Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (7): 1063-1068.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.07.014
Previous Articles Next Articles
Establishment of diabetic cystopathy guinea pig model and its urodynamic evaluation
Luo Guang-cheng1, He Zhi-hua1, Luo Jian-zhen1, Xu Yi-ming1, Ma Hong2
- 1Department of Urology, Zhongshan Hospital of Xiamen University (Teaching Hospital of Fujian Medical University), Xiamen 361004, Fujian Province, China; 2Department of Endocrine, Zhongshan Hospital of Xiamen University (Teaching Hospital of Fujian Medical University), Xiamen 361004, Fujian Province, China
-
Revised:2013-12-11Online:2014-02-12Published:2014-02-12 -
Contact:Ma Hong, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Endocrine, Zhongshan Hospital of Xiamen University (Teaching Hospital of Fujian Medical University), Xiamen 361004, Fujian Province, China -
About author:Luo Guang-cheng, M.D., Chief physician, Department of Urology, Zhongshan Hospital of Xiamen University (Teaching Hospital of Fujian Medical University), Xiamen 361004, Fujian Province, China -
Supported by:the grant by Xiamen Municipal Science and Technology Plan, No. 3502Z20124015
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Luo Guang-cheng, He Zhi-hua, Luo Jian-zhen, Xu Yi-ming, Ma Hong . Establishment of diabetic cystopathy guinea pig model and its urodynamic evaluation[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(7): 1063-1068.
share this article
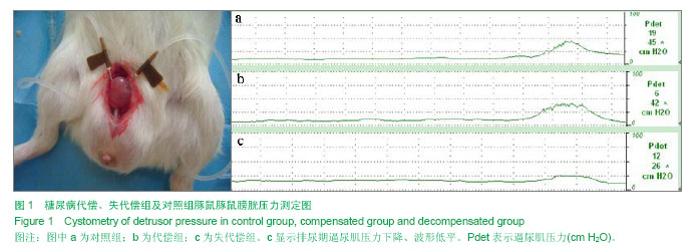
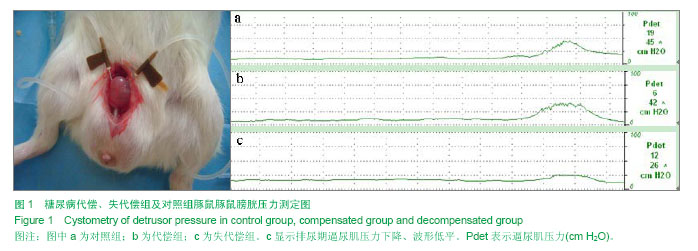
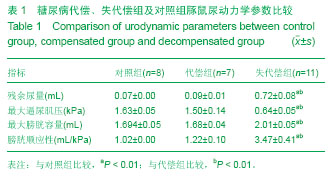
2.1 糖尿病豚鼠诱导成功率 实验组豚鼠42只,其中3只注射链脲佐菌素后10 d内死亡,死亡原因考虑为链脲佐菌素毒性反应,剩余的39只,连续测定1周,其中20只豚鼠随机血糖≥16.7 mmol/L,糖尿病豚鼠诱导成功率为47.6%(20/40)。20只糖尿病豚鼠,在后续的喂养中又有2只死亡,死亡原因为糖尿病并发症。故共18只实验组糖尿病豚鼠和8只对照组豚鼠进入结果分析。 2.2 豚鼠糖尿病膀胱病成模率 糖尿病豚鼠诱导9周后,第一批尿动力学检查9只糖尿病豚鼠,6只膀胱功能代偿,3只失代偿。12周后,第二批9只糖尿病组豚鼠,1只膀胱功能代偿,8只失代偿(88.89%)。失代偿豚鼠膀胱残余尿量>10%膀胱容量,代偿组合对照组豚鼠无残余尿或残余尿量10%膀胱容量。 2.3 尿动力学参数比较 比较糖尿病性膀胱病失代偿组豚鼠(n=11)、代偿组豚鼠(n=7)及对照组豚鼠(n=8)的尿动力学参数,包括最大逼尿肌压、膀胱容量、残余尿、膀胱顺应性。失代偿组豚鼠膀胱残余尿为(0.72±0.08) mL、最大逼尿肌压力为(0.64±0.05) kPa、膀胱容量为 (2.01±0.05) mL、膀胱顺应性为(4.47±0.41) mL/kPa,与对照组及代偿组比较,各参数差异均存在显著性意义(P < 0.01,表1、图1)。代偿组与对照组相比,各参数差异均无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。"
| [1] Yang W, Lu J, Weng J, et al. Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med. 2010;362(12): 1090-1101.[2] Daneshgari F and Moore C. Diabetic uropathy. Semin Nephrol. 2006;26(2):182-185.[3] Golbidi S, Laher I. Bladder dysfunction in diabetes mellitus. Front Pharmacol. 2010;1:136.[4] Lin TL, Chen GD, Chen YC, et al. Aging and recurrent urinary tract infections are associated with bladder dysfunction in type 2 diabetes. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2012;51(3): 381- 386.[5] Gomez CS, Kanagarajah P, Gousse AE. Bladder dysfunction in patients with diabetes. Curr Urol Rep. 2011;12(6):419-426. [6] Lee WC, Wu HP, Tai TY, et al. Investigation of urodynamic characteristics and bladder sensory function in the early stages of diabetic bladder dysfunction in women with type 2 diabetes. J Urol. 2009;181(1):198-203.[7] Alimohammadi S, Hobbenaghi R, Javanbakht J, et al. Protective and antidiabetic effects of extract from Nigella sativa on blood glucose concentrations against streptozotocin (STZ)-induced diabetic in rats: an experimental study with histopathological evaluation. Diagn Pathol.2013;15(8):137- 144.[8] Chaudhry ZZ, Morris DL, Moss DR, et al. Streptozotocin is equally diabetogenic whether administered to fed or fasted mice. Lab Anim. 2013;47(4):257-265. [9] 孙丽华,崔海峰,孙明杰,等.链脲佐菌素制备糖尿病大鼠模型探讨[J].中国实验动物学报,2012,12(6):15-19.[10] Li Y, Sun Y, Zhang Z, et al. Cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 are associated with bladder dysfunction in an experimental diabetic rat model. BJU Int. 2013;112(2):E143-150.[11] Jiang YJ, Gong DX, Liu HB, et al. Ability of alpha-lipoic acid to reverse the diabetic cystopathy in a rat model. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2008n;29(6):713-719. [12] Sasaki K, Chancellor MB, Goins WF, et al. Gene therapy using replication-defective herpes simplex virus vectors expressing nerve growth factor in a rat model of diabetic cystopathy. Diabetes. 2004;53(10):2723-2730.[13] Mustafa S. Effect of diabetes on the ion pumps of the bladder. Urology. 2013;81(1):211.e17-21. [14] Wang Z, Cheng Z, Cristofaro V, et al. Inhibition of TNF-α improves the bladder dysfunction that is associated with type 2 diabetes. Diabetes. 2012;61(8):2134-2145. [15] Bansal R, Agarwal MM, Modi M, et al. Urodynamic profile of diabetic patients with lower urinary tract symptoms: association of diabetic cystopathy with autonomic and peripheral neuropathy. Urology. 2011;77(3):699-705. [16] Li WJ, Oh SJ. Diabetic cystopathy is associated with PARP/JNK/mitochondrial apoptotic pathway-mediated bladder apoptosis. Neurourol Urodyn.2010;29(7):1332-1337. [17] Saito M,Wada Y,Ireda K,et al.Gene expression,localization, and pharmacololgical characterization of endothelin receptors in diabetic rat bladder dome.Eur J Pharmacol. 2000;387(3): 253-263.[18] 李世芬,王心如,王玉翠,等.SD大鼠糖尿病肾病模型构建的比较[J]. 南京医科大学学报(自然科学版),2010,30(8):1123-1128.[19] Joseph DiMattio. Alterations in ascorbic acid transport into the lens of streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats and guinea pig. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1992;33(10):2926-2935.[20] Hagstroem S, Kamperis K, Rittig S, et al. Monosymptomatic nocturnal enuresis is associated with abnormal nocturnal bladder emptying.J Urol.2004;171(6 Pt. 2):2562-2566.[21] Daneshgari F, Huang X, Liu G, et al. Temporal differences in bladder dysfunction caused by diabetes, diuresis, and treated diabetes in mice. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2006; 290(6):R1728-1735.[22] Kebapci N, Yenilmez A, Efe B, et al. Bladder dysfunction in type 2 diabetic patients. Neurourol Urodyn. 2007;26(6):814-819.[23] Daneshgari F, Leiter EH, Liu G, et al. Animal Models of Diabetic Uropathy. J Urol. 2009;182(6 Suppl):S8-13.[24] 曹石金,何朝辉,李逊,等.糖尿病大鼠膀胱结构与功能的改变[J]. 广东医学,2012,33(16):2372-2375.[25] 冯建华,邓丽萍,曾祥建,等. 糖尿病大鼠膀胱逼尿肌超微结构的改变[J]. 中国热带医学,2012,12(1):15-17.[26] Daneshgari F, Liu G, Imrey PB. Time dependent changes in diabetic Cystopathy in rats include compensated and decompensated bladder function. J Urol. 2006;176(1): 380-386.[27] 李维仁,王勤章,丁国富,等.豚鼠糖尿病膀胱模型的建立[J].现代泌尿外科杂志,2008,13(5):368-370.[28] Lee MS,Song KD,Yang HJ, et al. Development of a type II diabetic mellitus animal model using micropig. Lab Anim Res. 2012;28(3):205-208.[29] Turner WH,Brading AF. Smooth muscle of the bladder in the normal and the diseased state: pathophysiology, diagnosis and treatment. Pharmacol Ther. 1997;75(2):77-110.[30] 毕铮铮,郭剑超,郑少雄,等.早期糖尿病性膀胱病的无创尿动力学变化[J].中国医师进修杂志,2010,32(7):19-21.[31] 高宏飞,王东文.2型糖尿病膀胱重构的受体机制研究[J].中西医结合心脑血管病杂志,2013,11(6):716-718.[32] Sasaki K, Chancellor MB, GoinsS WF, et al. Gene therapy using replication-defective herpes simplex virus vectors expressing nerve growth factor in a rat model of diabetic cystopathy. Diabetes. 2004;53(10):2723-2730.[33] Kikuno N, Kawamoto K, Hirata H, et al. Nerve growth factor combined with vascular endothelial growth factor enhances regeneration of bladder acellular matrix graft in spinal cord injury-induced neurogenic rat bladder. BJU Int. 2009;103(10): 1424-1428.[34] Ichiyanagi N, Tsujii T, Masuda H, et al. Changed responsiveness of the detrusor in rabbits with alloxan induced hyperglycemia: possible role of 5-hydroxytryptamine for diabetic bladder dysfunction. J Urol. 2002;168(1):303-307.[35] Bezuijen MW,Levendusky MC,Longhurst PA.Functional response of bladder strips from streplozotocon diabetic rats depends on bladder mass. J Uro. 2003;169(6):2397-2401.[36] Oberbach A, Jehmlich N, Schlichting N, et al. Molecular fingerprint of high fat diet induced urinary bladder metabolic dysfunction in a rat model. PLoS One. 2013;8(6): e66636. [37] Kanika ND, Chang J, Tong Y, et al. Oxidative stress status accompanying diabetic bladder cystopathy results in the activation of protein degradation pathways. BJU Int. 2011; 107(10):1676-1684. [38] Li Y, Sun Y, Zhang Z, et al. Cannabinoid receptors 1 and 2 are associated with bladder dysfunction in an expenrimental diabetic rat model. BJU Int. 2013;112(2):E140-150.[39] Leiria LO, Mónica FZ, Carvalho FD, et al. Functional, morphological and molecular characterization of bladder dysfunction in streptozotocin-induceddiabetic mice: evidence of a role for L-type voltage-operated Ca2+ channels. Br J Pharmacol.2011;163(6):1276-1288.[40] Fedele D. Therapy insight: sexual and bladder dysfunction associated with diabetes mellitus. Nat Clin Pract Urol. 2005; 2(6):282-290. [41] Van Poppel H, Stessens R, Van Damme B, et al. Diabetic cystopathy: neuropathological examination of urinary bladder biopsies. Eur Urol.1998;15(1-2):128-131.[42] Brown JS, Wessells H, Chancellor MB, et al. Urologic complications of diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2005;28(1):177-185.[43] 郭学敬,白艳,王秀丽,等. 神经生长因子对糖尿病大鼠膀胱病变的影响[J]. 中华实验外科杂志,2013,30(9):1909-1911.[44] Apodaca G. The uroepithelium: not just a passive barrier. Traffic. 2004;5(3):117-128.[45] Apodaca G, Kiss S, Ruiz W, et al. Disruption of bladder epithelium barrier function after spinal cord injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol.2003;284(5):F966-976.[46] 李云飞,丁国富,蔡志强,等. 豚鼠糖尿病性膀胱病逼尿肌中c-kitmRNA和蛋白的表达变化及意义[J].中国病理生理杂志, 2010,25(2):345-348.[47] Kanika ND, Chang J, Tong Y, et al. Oxidative stress status accompanying diabetic bladder cystopathy results in the activation of protein degradation pathways. BJU Int. 2011; 107(10):1676-1684. [48] Johnston L, Carson C, Lyons AD, et al. Cholinergie induced Ca^2+ signaling in interstitial cells of Cajal from the guinea pig bladder. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2008;294(3):R645- R655.[49] Lee WC, Wu CC, Wu HP, et al. Lower urinary tract symptoms and uroflowmetry in women with type 2 diabetes mellitus with and without bladder dysfunction. Urology. 2007;69(4): 685-690.[50] Li WJ, Shin MK, Oh SJ. Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase is involved in the development of diabetic cystopathy via regulation of nuclear factor kappa B. Urology. 2011;77(5): 1265.e1-8.[51] Rasmussen H, Rumessen JJ, Hansen A, et al. Ultrastructure of Cajal-like interstitial cells in the human detrusor. Cell Tissue Res. 2009;335(3):517-527. |
| [1] | Chen Ziyang, Pu Rui, Deng Shuang, Yuan Lingyan. Regulatory effect of exosomes on exercise-mediated insulin resistance diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 4089-4094. |
| [2] | Gao Shan, Huang Dongjing, Hong Haiman, Jia Jingqiao, Meng Fei. Comparison on the curative effect of human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cells and induced islet-like cells in gestational diabetes mellitus rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3981-3987. |
| [3] | Liu Yulin, Li Guotai. Combined effects of hyperbaric oxygen, vibration training and astaxanthin on bone mineral density, glucose metabolism and oxidative stress in diabetic osteoporosis rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3117-3124. |
| [4] | Tian Lin, Shi Xiaoqing, Duan Zhenglan, Wang Kuan, Zhang Li, Wang Peimin. Efficacy and safety of transverse tibial bone transport technique in the treatment of diabetic foot:a meta-analysis#br# [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3275-3280. |
| [5] | Xia Wenshen, He Renjiao, Ai Jinwei, Wang Jun, Li Desheng, Pei Bin. Stem cell transplantation for diabetic patients with lower-extremity arterial disease: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3110-3116. |
| [6] | Luo Yicai, Li Hao. Effect of enhanced aryl hydrocarbon receptor expression on inflammatory response and healing of alveolar bone defects in diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2166-2171. |
| [7] | Wang Xiaobo, Wang Changan, Han Jianle, Yang Qingyan, Yang Shuaiping, Yang Junwei. Influence of conversion from cyclosporine to tacrolimus on glucose metabolism and cardiovascular risk profiles in stable kidney transplant patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2236-2240. |
| [8] | Guo Xuan, Xie Jun, Suo Jinrong, Li Yingrui, Huang Lei, Ma Munan, Li Jingjing, Fu Songtao. Transplantation of islet-like cells induced by human umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells via different ways for the treatment of type 1 diabetic mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 78-83. |
| [9] | Liu Yongpan, Gong Xiaofang. Effects of dexmedetomidine on perioperative brain protection in patients undergoing craniocerebral surgery under inhalation anesthesia with sevoflurane: a randomized controlled study [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5688-5694. |
| [10] |
Zheng Haijun, Jin Hui, Cui Hongling, Zhu Yakun, Zeng Hui, Han Fengjie, Qiu Cuiting, Liu Jing.
Safety of drug-coated balloon versus drug-eluting stents in the treatment of type 2 diabetes mellitus complicated by coronary artery small vessel disease in older adult patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(28): 4573-4579. |
| [11] | Lu Pengcheng, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Liu Bo. Mechanism by which autophagy-mediated exercise improves bone metabolic disorder in type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(20): 3256-3262. |
| [12] | Fu Yunyu, Qiu Xiaotang, Yang Wenkui, Mo Shian, Wu Xiaocui, Wu Yingping. Berberine alleviates ischemia/reperfusion injury in type 2 diabetic rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 230-235. |
| [13] | Zhang Shuangyuan, Li Wenjin, Zhu Li, Wang Yu, Wei Zhoudan, Zhao Jiaoyang, Chen Yanan. Meta-analysis of dental implantation success rate in diabetic patients with 6% < glycated hemoglobin level < 8% [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(16): 2620-2624. |
| [14] | Liu Xiaochen, Fu Weili. Selection of animal models of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(11): 1769-1776. |
| [15] | Li Bopeng, Chen Shuchun, Tang Yong, Ren Luping. Alpha-lipoic acid increases circulating endothelial progenitor cells in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 803-808. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||