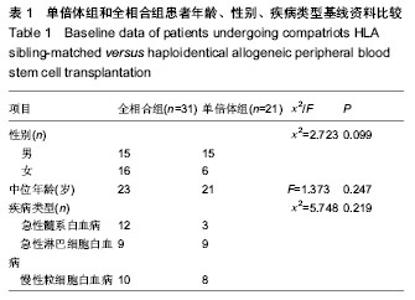
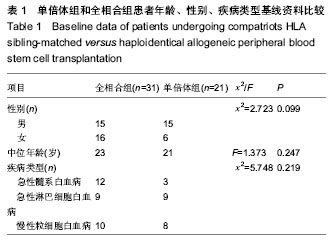
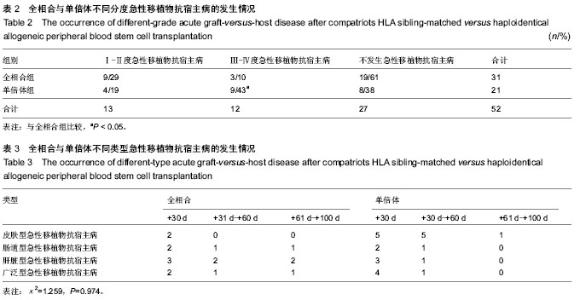
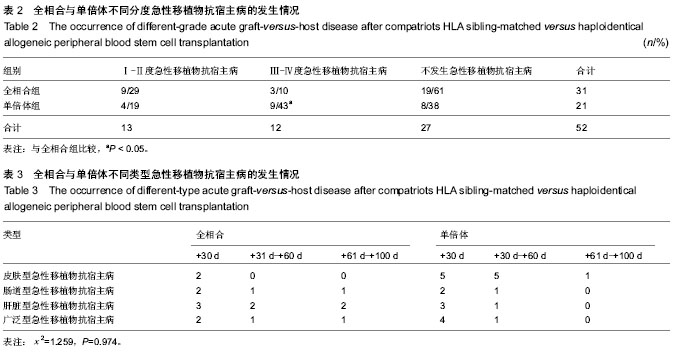
| [1] 张之南,沈悌.血液病诊断及疗效标准[M].3版.北京:科学出版社, 2007.
[2] 陈晓霞,王智明,罗贤生,等. 改良BU/CY预处理方案在外周血造血干细胞移植中的临床应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010, 14(14): 2638-2642.
[3] Chang YJ, Huang XJ.Use of G-CSF-stimulated marrow in allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation settings: a comprehensive review.Clin Transplant. 2011;25(1):13-23.
[4] 万鼎铭,康轶青,孙慧,等. 改良BU/CY预处理方案行异基因造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病的临床研究[J].中国实用内科杂志, 2009, 29(7): 648-649.
[5] Ji SQ, Chen HR, Wang HX,et al.G-CSF-primed haploidentical marrow transplantation without ex vivo T cell depletion: an excellent alternative for high-risk leukemia.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;30(12):861-866.
[6] 万鼎铭,邵运丽,秦童,等. HLA单倍体与全相合异基因造血干细胞移植治疗恶性血液病[J].中国组织工程研究,2012,16(32): 6076-6080.
[7] Glucksberg H, Storb R, Fefer A,et al.Clinical manifestations of graft-versus-host disease in human recipients of marrow from HL-A-matched sibling donors.Transplantation. 1974;18(4): 295-304.
[8] Basara N, Baurmann H, Kolbe K,et al. Antithymocyte globulin for the prevention of graft-versus-host disease after unrelated hematopoietic stem cell transplantation for acute myeloid leukemia: results from the multicenter German cooperative study group.Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005;35(10): 1011-1018.
[9] Zeiser R, Marks R, Bertz H,et al. Immunopathogenesis of acute graft-versus-host disease: implications for novel preventive and therapeutic strategies.Ann Hematol. 2004; 83(9):551-565.
[10] Mielcarek M, Storer BE, Sandmaier BM,et al.Comparable outcomes after nonmyeloablative hematopoietic cell transplantation with unrelated and related donors.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2007;13(12):1499-1507.
[11] Hogan WJ, Storb R.Use of cyclosporine in hematopoietic cell transplantation.Transplant Proc. 2004;36(2 Suppl):367S- 371S.
[12] Zander AR, Kröger N, Schleuning M,et al. ATG as part of the conditioning regimen reduces transplant-related mortality (TRM) and improves overall survival after unrelated stem cell transplantation in patients with chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).Bone Marrow Transplant. 2003;32(4): 355-361.
[13] 刘代红,黄晓军,陈欢,等. 异基因造血干细胞移植后供者外周血造血干细胞输注预防高危白血病复发[J].中华血液学杂志, 2006, 27(1): 6-9.
[14] 凌奕文,刘启发,刘灿,等. 粒细胞集落刺激因子对骨髓和外周血中骨髓来源的抑制细胞影响的初步研究[J]. 南方医科大学学报, 2011, 31(7): 1190-1192.
[15] Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S.Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system.Nat Rev Immunol. 2009; 9(3):162-174.
[16] 陈瑶,陆道培,刘开彦. 异基因造血干细胞移植后急性移植物抗宿主病151例危险因素分析[J]. 中华血液学杂志, 2005, 26(2): 74-77.
[17] Kanda Y, Chiba S, Hirai H,et al.Allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation from family members other than HLA-identical siblings over the last decade (1991-2000). Blood. 2003;102(4):1541-157.
[18] Bacigalupo A.Antilymphocyte/thymocyte globulin for graft versus host disease prophylaxis: efficacy and side effects. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2005;35(3):225-231.
[19] Ho VT, Soiffer RJ.The history and future of T-cell depletion as graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis for allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Blood. 2001;98(12): 3192-3204.
[20] Theurich S, Fischmann H, Chakupurakal G,et al. Anti-thymocyte globulins for post-transplant graft-versus-host disease prophylaxis-A systematic review and meta-analysis. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol. 2013;88(1):178-186.
[21] Lemos G, Pizzatti L, Pinto DO, et al. High-Resolution Multidimensional Proteomic Analysis of Circulating Biomarkers in Patients with Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease (aGVHD) . Biology Blood Marrow Transplantation.2012; 18(2): S262.
[22] 黄科,黄绍良,周敦华,等. 骨髓腔输注间充质干细胞对骨髓移植后造血重建和移植物抗宿主病作用的实验研究[J].中华血液学杂志, 2007, 28(2): 87-92.
[23] Deeg HJ.How I treat refractory acute GVHD.Blood. 2007 ; 109(10):4119-4126.
[24] Mohty M, Brissot E, Savani BN,et al.Effects of bortezomib on the immune system: a focus on immune regulation.Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2013;19(10):1416-1420.
[25] Qian L, Wu Z, Shen J.Advances in the treatment of acute graft-versus-host disease.J Cell Mol Med. 2013;17(8):966- 975.
[26] Sun Y, Tawara I, Toubai T,et al. Pathophysiology of acute graft-versus-host disease: recent advances.Transl Res. 2007; 150(4):197-214. |