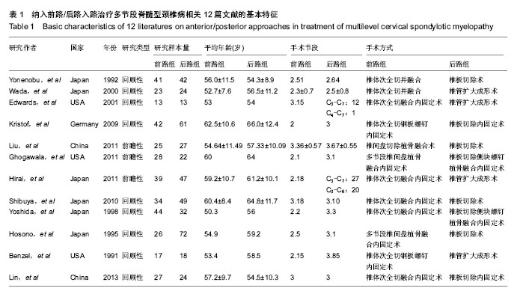
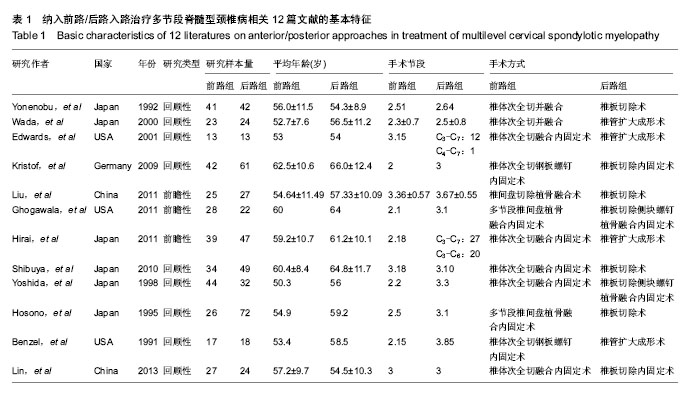
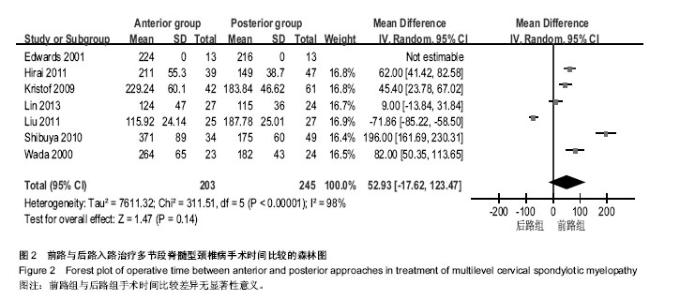
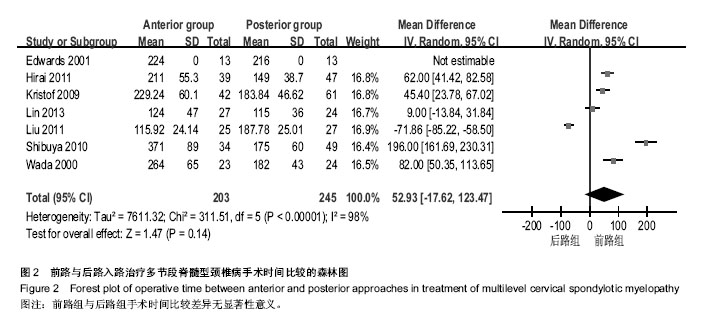
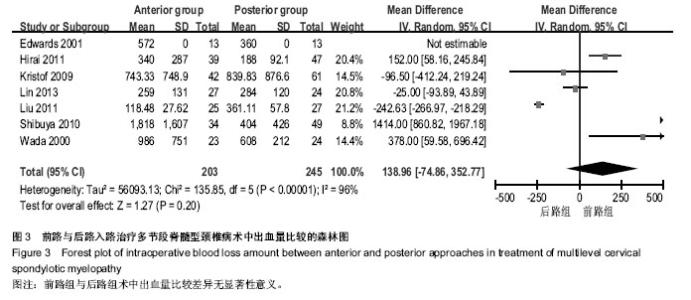
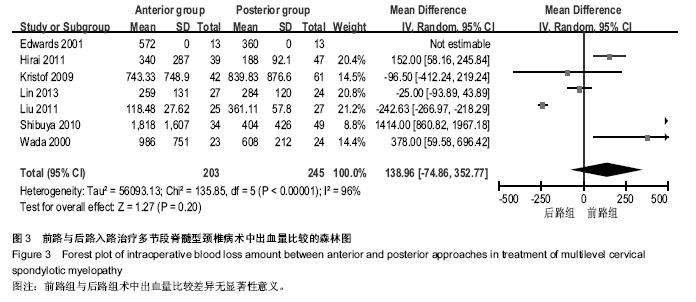
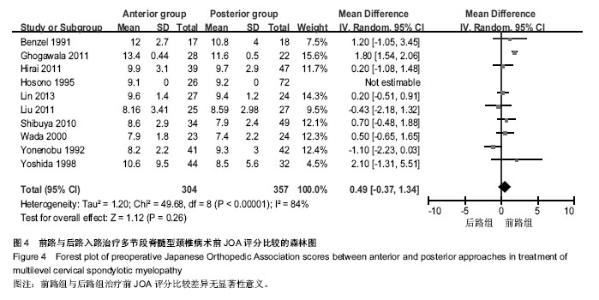
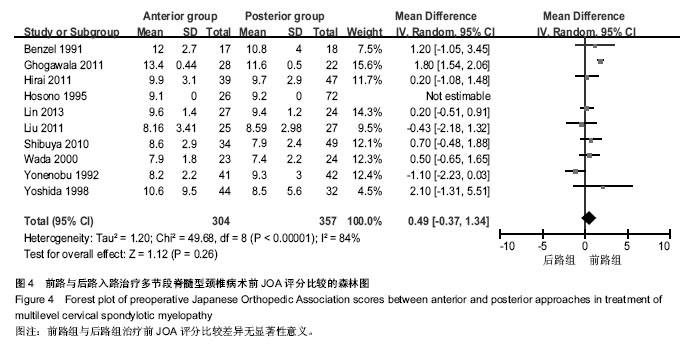
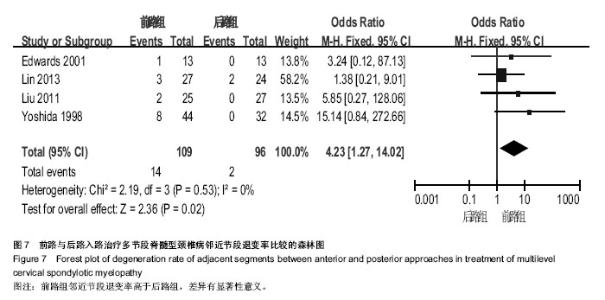
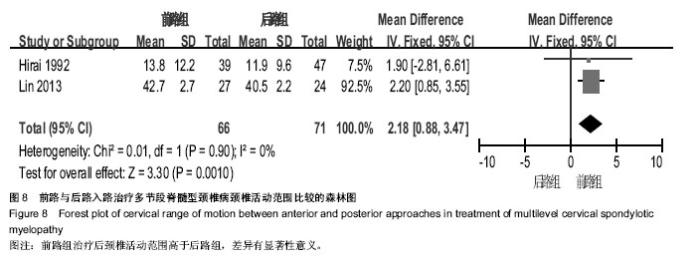
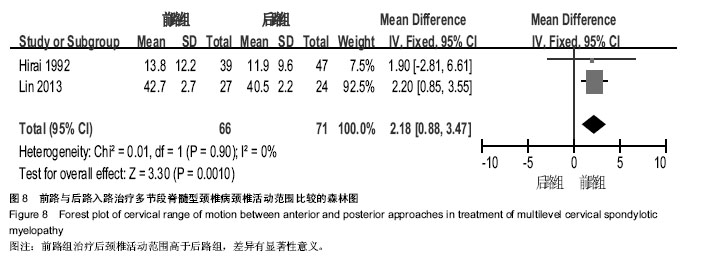
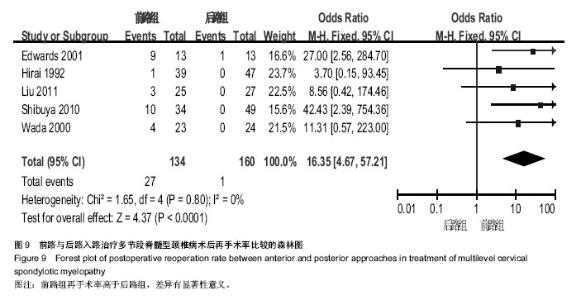
| [1] Edwards CC 2nd, Riew KD, Anderson PA,et al.Cervical myelopathy. current diagnostic and treatment strategies.Spine J. 2003;3(1):68-81.
[2] Muthukumar N.Surgical management of cervical spondylotic myelopathy.Neurol India. 2012;60(2):201-209.
[3] 祁敏,王新伟,刘洋,等.三种颈前路减压术式治疗多节段脊髓型颈椎病的并发症比较[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2012,22(11):963-968.
[4] Miyata K, Marui T, Miura J,et al.Kinetic analysis of the cervical spinal cord in patients after spinous process-splitting laminoplasty using a kinematic magnetic resonance imaging technique.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2006;31(19):E690-E697.
[5] 刘永恒, 张明友, 周其璋. 改良颈椎管扩大成形术治疗脊髓型颈椎病[J]. 中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2006,21(2):120-121.
[6] Woods BI, Hohl J, Lee J,et al.Laminoplasty versus laminectomy and fusion for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy.Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2011;469(3):688-695.
[7] Cabraja M, Abbushi A, Koeppen D,et al.Comparison between anterior and posterior decompression with instrumentation for cervical spondylotic myelopathy: sagittal alignment and clinical outcome.Neurosurg Focus. 2010;28(3):E15.
[8] Guo Q, Bi X, Ni B, Lu X,et al.Outcomes of three anterior decompression and fusion techniques in the treatment of three-level cervical spondylosis.Eur Spine J. 2011; 20(9): 1539-1544.
[9] Yonenobu K, Hosono N, Iwasaki M,et al.Laminoplasty versus subtotal corpectomy. A comparative study of results in multisegmental cervical spondylotic myelopathy.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1992;17(11):1281-1284.
[10] Wada E, Suzuki S, Kanazawa A,et al.Subtotal corpectomy versus laminoplasty for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy: a long-term follow-up study over 10 years.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2001;26(13):1443-1447.
[11] Edwards CC 2nd, Heller JG, Murakami H.Corpectomy versus laminoplasty for multilevel cervical myelopathy: an independent matched-cohort analysis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(11):1168-1175.
[12] Kristof RA, Kiefer T, Thudium M,et al.Comparison of ventral corpectomy and plate-screw-instrumented fusion with dorsal laminectomy and rod-screw-instrumented fusion for treatment of at least two vertebral-level spondylotic cervical myelopathy. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(12):1951-1956.
[13] Liu T, Yang HL, Xu YZ,et al.ACDF with the PCB cage-plate system versus laminoplasty for multilevel cervical spondylotic myelopathy.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011;24(4):213-220.
[14] Ghogawala Z, Martin B, Benzel EC,et al. Comparative effectiveness of ventral vs dorsal surgery for cervical spondylotic myelopathy.Neurosurgery. 2011;68(3):622-630.
[15] Hirai T, Okawa A, Arai Y,et al.Middle-term results of a prospective comparative study of anterior decompression with fusion and posterior decompression with laminoplasty for the treatment of cervical spondylotic myelopathy.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36(23):1940-1947.
[16] Shibuya S, Komatsubara S, Oka S,et al.Differences between subtotal corpectomy and laminoplasty for cervical spondylotic myelopathy.Spinal Cord. 2010;48(3):214-220.
[17] Yoshida M, Tamaki T, Kawakami M,et al.Indication and clinical results of laminoplasty for cervical myelopathy caused by disc herniation with developmental canal stenosis.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1998 ;23(22):2391-2397.
[18] Hosono N, Yonenobu K, Ono K.Neck and shoulder pain after laminoplasty. A noticeable complication.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 1996;21(17):1969-1973.
[19] Benzel EC, Lancon J, Kesterson L,et al.Cervical laminectomy and dentate ligament section for cervical spondylotic myelopathy. J Spinal Disord. 1991;4(3):286-295.
[20] Lin D, Zhai W, Lian K,et al.Anterior versus posterior approach for four-level cervical spondylotic myelopathy.Orthopedics. 2013;36(11):e1431-e1436.
[21] 杨有庚,任宪盛,杨晨,等.剖析颈椎病外科治疗的策略 提高颈椎病前路手术的疗效[J]. 脊柱外科杂志,2009,7(5):260-262.
[22] 陈德玉,贾连顺,赵定麟,等.颈椎病前路减压术后再手术[J].中华骨科杂志,2002,22(3): 134-137. |