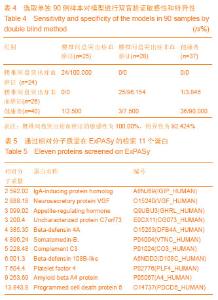
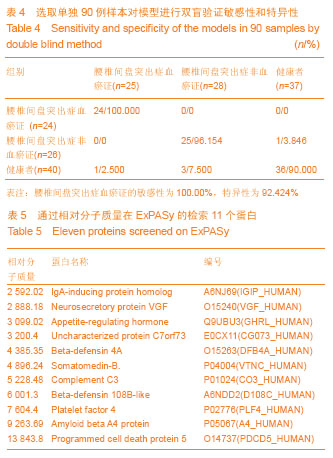
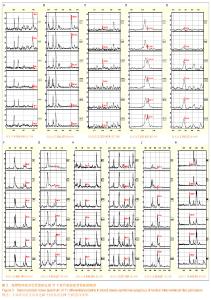
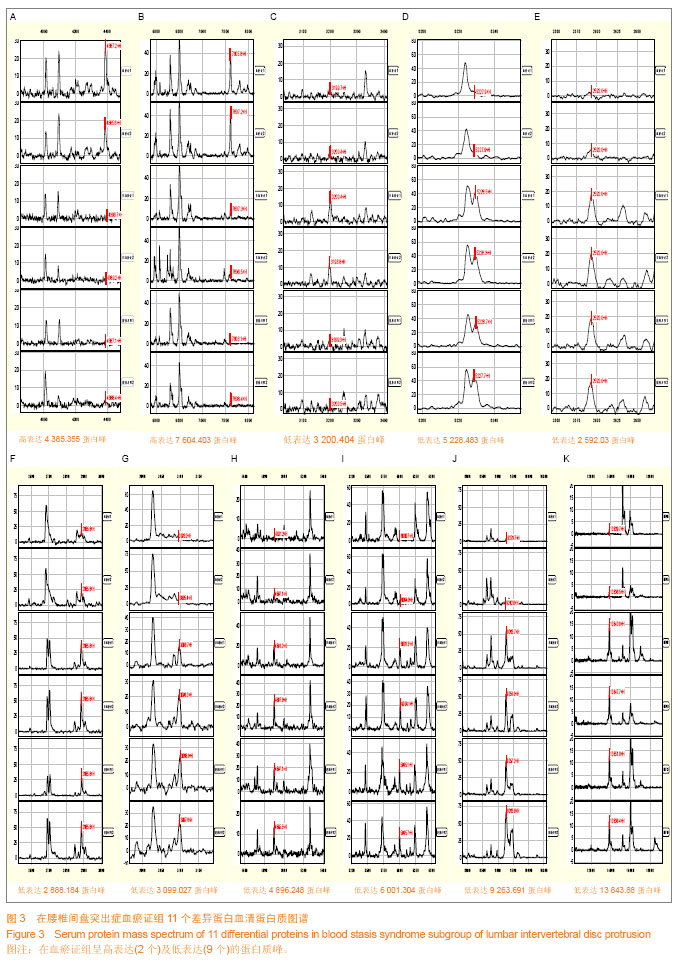
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (5): 724-729.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.05.012
Previous Articles Next Articles
Serum protein fingerprint pattern model for diagnosing blood stasis syndrome of lumbar intervertebral disc protrusion
Xu Jian-wen1, Wei Gui-kang2, Zhong Yuan-ming1, Yin Li-jun1, Zhou Bin-bin1, Wei Yu-lan2, Li Zhi-fei1, Song Quan-sheng1, Hu Bing3, Ji Jing4
- 1Department of Orthopedics, First Affiliated Hospital of Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530023, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 2Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 3Grade 2009 candidate for the Master’s degree, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China; 4Grade 2008 candidate for the Master’s degree, Guangxi University of Chinese Medicine, Nanning 530001, Guangxi Zhuang Autonomous Region, China