Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2014, Vol. 18 ›› Issue (5): 773-778.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2014.05.020
Previous Articles Next Articles
A breakthrough in antibody-drug conjugates in anti-immune rejection
Guo Cai-long, Mang Yuan-yi, Zhang Lei
- Department of General Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150086, Heilongjiang Province, China
-
Revised:2013-12-08Online:2014-01-29Published:2014-01-29 -
Contact:Zhang Lei, M.D., Chief physician, Department of General Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150086, Heilongjiang Province, China -
About author:Guo Cai-long, Studying for master’s degree, Department of General Surgery, Second Affiliated Hospital of Harbin Medical University, Harbin 150086, Heilongjiang Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81172819
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guo Cai-long, Mang Yuan-yi, Zhang Lei. A breakthrough in antibody-drug conjugates in anti-immune rejection[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 773-778.
share this article
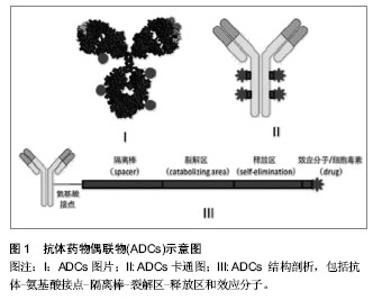
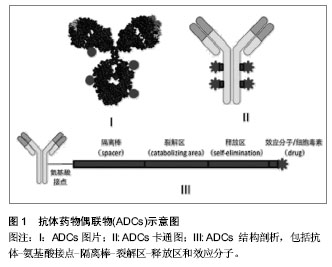
2.1 抗体药物偶联物的结构特点 2.1.1 概念 抗体药物偶联物是由抗体和效应分子通过化学结合子(linker)偶联而成,能够高效特异地识别并杀伤目的细胞。根据效应分子的不同,可将其分为化学免疫偶联物、免疫毒素、放射性免疫偶联物等3类。这种药物与普通药物或者抗体相比,能极大的提高药物的杀伤效力,并具有很低的毒副作用。泛义的抗体药物偶联物通常由抗体、接头(linker)和效应分子等3部分组成,其设计原则是在体循环中保持其稳定性,而到达靶细胞后能有效释放运载的毒性物质[2]。一种成功的抗体药物偶联物的设计不仅需要优化每一个组成部分,而且也要注重每个组成部分的配搭和相互影响。抗体药物偶联物结构如图1所示[3]。"
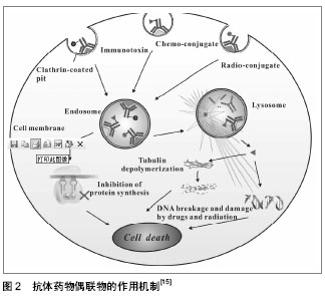
2.1.2 抗体 抗体是抗体药物偶联物的制导系统,其选择取决于相应的靶向抗原,对抗体药物偶联物的成功起着关键性的作用。实际过程中抗体、抗原以及偶联物的性能都会影响抗体内化的效率和速率,进而偶联物的安全性和细胞吞噬都会受到影响[4],其中抗原的分布和丰度决定着抗体类型的选择。抗体对抗原的亲和力以及抗体相对分子质量的大小等性能是决定偶联物对靶向细胞粘合性和渗透性的主要因素。 一般来讲,理想的抗体是单克隆抗体或抗体片段,能高效率识别、结合特异性抗原或肿瘤相关抗原,并能在靶细胞内释放效应分子。除此之外,抗体或抗体片段必须能保持其原有特征,比如保持IgG1抗体Fc链引入的免疫效应、抗体引起的抗体依赖性细胞毒性[5]、吞噬或Fc介导的补体依赖性细胞毒性(CDC)等[6]。然而完整抗体的相对分子质量较大,影响其穿透组织能力。目前小型化的抗体片段如 Fab、F(ab)’2、单链抗体(scFv)、双链抗体(diabodies)、三链抗体、微型抗体(minibodies)等在抗体药物偶联物抗体的选择上应用广泛[7-8]。 2.1.3 效应分子 效应分子是抗体药物偶联物的弹头部分,可分为以下3类:细胞毒性药物、蛋白毒素和放射性核素。细胞毒性药物是经典的化疗药物,疗效肯定。将细胞毒性药物与具有靶向作用的生物大分子偶合,增强细胞毒药物的靶向作用,成为细胞毒性药物研发的新趋势。现如今,常用于合成抗体药物偶联物的细胞毒性药物有美登素、海兔毒素及卡里奇霉素[1]。蛋白毒素主要指的是通过基因工程技术制备的细菌或者是来源于植物的毒素[9]。基因重组技术可改造毒性结构,如去除毒素的细胞结合域来降低毒性及通过点突变来增强毒素的杀伤效力等[10-11]。目前最常用的细菌毒素是改造后的白喉毒素和假单胞菌外毒素,而植物毒素则是去糖基化的蓖麻毒素等。常用的放射性同位素分为两类:β放射体和α放射体。β放射体包括131I和90Y,由于其独特的放射特异性,易获得性,易于偶联和相对较长的半衰期,在放射性免疫偶联物中最常使用。而α发射体相比于β发射体,对正常细胞的非特异毒性较小,正处于研究状态。 2.1.4 接头 接头是组成抗体药物偶联物的另一重要成分,它对保持药物在循环系统中的完整性起关键性作用。理想的接头必须能使效应分子在靶细胞中有效释放且产生活性,同时不会对正常组织产生损害。接头类型的选择对抗体药物偶联物的疗效极为显著。相同的抗体及效应分子通过不同种类的接头偶联后其药效也不尽相同。根据化学结合子选取的不同分为两大类杀伤、代谢机制不同的药物,即易裂解型(cleavable type)和稳定型(non-cleavable type)[2]。其中,易裂解型可分为3类,分别是二硫键、肽链型以及酸不稳定性腙接头;稳定型接头主要是指硫醚键。采用稳定性接头形成的抗体药物偶联物安全性要更高一些,可能是由于在循环系统裂解的药物更少,更有益于临床应用。 2.2 抗体药物偶联物的作用机制 抗体药物偶联物随体循环到达靶细胞后需释放有效的细胞毒性药物。通常细胞毒性药物从抗体上释放出来包括以下两种方式:二硫键还原、蛋白酶水解或裸露到酸性环境[12]。通过二硫键连接的药物往往需要还原反应来释放,由肽键连接到抗体的蛋白毒素药物,则通过蛋白酶的水解来释放。而以硫醚键为代表的稳定型接头,则需要在溶酶体完全降解单抗而释放药物。进入细胞后的抗体药物偶联物发挥作用有以下两种途径:第一种是效应分子仍偶联在抗体上起效,第二种则是在释放后起效。释放的细胞毒性物质需到达胞质内相应的位点,而溶酶体、内体以及内质网对这些物质的起效起关键性的作用。免疫毒素大多数为不同类型的蛋白质合成抑制剂。例如,蓖麻毒素可以将核糖体60s亚基中20s rRNA上4 324位的腺嘌呤残基的 N-糖苷键水解,进而使核糖体失活,这类蛋白毒素统称为核糖体失活蛋白质[13]。细胞毒素如海兔毒素和美登素及其类似物美登木素生物碱能解聚微管蛋白,成功阻止细胞增殖,而卡里奇霉素能使DNA双链断裂,最终导致细胞死亡。放射性核素在胞内能通过持续性辐射,使细胞周期中放射性最敏感的G2/M期阻滞,抑制靶细胞DNA修复[14],而导致细胞死亡。抗体药物偶联物作用机制如图2所示[15]。"
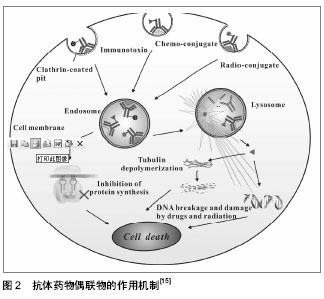

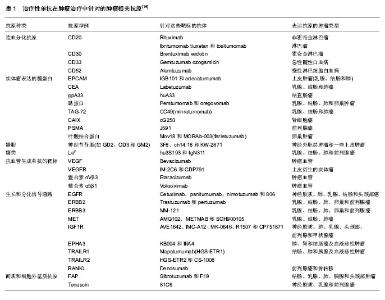
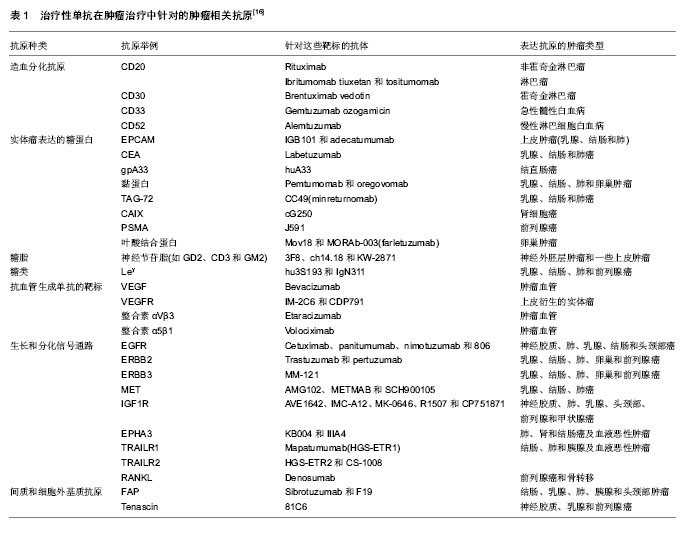
抗体药物偶联物中使用的效应分子同样包括细胞毒性抗肿瘤药物、蛋白毒素和放射性核素3种[17],而目前已经批准上市和进入临床研究的药物主要是细胞毒性药物,其中应用较多的包括美登素(Maytansine)、卡奇霉素(Calicheamicin)和Auristantin及其衍生物,在治疗早期乳腺癌,卵巢癌及恶性血液系统肿瘤中取得显著疗效[18-20]。基因泰克公司将单克隆抗体赫赛汀(曲妥珠单抗)与美登素相结合,制造抗体药物偶联物—T-DM1临床疗效显著[21]。曲妥珠单抗可靶向作用于乳腺癌和胃癌人表皮生长因子受体2(HER2),而美登素的合成衍生物小分子毒素,可与微管蛋白结合,抑制微管形成。T-DM1综合了靶向HER2受体的曲妥珠单抗与高效的细胞毒性药物优势而杀死肿瘤细胞[22],体内外实验均表明,相比于曲妥珠单抗,T-DM1毒性较低,并且具有更好的药代动力学特性和整体疗效[23]。在卵巢癌治疗方面,将曲妥珠单抗与细胞毒性药物偶联运用,不仅降低了不良反应,而且提高了患者的生存期[24]。临床研究显示曲妥珠单抗与含美登醇衍生物 DM1偶联后,偶联物对肿瘤细胞具有明显的选择性和有效性,对大部分过表达 HER2的卵巢癌细胞活性明显,而不会影响低表达HER2的卵巢癌细胞。 国外学者根据不同类型的抗体药物偶联物杀伤效应和药物代谢动力学的有所不同对稳定型和易裂解型抗体药物偶联物进行深入研究表明,抗体药物偶联物在抗肿瘤中具有更高效的杀伤效应和更小的毒副作用,主要因为稳定结合子型抗体药物偶联物能够确切的将药物携带至细胞内,而在外周血和细胞表面很少降解,同等给药剂量,使用稳定型抗体药物偶联物更像缓释剂一样能够长时间在血液保持有效的杀伤浓度而不释放出多余的毒素,从而减少药物毒副作用[25-29]。随着抗体药物偶联物在技术上的日趋成熟以及前沿的药物设计理念,通过其精确的靶向肿瘤药物输送系统,将来有希望成为抗肿瘤领域生物抗体的主流药物。 2.4 抗体药物偶联物在器官移植中的应用 同种异体器官移植已经成为终末器官衰竭患者修复病损的组织和器官,并重建其功能的必要治疗方法[30]。目前国内外已开展同种肝脏、心脏、肺、小肠、脾、骨髓、胰岛移植,以及肺、胰、肾、肝十二指肠联合移植和腹部多器官联合移植,其临床效果差强人意,其中主要原因之一就是存在宿主和移植物间的免疫排斥反应[31]。虽然免疫抑制剂可以用来维持移植物在宿主体内的存活,但由于它的非特异性及毒副作用,长期应用该类药物会导致受者免疫力低下而出现易感染、癌症等副作用。然而一类新型的生物类免疫抑制剂尤其是免疫毒素可以通过其靶向作用,清除相应的抗原特异性T细胞,毒副作用明显减小,有更好的发展潜力[32]。 免疫毒素隶属于抗体药物偶联物的范畴,是由导向能力的抗体或抗体片段和细胞毒性物质偶联而成的。它结合于细胞表面特定的抗原或受体后通过抑制蛋白质合成导致靶细胞死亡,而不损伤周围正常组织,在治疗恶性肿瘤、移植排斥等方面显示出巨大的应用潜力[33]。免疫毒素分子的抗体部分包括单克隆抗体和某些具有重要生物学功能的受体或配体;免疫毒素分子的毒素部分主要包括植物来源毒素、细菌毒素和人源性蛋白毒素。植物来源的蛋白毒素分为两类:一类是完整毒素,主要有思子毒素和蓖麻子毒素等,另一类是单链毒素,主要以肥皂草毒素(saporin)为代表;细菌毒素主要有白喉毒素和绿脓杆菌外毒素;人源性蛋白毒素主要有促凋亡蛋白等[34-35]。另外其他来源的毒素如来自蜜蜂的蜂毒肽,也可用于构建毒素。 植物蛋白毒素(saporin,SAP)是核糖体灭活蛋白,已被广泛用于药学和生物学研究领域,大多通过基因工程技术制备成免疫毒素,有明显的靶细胞毒性。Tazzari等[36]用化学方法将重组人抗 CTLA-4单链抗体和saporin耦联,制备得到新型免疫毒素83- Saporin,实验结果显示83-Saporin延长了异体移植物的存活期,可能成为预防急性移植物抗宿主疾病和移植排斥的新工具,如果在移植早期给药,可以改善临床疗效[33]。同样,已经有丰厚的资料表明CD8效应细胞是通过CD103分子特异地识别上皮细胞配体E-Cadherin攻击胰岛移植物上皮成分的[37-38],并且进一步证实了CD103免疫毒素M290-SAP具有体内杀伤CD103表达细胞的能力,能够显著地延长胰岛同种移植物的存活时间[25,39-40]。但现有的免疫毒素杀伤片段存在一些缺点:毒副作用大,不易经肾小管清除而在体内堆积,容易引起多器官损害,导致非特异性损伤[25];相对分子质量相对较大,组织穿透性差;需要分子内化过程,作用时间长,易产生耐药性等。 目前,把具有导向作用的anti -CTLA -4和具有杀伤片段的膜通道形成肽-人源化含穿孔素孔道形成域的小分子肽连接,构建具有高效低毒的重组免疫毒素[41]。体内外实验均显示其显效快,无明显毒副作用,延长了移植物存活时间。在效应分子的选择上,国外较为成熟、安全的毒素药物,如:Seattle Genetics药物MMAE与anti-CD30+抗体偶联制备Adcetris注射液(brentuximab vedotin)已在临床用于治疗霍奇金淋巴瘤以及复发性间变性大细胞淋巴瘤(ALCL),罗氏公司用于治疗乳腺癌的新药:T-DM1(trastuzumab-DM1)即是赫赛汀抗体-药物偶联物。这些毒素相比于植物毒素SAP,毒副作用明显减小,如应用它们来制备抗体药物偶联物,和M290-SAP相比较,可能是一种更有潜力应用于阻断CD103/ E-Cadherin通路,进而为同种胰岛移植抗排斥反应提供新颖的治疗靶点的研究药物[15-19],初步研究结果已支持了这一观点。此外,抗体药物偶联物对体内正常免疫细胞杀伤能否促进同种胰岛移植物的长期存活具有复杂的机制,而不是单纯的免疫抑制,如有研究发现在胰岛移植前后不同的时间点给予单克隆抗体CD3能诱导免疫耐受从而减轻排斥反应并证实了抗体制剂在治疗免疫排斥中拥有治疗时间窗[42]。 2.5 抗体药物偶联物目前所面临的问题 理想的抗体药物偶联物就是把具有临床效果很好的靶向特异性抗体和特定的小分子化学药物的药代动力学结合起来的化合物。目前,抗体药物偶联物仍面临技术上的问题。例如,首先是利用单克隆抗体把特定的细胞毒性药物带到靶细胞,在实际操作中是一项十分复杂的技术。其次,单克隆抗体与有治疗效果明显的细胞毒性药物结合必须足够稳定,否则可能大量的细胞毒性药物进入体循环,进而引起许多意想不到的副作用,包括肝脏毒性、骨髓抑制以及外周神经毒性等,这可能与药物的脱靶有关。最后,抗体药物偶联物制备后,应该保证该药物对靶点的高度识别。尽管目前有些抗体药物偶联物临床前研究数据很理想,但在后期临床试验及应用中却显示出了缺乏显著地抗体药物与靶细胞亲和力的弊端。因此下一阶段面临几个关键问题:①定位偶联技术,这是一种可控制偶联物位置的更精确技术。②定量偶联技术,抗体偶联的药物分子数目的多少将会直接影响其在体内的分布及其稳定性。③如何进一步优化抗体,使其能够透过毛细管内皮层和穿过靶细胞外间隙到达靶细胞内部,从而提高药效。④运用蛋白质工程学技术进一步的使抗体人源化,进而降低人对抗体偶联药物的免疫反应[42]。⑤通过调整给药剂量观察临床疗效,并且注意患者对于抗体偶联药物副作用的耐受情况,为选择合适的给药剂量提供参考依据[43]。"

| [1] Dosio F, Brusa P, Cattel L. Immunotoxins and anticancer drug conjugate assemblies: the role of the linkage between components.Toxins (Basel). 2011;3(7):848-883. [2] Polson AG, Calemine-Fenaux J, Chan P,et al. Antibody-drug conjugates for the treatment of non-Hodgkin's lymphoma: target and linker-drug selection. Cancer Res. 2009;69(6):2358-2364. [3] Zhu GD, Fu YX. Design of next generation antibody drug conjugates.Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2013;48(7):1053-1070.[4] Thurber GM, Schmidt MM, Wittrup KD. Antibody tumor penetration: transport opposed by systemic and antigen-mediated clearance.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2008; 60(12): 1421-1434. [5] Hagenbeek A, Gadeberg O, Johnson P,et al. First clinical use of ofatumumab, a novel fully human anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody in relapsed or refractory follicular lymphoma: results of a phase 1/2 trial.Blood. 2008;111(12):5486-5495. [6] Miao QF, Shao RG, Zhen YS. An overview of antibody-based cancer therapy.Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012; 47(10):1261-1268.[7] Watanabe TS, Ohtori S, Koda M, et al. Adenoviral gene transfer in the peripheral nervous system.J Orthop Sci. 2006; 11(1):64-69.[8] 甄永苏.抗体药物与肿瘤靶向治疗[J].医学研究杂志, 2007,36(2): 1-2.[9] Pastan I, Hassan R, FitzGerald DJ,et al. Immunotoxin treatment of cancer.Annu Rev Med. 2007;58:221-237.[10] Laske DW, Muraszko KM, Oldfield EH,et al.Intraventricular immunotoxin therapy for leptomeningeal neoplasia. Neurosurgery. 1997;41(5):1039-1049. [11] Weaver M, Laske DW.Transferrin receptor ligand-targeted toxin conjugate (Tf-CRM107) for therapy of malignant gliomas. J Neurooncol. 2003;65(1):3-13.[12] Sun Y, Yu F, Sun BW. Antibody-drug conjugates as targeted cancer therapeutics.Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2009;44(9):943-952.[13] 詹金彪,郑树.天然蛋白毒素的研究和临床应用展望[J].浙江大学学报:医学版,2005,34(3):197-200.[14] Shenoi J, Gopal AK, Press OW, et al. Recent advances in novel radioimmunotherapeutic approaches for allogeneic hematopoietic cell transplantation.Curr Opin Oncol. 2010; 22(2):143-149. [15] Lin L, Ding Q, Tang Q,et al. Antibody-drug conjugates and their application in the treatment of hematological malignancies.Yao Xue Xue Bao. 2012;47(10):1287-1296.[16] Scott AM,Wolchok JD,Old LJ. Antibody therapy of cancer.Nat Rev Cancer.2012;12:278-287.[17] Govindan SV, Goldenberg DM. Designing immunoconjugates for cancer therapy. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2012;12(7): 873-890. [18] Saini KS, Azim HA Jr, Metzger-Filho O,et al. Beyond trastuzumab: new treatment options for HER2-positive breast cancer.Breast. 2011;20 Suppl 3:S20-27.[19] Lewis Phillips GD, Li G, Dugger DL,et al. Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer with trastuzumab-DM1, an antibody-cytotoxic drug conjugate.Cancer Res. 2008;68(22): 9280-9290.[20] Amadori S, Stasi R. Monoclonal antibodies and immunoconjugates in acute myeloid leukemia.Best Pract Res Clin Haematol. 2006;19(4):715-736.[21] 张敏,朱虹光.抗HER2单克隆抗体研究新进展[J].国外医学:生理、病理科学与临床分册, 2003,23(3):257-259.[22] Shak S.Overview of the trastuzumab (Herceptin) anti-HER2 monoclonal antibody clinical program in HER2-overexpressing metastatic breast cancer. Herceptin Multinational Investigator Study Group.Semin Oncol. 1999;26(4 Suppl 12):71-77.[23] Pegram MD, Slamon DJ.Combination therapy with trastuzumab (Herceptin) and cisplatin for chemoresistant metastatic breast cancer: evidence for receptor-enhanced chemosensitivity.Semin Oncol. 1999;26(4 Suppl 12):89-95.[24] Cirstoiu-Hapca A, Buchegger F, Lange N,et al. Benefit of anti-HER2-coated paclitaxel-loaded immuno-nanoparticles in the treatment of disseminated ovarian cancer: Therapeutic efficacy and biodistribution in mice.J Control Release. 2010; 144(3):324-331.[25] 张雷,Gregg Hadley.CD103免疫毒素在同种胰岛移植中的应用[J].中华实验外科杂志,2011,28(2):194-196.[26] Oflazoglu E, Stone IJ, Gordon K,et al. Potent anticarcinoma activity of the humanized anti-CD70 antibody h1F6 conjugated to the tubulin inhibitor auristatin via an uncleavable linker.Clin Cancer Res. 2008;14(19):6171-6180.[27] Junutula JR, Flagella KM, Graham RA,et al. Engineered thio- trastuzumab-DM1 conjugate with an improved therapeutic index to target human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive breast cancer.Clin Cancer Res. 2010;16(19):4769-4778. [28] Hamblett KJ, Senter PD, Chace DF,et al. Effects of drug loading on the antitumor activity of a monoclonal antibody drug conjugate.Clin Cancer Res. 2004;10(20):7063-7070.[29] Lewis Phillips GD, Li G, Dugger DL, et al.Targeting HER2-positive breast cancer with trastuzumab-DM1, an antibody-cytotoxic drug conjugate.Cancer Res. 2008;68(22): 9280-9290. [30] Riley JL, June CH, Blazar BR. Human T regulatory cell therapy: take a billion or so and call me in the morning. Immunity. 2009;30(5):656-665. [31] Mori M, Muroi K, Matsuyama T,et al. Benefits of mycophenolate mofetil for refractory graft-versus-host disease. Rinsho Ketsueki. 2007;48(8):624-631.[32] 郭怡,蔡常洁.CTLA4Ig诱导免疫耐受作用的研究进展[J].国际内科学杂志,2007,34(7):427-431.[33] 金海龙,石炳毅. CTLA-4相关药物与移植免疫研究进展[J].西南国防医药, 2011, 21(12):1410-1412.[34] 罗良生,黄强.基因重组免疫毒素研究进展[J].国外医学:肿瘤学分册,2000,27(5):269-273.[35] 卢丽琨,田利源,汪莉.人源化免疫毒素的研究进展[J].国际药学研究杂志,2009,36(6): 426-430.[36] Tazzari PL, Polito L, Bolognesi A,et al. Immunotoxins containing recombinant anti-CTLA-4 single-chain fragment variable antibodies and saporin: in vitro results and in vivo effects in an acute rejection model.J Immunol. 2001;167(8):4222-4229.[37] Feng Y, Wang D, Yuan R,et al. CD103 expression is required for destruction of pancreatic islet allografts by CD8(+) T cells. J Exp Med. 2002;196(7):877-886.[38] 张雷,Gregg Hadley.CD103分子介导CD8+T淋巴细胞对同种胰岛移植物的损伤[J].中华器官移植杂志,2011,32(2):91-94.[39] Zhang L, Hadley GA. Application of anti-CD103 immunotoxin for saving islet allograft in context of transplantation.Chin Med J (Engl). 2010;123(24):3644-3651.[40] Zhang L, Moffatt-Bruce SD, Gaughan AA,et al. An anti-CD103 immunotoxin promotes long-term survival of pancreatic islet allografts.Am J Transplant. 2009;9(9):2012-2023. [41] Zeng L, Wan L, Chen L,et al. Selective depletion of activated T cells by recombinant immunotoxin containing anti-CTLA-4 single-chain fragment of variable antibody and N-terminal fragment of perforin.Transplant Proc. 2006;38(7):2151-2153.[42] You S, Zuber J, Kuhn C,et al. Induction of allograft tolerance by monoclonal CD3 antibodies: a matter of timing.Am J Transplant. 2012;12(11):2909-2919. [43] 王宗凯,刘煜.抗体偶联药物的有关进展[J].药物生物技术,2011, 18(4): 359-363. |
| [1] | Chen Chang-qing, Shi Bing-yi, Cai Ming, Zhao Yu-bo, Jin Bo-quan, Wang Chun-yan, Han Yong, Xiao Li, Zhou Wen-qiang, Li Zhou-li. Cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 in acute rejection after renal transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 730-735. |
| [2] | Yu Xiao-di, Wang Wei-zhong, Jiao Jie-ying, Zheng Jian-yong, Zhao Zheng-wei. Effect of artesunate on acute rejection after small intestine transplantation in rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 761-766. |
| [3] | Cai Qiu-cheng. T lymphocytes and immune tolerance of liver transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(5): 791-796. |
| [4] | Yu Li-chong, Qian Ye-yong, Shi Bing-yi, Fan Yu, Liu Lu-peng, Yu Fei. Genomics and gene polymorphism of immunosuppressive drugs after kidney transplantation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(46): 7509-7514. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||