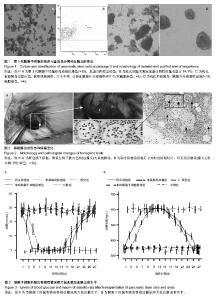
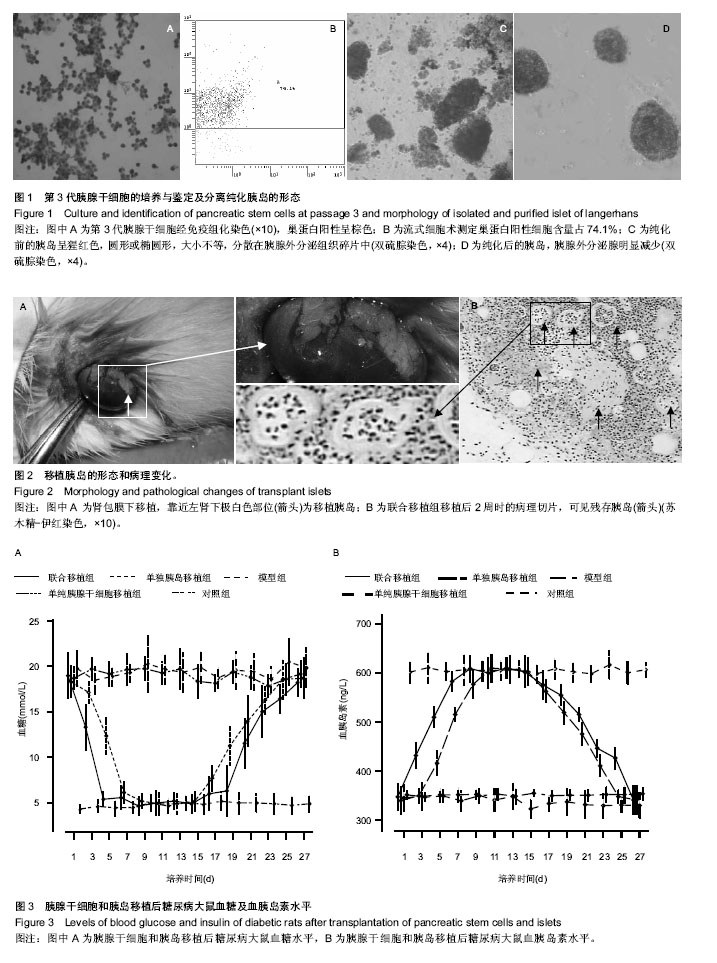
| [1] Shapiro AM, Lakey JR, Ryan EA, et al. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid-free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(4):230-238.
[2] Shapiro AM, Ricordi C, Hering BJ, et al. International trial of the Edmonton protocol for islet transplantation. N Engl J Med. 2006;355(13):1318-1330.
[3] 刘宝林,刘世庆,曹献馗.胰岛移植的临床与科研现状及展望[J].世界华人消化杂志,2011,20(33):3186-3190.
[4] 唐成佳,杜成友,刘定志,等.新鲜与短期培养胰岛细胞移植对移植胰岛存活的影响[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版, 2013,33(6): 763-767.
[5] 刘定志,杜成友,罗诗樵,等.三种消化酶分离胰岛对移植胰岛存活的影响[J].上海交通大学学报:医学版,2012,32(5):567-571.
[6] Prockop DJ, Gregory CA, Spees JL. One strategy for cell and gene therapy: harnessing the power of adult stem cells to repair tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100 Suppl 1: 11917-11923.
[7] Munoz JR, Stoutenger BR, Robinson AP, et al. Human stem/progenitor cells from bone marrow promote neurogenesis of endogenous neural stem cells in the hippocampus of mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005; 102(50):18171-18176.
[8] Spees JL, Olson SD, Ylostalo J, et al. Differentiation, cell fusion, and nuclear fusion during ex vivo repair of epithelium by human adult stem cells from bone marrow stroma. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2003;100(5):2397-2402.
[9] Spees JL, Olson SD, Whitney MJ, et al. Mitochondrial transfer between cells can rescue aerobic respiration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(5):1283-1288.
[10] Lee RH, Seo MJ, Reger RL, et al. Multipotent stromal cells from human marrow home to and promote repair of pancreatic islets and renal glomeruli in diabetic NOD/scid mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2006;103(46):17438-17443.
[11] Scuteri A, Cassetti A, Tredici G. Adult mesenchymal stem cells rescue dorsal root ganglia neurons from dying. Brain Res. 2006;1116(1):75-81.
[12] Baffour R, Pakala R, Hellinga D, et al. Bone marrow-derived stem cell interactions with adult cardiomyocytes and skeletal myoblasts in vitro. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2006;7(4): 222-230.
[13] Chang Liu Z, Chang TM. Coencapsulation of hepatocytes and bone marrow cells: in vitro and in vivo studies. Biotechnol Annu Rev. 2006;12:137-151.
[14] Lacy PE, Kostianovsky M. Method for the isolation of intact islets of Langerhans from the rat pancreas. Diabetes. 1967; 16(1):35-39.
[15] Fraidenraich D, Stillwell E, Romero E, et al. Rescue of cardiac defects in id knockout embryos by injection of embryonic stem cells. Science. 2004;306(5694):247-252.
[16] Kerr DA, Lladó J, Shamblott MJ, et al. Human embryonic germ cell derivatives facilitate motor recovery of rats with diffuse motor neuron injury. J Neurosci. 2003;23(12): 5131-5140.
[17] Lladó J, Haenggeli C, Maragakis NJ, et al. Neural stem cells protect against glutamate-induced excitotoxicity and promote survival of injured motor neurons through the secretion of neurotrophic factors. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2004;27(3):322-331.
[18] Johansson U, Elgue G, Nilsson B, et al. Composite islet-endothelial cell grafts: a novel approach to counteract innate immunity in islet transplantation. Am J Transplant. 2005;5(11):2632-2639.
[19] 贺德,詹文华,彭翔,等.Sertoli细胞诱导大鼠肝内胰岛移植物免疫豁免的实验研究[J].中华实验外科杂志,2004,21(9):1056-1057.
[20] Soto-Montenegro L, Zugasti-Murillo A, Rollán E, et al. Influence of hepatocyte-rich liver cell mixture and liver fibroblasts on prolonging graft islet survival in rats without immunosuppressive drugs. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2004;112(10):580-586.
[21] Yin Z, Wu W, Fung JJ, et al. Cotransplanted hepatic stellate cells enhance vascularization of islet allografts. Microsurgery. 2007;27(4):324-327.
[22] Oh BJ, Oh SH, Jin SM, et al. Co-transplantation of bone marrow-derived endothelial progenitor cells improves revascularization and organization in islet grafts. Am J Transplant. 2013;13(6):1429-1440.
[23] Rackham CL, Dhadda PK, Chagastelles PC, et al. Pre-culturing islets with mesenchymal stromal cells using a direct contact configuration is beneficial for transplantation outcome in diabetic mice. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(4):449-459.
[24] Rackham CL, Jones PM, King AJ. Maintenance of islet morphology is beneficial for transplantation outcome in diabetic mice. PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e57844.
[25] Kerby A, Jones ES, Jones PM, et al. Co-transplantation of islets with mesenchymal stem cells in microcapsules demonstrates graft outcome can be improved in an isolated-graft model of islet transplantation in mice. Cytotherapy. 2013;15(2):192-200.
[26] Olerud J, Kanaykina N, Vasylovska S, et al. Neural crest stem cells increase beta cell proliferation and improve islet function in co-transplanted murine pancreatic islets. Diabetologia. 2009; 52(12):2594-2601.
[27] 张育森,周汉新,张悦,等.与胎鼠胰腺干细胞共培养保护大鼠胰岛活性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(12): 2313-2316.
[28] 周淑艳,张毅,齐晖,等.保护胰岛β细胞的体外研究进展[J].生命科学,2012,24(10):1207-1210.
[29] Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005; 105(4):1815-1822.
[30] Bonde S, Zavazava N. Immunogenicity and engraftment of mouse embryonic stem cells in allogeneic recipients. Stem Cells. 2006;24(10):2192-2201..
[31] Einstein O, Fainstein N, Vaknin I, et al. Neural precursors attenuate autoimmune encephalomyelitis by peripheral immunosuppression. Ann Neurol. 2007;61(3):209-218.
[32] 张剑,张琪,张英才,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对异种胰岛移植排斥反应的影响[J].器官移植,2011,2(6):350-353.
[33] Perez-Basterrechea M, Obaya AJ, Meana A, et al. Cooperation by fibroblasts and bone marrow-mesenchymal stem cells to improve pancreatic rat-to-mouse islet xenotransplantation. PLoS One. 2013;8(8):e73526. |