Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2018, Vol. 22 ›› Issue (27): 4348-4353.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0351
Previous Articles Next Articles
Peek Prevail anterior cervical interbody fusion for herniation of cervical intervertebral disc: a 12-month follow-up
Li Guo, He Yue, Gu Zu-chao, Zhang Yu, Liu Jin
- Department of Spine Surgery, Chengdu First People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
-
Online:2018-09-28Published:2018-09-28 -
Contact:He Yue, Master, Physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Chengdu First People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China -
About author:Li Guo, Master, Attending physician, Department of Spine Surgery, Chengdu First People’s Hospital, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Guo, He Yue, Gu Zu-chao, Zhang Yu, Liu Jin. Peek Prevail anterior cervical interbody fusion for herniation of cervical intervertebral disc: a 12-month follow-up[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2018, 22(27): 4348-4353.
share this article
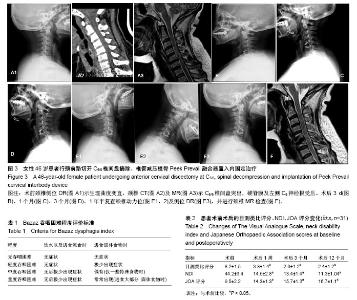
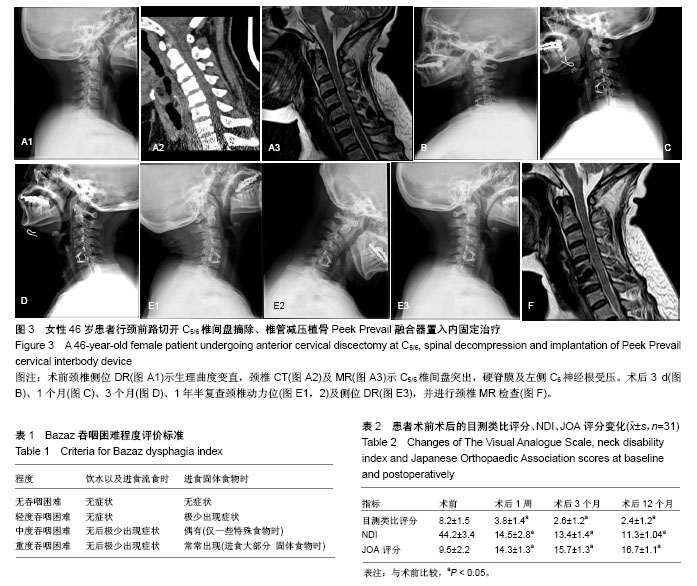
2.2 一般情况 31例患者手术时间平均(63.0±12.5) min,术中出血量平均(25.0±7.4) mL。术后未发生切口感染、神经血管损伤、食管瘘,喉头水肿等并发症。 2.3 治疗后患者吞咽困难情况、目测类比评分、NDI及JOA评分变化 3例患者术后2 d出现不同程度的吞咽不适,2例轻度,1例中度,对症处理后,2周内均完全消失。所有患者术后临床症状与神经功能均得到改善。目测类比评分、NDI及JOA评分较治疗前均有显著改善(P < 0.05),见表2。 2.4 相邻椎间盘退变情况 相邻椎间盘术前信噪比为20.3±2.1,术后12个月为19.1±1.8,差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05),表明Peek Prevail椎间融合器治疗颈椎病短期内未加速相邻椎间盘的退变。 2.5 支撑、固定疗效及不良事件 治疗后3个月、1年常规拍摄颈椎正侧位X射线片,椎间融合率为100%。未发现内固定下沉,未见邻近节段异位骨化。 2.6 典型病例 46岁女性患者,主诉颈肩部疼痛3年加重伴左上肢疼痛麻木3个月入院。术前颈椎侧位DR(图3A1)示生理曲度变直,颈椎CT(图3A2)及MR(图3A3)示C5/6椎间盘突出,硬脊膜及左侧C6神经根受压。患者行颈前路切开C5/6椎间盘摘除、椎管减压植骨Peek Prevail融合器置入内固定术。术后3 d(图3B)、1个月(图3C)、3个月(图3D)、1年半复查颈椎动力位(图3E1,2)及侧位DR(图3E3),并进行颈椎MR检查(图3F),术后患者症状改善明显,疗效满意,未见内固定松动断裂等并发症。 "
| [1] Smith GW, Robinson RA.The treatment of certain cervical-spine disorders by anterior removal of the intervertebral disc and interbody fusion.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1958;40-A(3):607-624.[2] Lee CH,Hyun SJ,Kim MJ,et al.Comparative analysis of 3 different construct systems for single-level anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: stand-alone cage, iliac graft plus plate augmentation and cage plus plating. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2013;26(2):112-118.[3] Fraser JF, Härtl R. Anterior approaches to fusion of the cervical spine: a meta analysis of fusion rates.J Neurosurg Spine. 2007;6(4):298-303.[4] Ralul B,Hood KA.Cervical total disc arthroplasty.Globa Spine J. 2012; 2(2):105-108.[5] Smith GW, Robinson RA. The treatment of certain cervical-spine disorders by anterior removal of the intervertebral disc and interbody fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1958;40:607-624.[6] Cloward RB. The anterior approach for removal of ruptured cervical disks. J Neurosurg. 1958;15:602-617.[7] Ba Z, Zhao W, Wu D, et al. Box cages packed with local decompression bone were efficient in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: five- to 10-year follow-up. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37: E1260–E1263.[8] Pitzen TR,Chrobok J,Stulik J,et al.Implant complications,fusion,loss of lordosis,and outcome after anterior cervical plating with dynamic or rigid plates:two-year results of a Multi-centric,randomized,controlled study. Spine. 2009;34(7):641-646.[9] Dnmont TM,Lin CT,Tranmer BI,et al. Pseudarthrosis failrites of anterior subaxial cervicalspine fusion using a plate with a single screw per vertebral body:a case series. World Neurosurg. 2014;82(1-2):225-230.[10] Kapu R,Singh M,Pande A,et al.Delayed anterior cervical plate dislodgement with pharyngeal wall perforation and oral extrusion of cervical plate screw after 8 years:a very rare complication. J Craniovertebr Junction Spine. 2012;3(1):19-22.[11] Ahn SS, Paik HK.The Fate of Adjacent Segments After Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion: The Influence of an Anterior Plate System. World Neurosurg. 2016;89:42-50.[12] Ahn SS, So WS.Radiologic Findings and Risk Factors of Adjacent Segment Degeneration after Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion : A Retrospective Matched Cohort Study with 3-Year Follow-Up Using MRI. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2016;59(2):129-136.[13] Vernon H, Mior S.The Neck Disability Index: a study of reliability and validity. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 1991;14(7):409-415.[14] Furlan JC, Catharine Craven B.Psychometric analysis and critical appraisal of the original, revised, and modified versions of the Japanese Orthopaedic Association score in the assessment of patients with cervical spondylotic myelopathy. Neurosurg Focus. 2016;40(6):E6.[15] Bazaz R, Lee MJ, Yoo JU. Incidence of dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: a prospective study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2002;27(22):2453-2458.[16] NEMA Standards Publication MS 1-2008, Determination of Signal-to-Noise Ratio (SNR) in Diagnostic Magnetic Resonance Imaging. Rosslyn: National Electrical Manufacturers Association, 2008.[17] Shao H, Chen J. Zero-profile implant versus conventional cage-plate implant in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion for the treatment of degenerative cervical spondylosis: a meta-analysis. J Orthop Surg Res. 2015;10:148.[18] Wang ZW, Jiang W, Li X, et al. The application of zero-profile anchored spacer in anterior cervical discectomy and fusion. Eur Spine J. 2015; 24(1):148-154.[19] Lee MJ,Bazaz R,Furey CG,et al.Influence of anterior cervical plate design on dysphagia: a 2-year prospective longitudinal follow-up study. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2005;18(5):406-409.[20] Joaquim AF.Murar J.Dysphagia after anterior cervical spine surgery: a systematic review of potential preventative measures.Spine J. 2014; 14(9):2246-2260.[21] Scholz M, Schnake KJ. A new zero-profile implant for stand-alone anterior cervical interbody fusion. Clin Orthop Relat Res.2011;469: 666-673.[22] Tortolani PJ,Tortolani PJ. A comparison of retraction pressure during anterior cervical plate surgery and cervical disc replacement: a cadaveric study.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2006;19(5):312-317.[23] Alimi M, Njoku I. Anterior Cervical Discectomy and Fusion (ACDF): Comparison Between Zero Profile Implants and Anterior Cervical Plate and Spacer. Cureus. 2016;8(4): e573. [24] Hofstetter CP, Kesavabhotla K. Zero-profile Anchored Spacer Reduces Rate of Dysphagia Compared With ACDF With Anterior Plating.J Spinal Disord Tech. 2015;28(5):E284-290.[25] Matsumoto M, Okada E. Anterior cervical decompression and fusion accelerates adjacent segment degeneration: comparison with asymptomatic volunteers in a ten-year magnetic resonance imaging follow-up study.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(1):36-43.[26] Yang B, Li H. The incidence of adjacent segment degeneration after cervical disc arthroplasty (CDA): a meta analysis of randomized controlled trials.PLoS One. 2012;7(4):e35032.[27] Harrod CC,Hilibrand AS.Adjacent segment pathology following cervical motion-sparing procedures or devices compared with fusion surgery: a systematic review.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2012;37(22 Suppl): S96-S112.[28] Park JB, Cho YS. Development of adjacent-level ossification in patients with an anterior cervical plate.J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2005; 87(3):558-563.[29] Ipsen BJ, Kim DH. Effect of plate position on clinical outcome after anterior cervical spine surgery.Spine J. 2007;7(6):637-642.[30] Chung JY, Kim SK. Clinical adjacent-segment pathology after anterior cervical discectomy and fusion: results after a minimum of 10-year follow-up. Spine J. 2014;14(10):2290-2298.[31] 王洪立,姜建元,吕飞舟,等.颈椎前路融合术后邻近节段退变性疾病的原因分析及治疗策略[J].中华骨科杂志,2014,34(9).915-922.[32] Urban JP,Roberts S.Degeneration of the intervertebral disc.Arthritis Res Ther. 2003; 5(3):120-130.[33] An HS.A Novel Rabbit Model of Mild, Reproducible Disc Degeneration by an Anulus Needle Puncture: Correlation Between the Degree of Disc Injury and Radiological and Histological Appearances of Disc Degeneration.Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(1):5-14.[34] Nassr A,Lee JY.Does incorrect level needle localization during anterior cervical discectomy and fusion lead to accelerated disc degeneration. Spine(Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(2):189-192. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [3] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [4] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [5] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [6] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [7] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [8] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [9] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| [10] | Xing Hao, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong. Advantages and disadvantages of repairing large-segment bone defect [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 426-430. |
| [11] | Tang Xiaokai, Li Weiming. Role and mechanism of Nel-like molecule-1 in promoting bone fusion after spinal fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(24): 3914-3920. |
| [12] | Chen Siqi, Xian Debin, Xu Rongsheng, Qin Zhongjie, Zhang Lei, Xia Delin. Effects of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells and human umbilical vein endothelial cells combined with hydroxyapatite-tricalcium phosphate scaffolds on early angiogenesis in skull defect repair in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3458-3465. |
| [13] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [14] | Mo Jianling, He Shaoru, Feng Bowen, Jian Minqiao, Zhang Xiaohui, Liu Caisheng, Liang Yijing, Liu Yumei, Chen Liang, Zhou Haiyu, Liu Yanhui. Forming prevascularized cell sheets and the expression of angiogenesis-related factors [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3479-3486. |
| [15] | Liu Chang, Li Datong, Liu Yuan, Kong Lingbo, Guo Rui, Yang Lixue, Hao Dingjun, He Baorong. Poor efficacy after vertebral augmentation surgery of acute symptomatic thoracolumbar osteoporotic compression fracture: relationship with bone cement, bone mineral density, and adjacent fractures [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3510-3516. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||