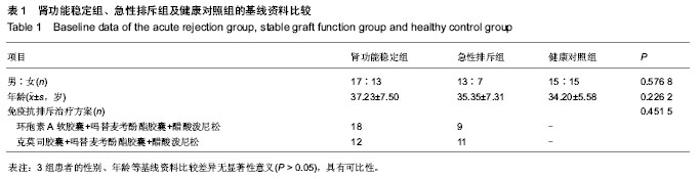
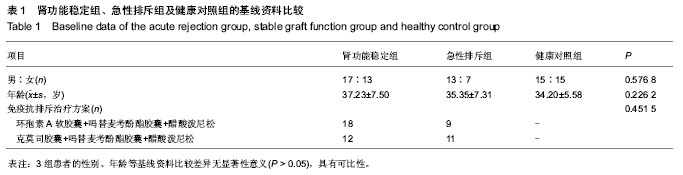
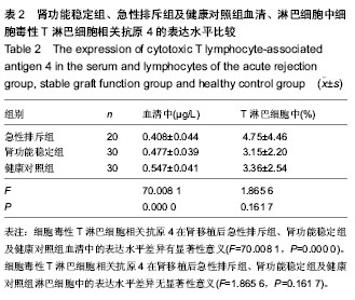
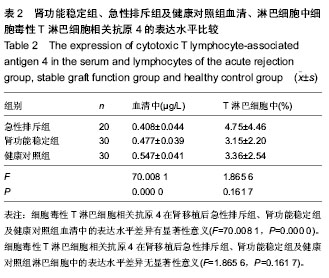
| [1] Moreso F, Hernández D.Has the survival of the graft improved after renal transplantation in the era of modern immunosuppression? Nefrologia. 2013;33(1):14-26[2] 陈江华,韩飞.移植肾急性排斥反应新认识[J].中华移植杂志: 电子版,2010,4(3):41-44.[3] Wadia PP, Tambur AR. Yin and Yan of cytokine regulation in solid organ graft rejection and tolerance. Clin Lab Med. 2008; 28(3):469-479.[4] Joffre O, Santolaria T, Calise D, et al. Prevention of acute and chronic allograft rejection with CD4+CD25+Foxp3+ regulatory T lymphocytes. Nat Med. 2008;14(1): 88-92. [5] Li J, Lai X, Liao W, et al. The dynamic changes of Th17/Treg cytokines in rat liver transplant rejection and tolerance. Int Immunopharmacol.2011;11(8): 962-967.[6] 刘文宇,张雷,朱有华.T淋巴细胞在肾移植排斥反应中的作用[J]. 中华器官移植杂志,2011,32(12):765-767.[7] 彭勇,龚建平.共刺激分子与移植免疫耐受[J].中国普外基础与临床杂志,2010,17(6):552-556.[8] Graca L, Honey K, Adams E, et al. Cutting edge:anti-CD154 therapeutic antibodies induce infectious transplantation tolerance. J Immunol. 2000;165(9): 4783-4786.[9] Shimizu K, Schnbeck U, Mach F, et al. Host CD40 ligand deficiency induces long-term allograft survival and donor-special tolerance in mouse cardiac transplantation but does not prevent graft arteriosclerosis. J Immunol. 2000; 165(6):3506-3518.[10] Liu SM, Sutherland AP, Zhang Z, et al.Overexpression of the CTLA-4 isoform lacking exons 2 and 3 causes autoimmunity. Immunol.2012;188(1):155-162. [11] Walunas TL, Lenschow DJ, Bakker CY, et al.CTLA-4 can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation. Immunity. 1994;1:405-413. [12] Tosti G, Cocorocchio E, Pennacchioli E.Anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 antibodies in melanoma. Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol. 2013;6:245-256.[13] Antczak A, Pastuszak-Lewandoska D, Górski P,et al.Ctla-4 expression and polymorphisms in lung tissue of patients with diagnosed non-small-cell lung cancer. Biomed Res Int. 2013; 2013:576486.[14] Lesterhuis WJ, Salmons J, Nowak AK,et al. Synergistic effect of CTLA-4 blockade and cancer chemotherapy in the induction of anti-tumor immunity. PLoS One. 2013;8(4): e61895.[15] Kow NY, Mak A. Costimulatory pathways: physiology and potential therapeutic manipulation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Dev Immunol. 2013;2013:245928.[16] Stumpf M, Zhou X, Bluestone JA. The B7-independent isoform of CTLA-4 functions to regulate autoimmune diabetes. J Immunol. 2013;190(3):961-969.[17] Watanabe N, Nakajima H.Coinhibitory molecules in autoimmune diseases. Clin Dev Immunol. 2012;2012:269756.[18] Pieper J, Herrath J, Raghavan S,et al. CTLA4-Ig (abatacept) therapy modulates T cell effector functions in autoantibody-positive rheumatoid arthritis patients. BMC Immunol. 2013;14:34.[19] Ruocco MG, Pilones KA, Kawashima N, et al. Suppressing T cell motility induced by anti-CTLA-4 monotherapy improves antitumor effects. Clin Invest. 2012;122(10): 3718-3730. [20] Lin H, Rathmell JC, Gray GS, et al. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen 4(CTLA4) blockade accelerates the acute rejection of cardiac allografts in CD28-deficient mice: CTLA4 can function independently of CD28.J Exp Med. 1998;188(1):199-204. [21] Zhou P, Szot GL, Guo Z, et al. Roles of STAT4 and STAT6 signaling in allograft rejection and CTLA4-Ig-mediated tolerance. J Immunol. 2000;165 (10):5580-5587.[22] Kwek SS, Dao V, Roy R,et al. Diversity of antigen-specific responses induced in vivo with CTLA-4 blockade in prostate cancer atients. Immunol. 2012;189(7):3759-3766.[23] Kroczek R, Hamelmann E. T cell costimulatory molecules: optimal targets for the treatment of allergic airway disease with monoclonal antibodies. J Allegry Clin Immunol. 2005; 116(4):906-909.[24] Grosso JF, Jure-Kunkel MN. CTLA-4 blockade in tumor models: an overview of preclinical and translational research. Cancer Immun. 2013;13: 5. [25] Teft WA, Kirchhof MG, Madrenas J. A molecular perspective of CTLA-4 function. Ann Rev Immunol. 2006;24:65-97.[26] Walunus TL, Lenschow DJ, Bakker CY, et al. CTLA-4 can function as a negative regulator of T cell activation. Immunity. 1994;1(15):405-413.[27] Auchincloss H, Turka LA. CTLA-4: not all costimulation is stimulatory. J Immunol. 2011;187: 3457-3458.[28] 蔡雷,于善谦,朱乃硕.抗人CTLA-4单克隆抗体的制备及其生物学活性研究[J].上海免疫学杂志,2002,22(3):168-172.[29] Krummel MF, Allison JP.CD28 and CTLA-4 have opposing effects on the response of T cells to stimulation. J Exp Med. 1995;182(2):459-465.[30] McGrath MM, Najafian N.The role of coinhibitory signaling pathways in transplantation and tolerance. Front Immunol. 2012;3:47. [31] Brunet JF, Denizot F, Luciani MF,et al. A new member of the immunoglobulin super- family--CTLA-4. Nature. 1987;328 (6127):267-270. [32] Schreiber RD, Old LJ, Smyth MJ. Cancer immunoediting: integrating immunity's roles in cancer suppression and promotion. Science. 2011;331:1565-1570.[33] Pentcheva-Hoang T, Corse E, Allison JP. Negative regulators of T cell activation: potential targets for therapeutic intervention in cancer, autoimmune disease, and persistent infections. Immunol Rev. 2009;229:67-87.[34] Yokosuka T, Kobayashi W, Takamatsu M, et al. Spatiotemporal basis of CTLA-4 costimulatory molecule-mediated negative regulation of T cell activation. Immunity. 2010;33:326-339.[35] Liu MF, Wang CR, Chen PC, et al. Increased expression of soluble cytotoxic T-lymphocyte -associated antigen-4 molecule in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Immunol. 2003;57(6): 568-572.[36] Tsai MK, Ho HN, Chien HF, et al. The role of B7 ligands (CD80 and CD86) in CD152-mediated allograft tolerance: a crosscheck hypothesis. Transplantation. 2004;77:48-54. [37] Wang X, Hao J, Metzger DL,et al. Blockade of both B7-H4 and CTLA-4 co-signaling pathways enhances mouse islet allograft survival. Islets. 2012;4(4):284-295.[38] Li J, Zhu H, Wang S, et al. Blockade of NKG2D synergized with CTLA4-Ig in promoting long-term graft survival in murine models of cardiac transplantation. Transplantation. 2012; 93(4):356-363.[39] Minguela A, Marín L, Torío A, et al. CD28/CTLA-4 and CD80/CD86 costimulatory molecules are mainly involved in acceptance or rejection of human liver transplant. Hum Immunol. 2000;61(7): 658-669.[40] Demirkiran A, Kok A, Kwekkeboom J, et al. Low circulating regulatory T-cell levels after acute rejection in liver transplantation. Liver Transpl. 2006;12(2): 277-284. |