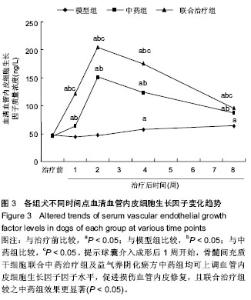
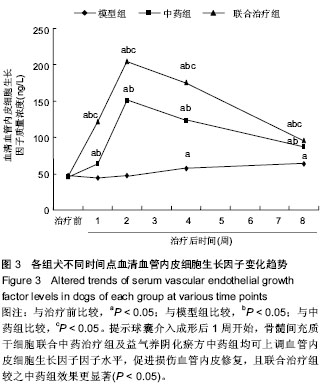
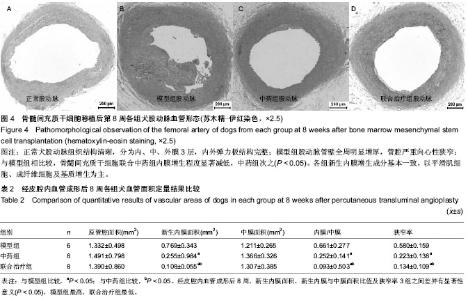
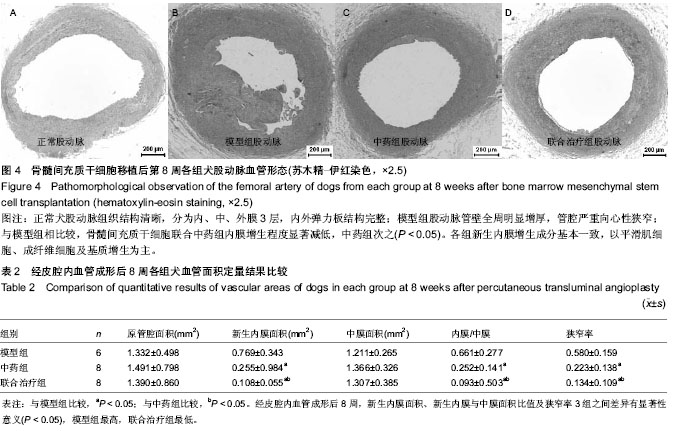
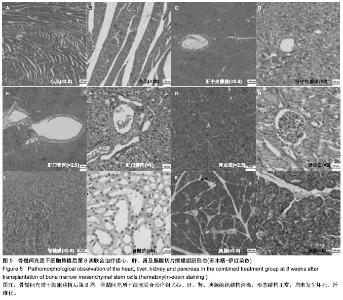
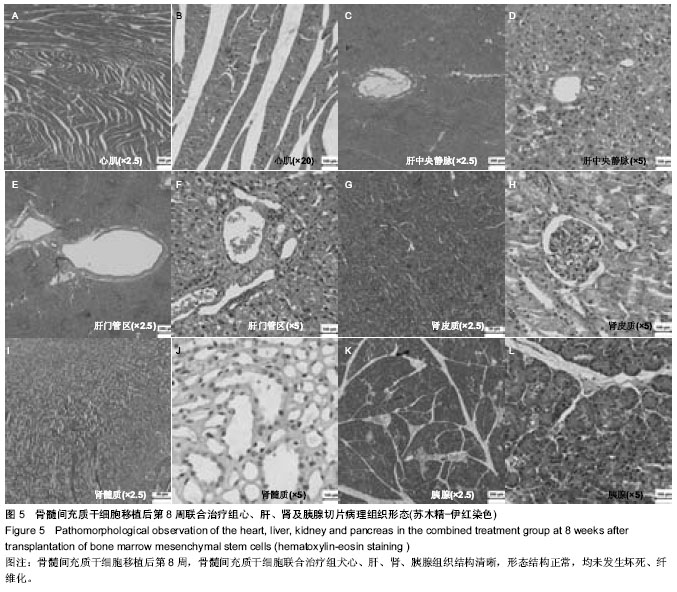
| [1] Min SK, Kenagy RD, Clowes AW. Induction of vascular atrophy as a novel approach to treating restenosis. A review. J Vasc Surg. 2008;47(3):662-670.
[2] Liistro F, Porto I, Angioli P, et al. Drug-eluting balloon in peripheral intervention for below the knee angioplasty evaluation (DEBATE-BTK): a randomized trial in diabetic patients with critical limb ischemia. Circulation. 2013;128(6): 615-621.
[3] 张文利,黄定. PCI术后冠状动脉再狭窄机制及防治研究进展[J].中国循证心血管医学杂志,2011,3(2):154-156.
[4] 韩劲草,刘喜林,顾海波,等.同强度不同波长β射线培养液对兔血管平滑肌细胞生长的影响[J].中国医药导刊,2004,6(1):39-40, 44.
[5] Niccoli G, Sgueglia GA, Montone RA, et al. Evolving management of patients treated by drug-eluting stent: Prevention of late events. Cardiovasc Revasc Med. 2014.
[6] Kallidonis PS, Georgiopoulos IS, Kyriazis ID, et al. Drug-eluting metallic stents in urology. Indian J Urol. 2014; 30(1):8-12.
[7] Bradshaw AC, Baker AH. Gene therapy for cardiovascular disease: perspectives and potential. Vascul Pharmacol. 2013;58(3):174-181.
[8] Chen LJ, Lim SH, Yeh YT, et al. Roles of microRNAs in atherosclerosis and restenosis. J Biomed Sci. 2012;19(1):79.
[9] Vassalli G, Vanderheyden M, Renders F, et al. Bone marrow stem cell therapy for cardiac repair: challenges and perspectives. Minerva Cardioangiol. 2007;55(5):659-667.
[10] Knight MN, Hankenson KD. Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Bone Regeneration. Adv Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2013;2(6): 306-316.
[11] Ikebe C, Suzuki K. Mesenchymal Stem Cells for Regenerative Therapy: Optimization of Cell Preparation Protocols. Biomed Res Int. 2014;2014:951512.
[12] Harada M, Qin Y, Takano H, et al. G-CSF prevents cardiac remodeling after myocardial infarction by activating the Jak-Stat pathway in cardiomyocytes. Nat Med. 2005;11(3): 305-311.
[13] 杜冠华,张均田.丹参现代研究概况与进展(续一)[J].医药导报, 2004,23(6):355-360.
[14] 林蓉,刘俊田,李旭,等.川芎嗪对血管内皮细胞损伤的保护作用[J].中国药理学与毒力学杂志,2000,14(6):425.
[15] 李秋梅.益气活血解毒方和血府逐瘀胶囊对家兔PTA术后再狭窄的防治作用研究[D].北京中医药大学,2004.
[16] 侯霄雷,李白翎,赵雷,等. 血府逐瘀胶囊对急性心肌梗死再灌注后心肌及内皮素-1、一氧化氮/一氧化氮合酶体系影响的实验研究[J].中西医结合学报,2008,6(4):381-386.
[17] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.
[18] Jelodar G, Razmi N, Gholampour V. Arginase alteration in the reproductive system of alloxan-diabetic dogs. J Reprod Dev. 2007;53(2):317-321.
[19] Manhiani MM, Cormican MT, Brands MW. Chronic sodium-retaining action of insulin in diabetic dogs. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2011;300(4):F957-965.
[20] 周贤用,傅红兴,刘云西,等. 1例Beagle犬的糖尿病建模分析[J].中国医药科学,2011,1(15):46-47.
[21] 王立梅,崔晓兰,丁明超,等. 自体骨髓间充质干细胞经动脉介入移植治疗犬糖尿病[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(19): 3545-3550.
[22] Won KB, Chang HJ, Hong SJ, et al. Prognostic usefulness of metabolic syndrome compared with diabetes in Korean patients with critical lower limb ischemia treated with percutaneous transluminal angioplasty. Yonsei Med J. 2014;55(1):46-52.
[23] Rekik S, Brunet J, Bayet G, et al. Percutaneous management of lower limb ischemia after the use of vascular closure devices. Can J Cardiol. 2013;29(11):1448-1453.
[24] Naleem A, Zaman A, Low K, et al. Functional lengths of the lower limb arterial tree measured by CT angiography centreline analysis: implications for catheter lengths in peripheral angioplasty. Surg Radiol Anat. 2013. [Epub ahead of print]
[25] Forte A, Rinaldi B, Sodano L, et al. Stem cell therapy for arterial restenosis: potential parameters contributing to the success of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2012;26(1):9-21.
[26] Oda Y, Tani K, Kanei T, et al. Characterization of neuron-like cells derived from canine bone marrow stromal cells. Vet Res Commun. 2013;37(2):133-138.
[27] Zhang W, Zhang F, Shi H, et al. Comparisons of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell isolation and culture methods in vitro. PLoS One. 2014;9(2):e88794.
[28] Li Q, Wang Z. Influence of mesenchymal stem cells with endothelial progenitor cells in co-culture on osteogenesis and angiogenesis: an in vitro study. Arch Med Res. 2013; 44(7):504-513.
[29] Kisiel AH, Mcduffee LA, Masaoud E, et al. Isolation, characterization, and in vitro proliferation of canine mesenchymal stem cells derived from bone marrow, adipose tissue, muscle, and periosteum. Am J Vet Res. 2012;73(8): 1305-1317.
[30] Volk SW, Wang Y, Hankenson KD. Effects of donor characteristics and ex vivo expansion on canine mesenchymal stem cell properties: implications for MSC-based therapies. Cell Transplant. 2012;21(10):2189- 2200.
[31] Sauerzweig S, Munsch T, Lessmann V, et al. A population of serum deprivation-induced bone marrow stem cells (SD-BMSC) expresses marker typical for embryonic and neural stem cells. Exp Cell Res. 2009;315(1):50-66.
[32] Hall SR, Jiang Y, Leary E, et al. Identification and isolation of small CD44-negative mesenchymal stem/progenitor cells from human bone marrow using elutriation and polychromatic flow cytometry. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2013;2(8):567-578.
[33] Chan AK, Heathman TR, Coopman K, et al. Multiparameter flow cytometry for the characterisation of extracellular markers on human mesenchymal stem cells. Biotechnol Lett. 2014;36(4):731-741.
[34] Feisst V, Brooks AE, Chen CJ, et al. Characterization of mesenchymal progenitor cell populations directly derived from human dermis. Stem Cells Dev. 2014;23(6):631-642.
[35] 廖耿,舒崖清,胡学强. 丹红注射液对家兔颈动脉PTA术后内膜增生及bFGF、TF表达的影响[J].中华神经医学杂志,2011,10(7): 673-678.
[36] Folkman J, Klagsbrun M. Angiogenic factors. Science. 1987; 235(4787):442-447.
[37] van der Zee R, Murohara T, Luo Z, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor/vascular permeability factor augments nitric oxide release from quiescent rabbit and human vascular endothelium. Circulation. 1997;95(4):1030-1037.
[38] Reyes M, Lund T, Lenvik T, et al. Purification and ex vivo expansion of postnatal human marrow mesodermal progenitor cells. Blood. 2001;98(9):2615-2625.
[39] Galmiche MC, Koteliansky VE, Briere J, et al. Stromal cells from human long-term marrow cultures are mesenchymal cells that differentiate following a vascular smooth muscle differentiation pathway. Blood. 1993;82(1):66-76.
[40] Oswald J, Boxberger S, Jorgensen B, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells can be differentiated into endothelial cells in vitro. Stem Cells. 2004;22(3):377-384.
[41] Silva GV, Litovsky S, Assad JA, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into an endothelial phenotype, enhance vascular density, and improve heart function in a canine chronic ischemia model. Circulation. 2005;111(2):150-156. |