dental pulp cells. J Dent Res. 2009;88(4):339-444.
[7]Bluteau G, Luder HU, De Bari C, et al. Stem cells for tooth engineering. Eur Cell Mater. 2008;31(16):1-9.
[8]Liu J, Jin TC, Chang S, et al. Matrix and TGF-beta-related gene expression during human dental pulp stem cell (DPSC) mineralization. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2007;43(3-4):120-128.
[9]Wang SN, Mu JQ, Fan ZP, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 can promote the osteogenic differentiation and osteogenesis of stem cells from apical papilla. Stem Cell Res. 2012;8(3):346-356.
[10]Yu Y, Mu JQ, Fan ZP, et al. Insulin-like growth factor 1 enhances the proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of human periodontal ligament stem cells via ERK and JNK MAPK pathways. Histochem Cell Biol. 2012;137(4): 513-525.
[11]He HX, Jin Y, Shi JN, et al. Effects of bFGF, TGF- β on proliferation and differentiation of human dental pulp cells the ability. 2004;14(7):359-363.
[12]Spradling A, Drummond-Barbosa D, Kai T. Stem cells find their niche. Nature. 2001;414:98-104.
[13]Karaoz E, Dogan BN, Aksov A, et al. Isolation and in vitro characterisation of dental pulp stem cells from natal teeth. Histochem Cell Biol. 2010;133(1):95-112.
[14]Sakai VT, Zhang Z, Dong Z, et al. SHED differentiate into functional odontoblasts and endothelium. J Dent Res. 2010; 89(8):791-796.
[15]Casagrande L, Demarco FF, Zhang Z, et al. Dentin-derived BMP-2 and odontoblast differentiation. J Dent Res. 2010; 89(6):603-608.
[16]Chadioiralla K, Yochim JM, Bahuleyan B, et al. Osteogenic differentiation of stem cells derived from human periodontal ligaments and pulp of human exfoliated deciduous teeth. Cell Tissue Res. 2012;340(2):323-333.
[17]Wang J, Wang X, Sun Z, et al. Stem cells from human-exfoliated deciduous teeth can differentiate into dopaminergic neuron-like cells. Stem Cells Dev. 2010; 19(9): 1375-1383.
[18]Morsczeck C, Vollner F, Saugspier M, et al. Comparison of human dental follicle cells (DFCs) and stem cells from human exfoliated deciduous teeth (SHED) after neural differentiation in vitro. Clin Oral Investig. 2010;14(4): 433-440.
[19]Gage FH. Mammalian neural stem cells. Science. 2000;287: 1433-1438.
[20]Prockop DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 1997;276:71-74.
[21]Weissman IL. Translating stem and progenitor cell biology to the clinic: barriers and opportunities. Science. 2000;287: 1442-1446.
[22]Pittenger MF, Mackay AM, Beck SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science 1999;284:143-147.
[23]Toma JG, Akhavan M, Fernandes KJ, et al. Isolation of multipotent adult stem cells from the dermis of mammalian skin. Nat Cell Biol. 2001;3:778-784.
[24]Gronthos S, Mankani M, Brahim J, et al. Postnatal human dental pulp stem cells (DPSCs) in vitro and in vivo. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2000;97:13625-13630.
[25]Feng MW. Kouqiang Shengwuxue. Beijing: People's Medical Publishing House. 2004
[26]Iohara K, Nakashima M, Ito M, et al. Dentin regeneration by dental pulp stem cell therapy with recombinant human bone morphogenetic protein 2. Dent Res. 2004;83:590-595.
[27]Bonewald LF, Mundy GR. Role of transforming growth factor beta in bone remodeling. Clin Orthop. 1990;250: 261-276.
[28]Feng YH, Diao ZH, Gao Y, et al. Ultrastructure changes of dog dental pulp cells transfected with bone morphogenetic proteins 2 in vitro. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012; 12(6):206-210.
[29]Yand X, Han G, Pang X, et al. Chitosan/collagen scaffold containing bone morphogenetic protein-7 Dna supports dental pulp stem cell differentiation in vitro and in vivo. J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012.
[30]Ding SS, Cui YL. heparin in the application of growth factors in the controlled release. Huaxue Jinzhan. 2008; 12(20):1998-2011.
[31]Rider CC. In Heparin/heparan sulphate binding in the TGF-beta cytokine superfamily. Biochem Soc Trans. 2006; 34(3):458-460.
[32]Lyon M, Rushton G, Gallagher JT. The Interaction of the Transforming Growth Factor- s with Heparin/Heparan Sulfate Is Isoform-specific. J Biol Chem. 1997;272(29): 18000-18006. |