Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (5): 803-808.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1560
Previous Articles Next Articles
Alpha-lipoic acid increases circulating endothelial progenitor cells in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes
Li Bopeng1, Chen Shuchun2, Tang Yong2, Ren Luping2
- 1Xingtai Fifth Hospital, Xingtai 054027, Hebei Province, China; 2First Department of Endocrinology, Hebei General Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050057, Hebei Province, China
-
Revised:2018-10-30Online:2019-02-18Published:2019-02-18 -
Contact:Chen Shuchun, MD, Chief physician, Professor, Master’s supervisor, First Department of Endocrinology, Hebei General Hospital, Shijiazhuang 050057, Hebei Province, China -
About author:Li Bopeng, Master, Attending physician, Xingtai Fifth Hospital, Xingtai 054027, Hebei Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Bopeng, Chen Shuchun, Tang Yong, Ren Luping. Alpha-lipoic acid increases circulating endothelial progenitor cells in newly diagnosed type 2 diabetes[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(5): 803-808.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
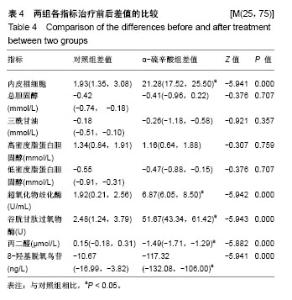
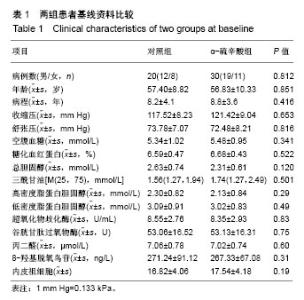
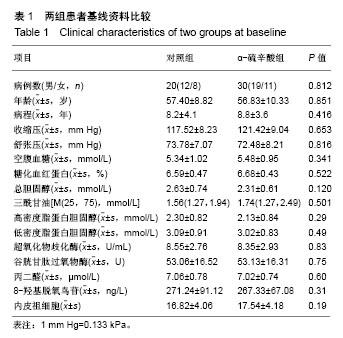
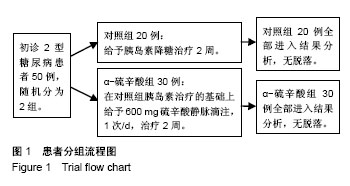
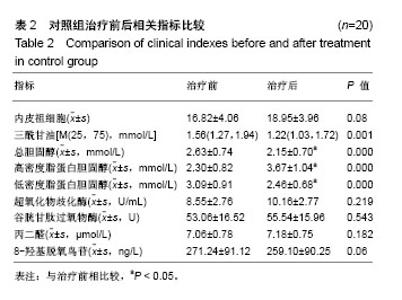
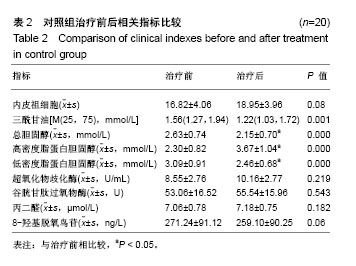
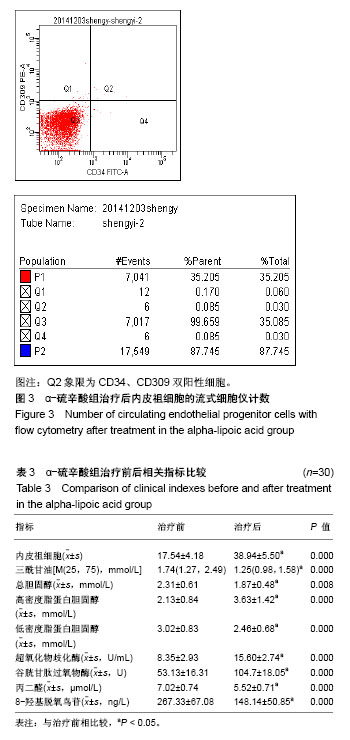
2.6 两组间各指标治疗前后差值的比较 α-硫辛酸组治疗前后内皮祖细胞数量差值与对照组比较显著增加(P < 0.05);α-硫辛酸组超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧物酶活性差值较对照组显著增加(P < 0.05),丙二醛、8-羟基脱氧鸟苷显著下降(P < 0.05),见表4。 2.7 内皮祖细胞数量与相关参数的相关性 以α-硫辛酸组治疗前后内皮祖细胞数量的差值作为因变量,超氧化物歧化酶、谷胱甘肽过氧物酶、丙二醛、8-羟基脱氧鸟苷、三酰甘油、总胆固醇、低密度脂蛋白胆固醇、高密度脂蛋白胆固醇、空腹血糖的差值为自变量进行多元线性回归分析,最优回归方程为:Y=6.349+0.195X2-3.335X3,X2代表谷胱甘肽过氧物酶差值(P=0.01),X3代表丙二醛差值(P=0.041),结果表明:内皮祖细胞数量与谷胱甘肽过氧物酶、丙二醛有线性回归关系,谷胱甘肽过氧物酶与内皮祖细胞数量呈正相关,丙二醛与内皮祖细胞数量呈负相关。"

| [1] Rao Kondapally Seshasai S, Kaptoge S, Thompson A, et al. Diabetes mellitus, fasting glucose, and risk of cause-specific death. N Engl J Med. 2011;364(9):829-841.[2] Bo S, Ciccone G, Gancia R, et al. Mortality within the first 10 years of the disease in type 2 diabetic patients. Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 2006;16(1):8-12.[3] Lombardo MF, Iacopino P, Cuzzola M, et al. Type 2 diabetes mellitus impairs the maturation of endothelial progenitor cells and increases the number of circulating endothelial cells in peripheral blood. Cytometry A. 2012;81(10):856-864.[4] Russell JS, Brown JM. Circulating mouse Flk1+/c-Kit+/CD45- cells function as endothelial progenitors cells (EPCs) and stimulate the growth of human tumor xenografts. Mol Cancer. 2014;13:177.[5] Pías-Peleteiro J, Campos F, Castillo J, et al.Endothelial progenitor cells as a therapeutic option in intracerebral hemorrhage.Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(4):558-561.[6] Hamed S, Brenner B, Roguin A. Nitric oxide: a key factor behind the dysfunctionality of endothelial progenitor cells in diabetes mellitus type-2. Cardiovasc Res. 2011;91(1):9-15.[7] 陈树春,宋光耀,孙阳,等. 初诊2型糖尿病患者外周血内皮祖细胞的研究[J]. 天津医药, 2010, 38(7): 549-551.[8] 夏文华,饶玉霞. 2型糖尿病患者内皮祖细胞数量和功能研究[J]. 咸宁学院学报(医学版), 2012, 26(1): 12-14.[9] Asahara T, Masuda H, Takahashi T, et al. Bone marrow origin of endothelial progenitor cells responsible for postnatal vasculogenesis in physiological and pathological neovascularization. Circ Res. 1999;85(3):221-228.[10] Hristov M, Schmitz S, Nauwelaers F, et al. A flow cytometric protocol for enumeration of endothelial progenitor cells and monocyte subsets in human blood. J Immunol Methods. 2012;381(1-2):9-13.[11] Ma XL, Sun XL, Wan CY, et al. Significance of circulating endothelial progenitor cells in patients with fracture healing process. J Orthop Res. 2012;30(11):1860-1866.[12] Sen S, McDonald SP, Coates PT, et al. Endothelial progenitor cells: novel biomarker and promising cell therapy for cardiovascular disease. Clin Sci (Lond). 2011;120(7): 263-283.[13] Zhou X, Patel D, Sen S, et al. Poly-ADP-ribose polymerase inhibition enhances ischemic and diabetic wound healing by promoting angiogenesis. J Vasc Surg. 2017;65(4):1161-1169.[14] Lin CP, Lin FY, Huang PH, et al. Endothelial progenitor cell dysfunction in cardiovascular diseases: role of reactive oxygen species and inflammation. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:845037.[15] Barton M. Prevention and endothelial therapy of coronary artery disease. Curr Opin Pharmacol. 2013;13(2):226-241.[16] Chen S, Sun L, Gao H, et al. Visfatin and oxidative stress influence endothelial progenitor cells in obese populations. Endocr Res. 2015;40(2):83-87.[17] 陈树春,宋光耀,孙阳,等. 2型糖尿病一级亲属内皮祖细胞与氧化应激[J].中华内科杂志,2012,51(3):197-200.[18] 陈树春,宋光耀.内皮祖细胞与氧化应激研究进展[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(6): 1119-1122.[19] Chen DD, Dong YG, Yuan H, et al. Endothelin 1 activation of endothelin A receptor/NADPH oxidase pathway and diminished antioxidants critically contribute to endothelial progenitor cell reduction and dysfunction in salt-sensitive hypertension. Hypertension. 2012;59(5):1037-1043.[20] Kulikowska-Karpińska E, Czerw K. Estimation of 8-hydroxy-2'-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) concentration in the urine of cigarette smokers. Wiad Lek. 2015;68(1):32-38.[21] Tabur S, Aksoy ?N, Korkmaz H, et al. Investigation of the role of 8-OHdG and oxidative stress in papillary thyroid carcinoma. Tumour Biol. 2015;36(4):2667-2674.[22] Liu JT, Chen YL, Chen WC, et al. Role of pigment epithelium-derived factor in stem/progenitor cell-associated neovascularization. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2012;2012:871272.[23] Zaragoza C, Gomez-Guerrero C, Martin-Ventura JL, et al. Animal models of cardiovascular diseases. J Biomed Biotechnol. 2011;2011:497841.[24] Tousoulis D, Andreou I, Antoniades C, et al. Role of inflammation and oxidative stress in endothelial progenitor cell function and mobilization: therapeutic implications for cardiovascular diseases. Atherosclerosis. 2008;201(2): 236-247.[25] Carracedo J, Merino A, Briceño C, et al. Carbamylated low-density lipoprotein induces oxidative stress and accelerated senescence in human endothelial progenitor cells. FASEB J. 2011;25(4):1314-1322.[26] Pickering RJ, Rosado CJ, Sharma A, et al. Recent novel approaches to limit oxidative stress and inflammation in diabetic complications. Clin Transl Immunology. 2018;7(4): e1016.[27] Sasaki S, Inoguchi T. The role of oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of diabetic vascular complications. Diabetes Metab J. 2012;36(4):255-261.[28] Ceretta LB, Réus GZ, Abelaira HM, et al. Increased oxidative stress and imbalance in antioxidant enzymes in the brains of alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Exp Diabetes Res. 2012;2012: 302682.[29] Hernández-Beltrán N, Moreno CB, Gutiérrez-Álvarez AM. Contribution of mitochondria to pain in diabetic neuropathy. Endocrinol Nutr. 2013;60(1):25-32.[30] Rochette L, Ghibu S, Muresan A, et al. Alpha-lipoic acid: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic potential in diabetes. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 2015;93(12):1021-1027.[31] 陈树春,宋光耀,章冬梅,等. α-硫辛酸对高糖状态下内皮祖细胞的影响[J]. 细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2012,28(3): 240-243.[32] Zhao M, Chen JY, Chu YD, et al.Efficacy of epalrestat plus α-lipoic acid combination therapy versus monotherapy in patients with diabetic peripheral neuropathy: a meta-analysis of 20 randomized controlled trials.Neural Regen Res. 2018; 13(6):1087-1095.[33] 王景尚,孙明月,黄烨,等. α-硫辛酸对血糖波动状态下2型糖尿病大鼠血管内皮细胞功能及PI3K/Akt/GSK-3β通路的影响[J]. 中国全科医学, 2017,20(24): 2965-2971. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | Pei Lili, Sun Guicai, Wang Di. Salvianolic acid B inhibits oxidative damage of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and promotes differentiation into cardiomyocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1032-1036. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Jiang Xin, Qiao Liangwei, Sun Dong, Li Ming, Fang Jun, Qu Qingshan. Expression of long chain non-coding RNA PGM5-AS1 in serum of renal transplant patients and its regulation of human glomerular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 741-745. |
| [6] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [7] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [8] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [9] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [10] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [11] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [12] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [13] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [14] | Jiang Tao, Ma Lei, Li Zhiqiang, Shou Xi, Duan Mingjun, Wu Shuo, Ma Chuang, Wei Qin. Platelet-derived growth factor BB induces bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to differentiate into vascular endothelial cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3937-3942. |
| [15] | Luo Anyu, Liu Hanlin, Xie Xiaofei, Huang Chen. Effect of antioxidant mixture on structural degeneration of an osteoarthritis rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(23): 3625-3629. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||