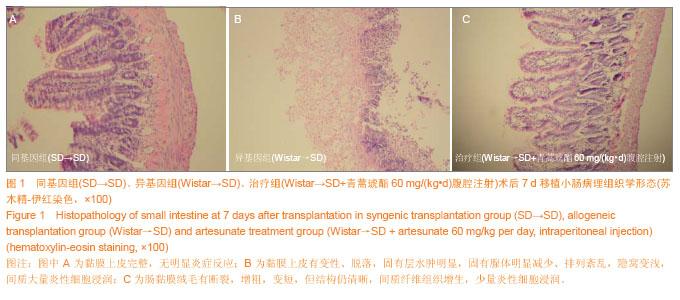
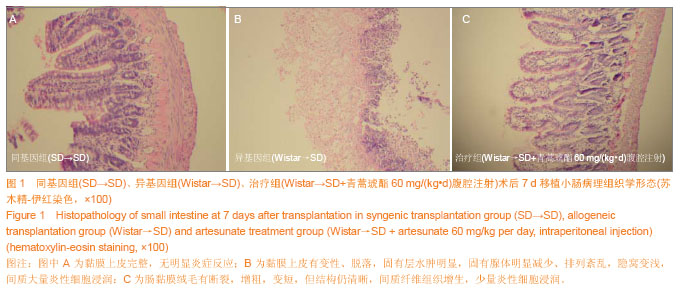
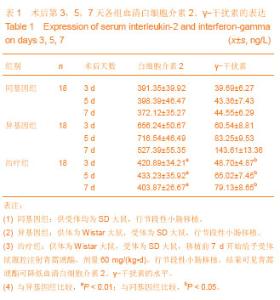
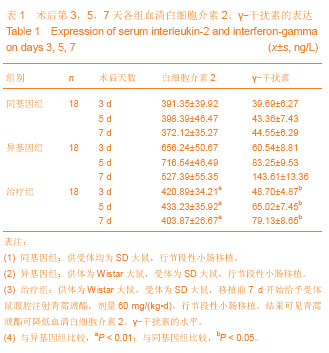
| [1] 伍晓汀,黎介寿.改进技术的大鼠全小肠移植术[J].中华显微外科杂志,1999,22(1):48-50.[2] 董光龙,李开宗,王为忠,等.双Cuff双造口大鼠异位小肠移植模型的建立[J].第四军医大学学报,2003,24(2):189.[3] Rosemurgy AS, Schraut WH. Small bowel allografts. Sequence of histologic changes in acute and chronic rejection. Am J Surg. 1986;151(4):470-475.[4] Schmid T, Oberhuber G, Körözsi G,et al. Histologic pattern of small bowel allograft rejection in the rat. Mucosal biopsies do not provide sufficient information. Gastroenterology. 1989; 96(6):1529-1532.[5] 吴波,周晓军.小肠移植后急性排斥反应的病理诊断标准[J].肠外与肠内营养,2005,12(6):378-381.[6] 夏穗生.临床移植医学[M].杭州:浙江科学技术出版社,1999: 438-442.[7] 张汝芝,高玉祥.青蒿琥酯对Ⅰ~Ⅳ型变态反应的影响[J].中华皮肤科杂志,1998,31(6):368-372.[8] 杨启超.青蒿素及其衍生物青蒿酯钠与青蒿醚的药理研究[J].广西医学,1984,6(6):292-294.[9] 徐继红,章元沛.二氢青蒿素与青蒿琥酯的抗孕作用[J].药学学报,1996,31(9):657-659.[10] Greenfeld K, Avraham R, Benish M,et al. Immune suppression while awaiting surgery and following it: dissociations between plasma cytokine levels, their induced production, and NK cell cytotoxicity. Brain Behav Immun. 2007;21(4):503-513.[11] 封光华,张喜平,朱炜,等.小肠移植患者可溶性白介素2受体的早期变化(附一例报道)[J].胃肠病学和肝病学杂志,2006,15(1): 98-99.[12] Williams JG, Jurkovich GJ, Maier RV. Interferon-gamma: a key immunoregulatory lymphokine. J Surg Res. 1993;54(1): 79-93.[13] 育柳英,林培英,张丹,等.青蒿琥酯对小鼠肝癌及S180实体瘤的抑制作用[J].实用癌症杂志,2001,16(3):245-247.[14] 林培英,冯昭明,潘竟锵.青蒿琥酯对小鼠免疫功能的影响[J].中国药理学报,1995,16(5):441-443.[15] Khan NU, Fildes JE, Al-Aloul M, et al. Increased serum concentrations of Th1 chemokines are associated with acute rejection following heart transplantation. The Journal of Heart and Lung Transplantation.2007;26(2):194.[16] Middleton SJ, Jamieson NV. The current status of small bowel transplantation in the UK and internationally. Gut. 2005;54(11): 1650-1657.[17] Matsuura T, Taguchi T, Hayashida M,et al. Relationship between real-time monitoring of the graft motility and mucosal histology in swine intestinal transplantation.Transplant Proc. 2006;38(6):1851-1852.[18] Tocci MJ, Matkovich DA, Collier KA, et al. The immunosuppressant FK506 selectively inhibits expression of early T cell activation genes. J Immunol. 1989; 143: 718-726.[19] Greenfeld K, Avraham R, Benish M, et al. Immune suppression while awaiting surgery and following it: Dissociations between plasma cytokine levels, their induced production, and NK cell cytotoxicity . Brain Behav Immun. 2007;21(4):503-513.[20] 金伯泉.细胞和分子免疫学[M].2版.北京:科学出版社,2001: 396-411.[21] Ziarkiewicz-Wróblewska B, Górnicka B, O?dakowska U,et al. Plasmacytic hyperplasia--the early form of posttransplant lymphoproliferative disorder--with atypical morphology and clinical course in patient after liver transplantation: a case report. Transplant Proc. 2003; 35(6):2320-2322. [22] Robert CD, Lacaille F, Canioni D,et al. EBV-negative lymphoproliferative disease with hyper-IgA, in a child with combined liver and small bowel transplantation. Pediatr Transplant. 2004;8(3):305-307.[23] 李泽林,杨立新,刘菊福,等.青蒿酯钠致畸作用的研究[J].中药通报,1988,13(4) :234-236.[24] Singh NP, Lai H. Selective toxicity of dihydroartemisinin and holotransferrin toward human breast cancer cells. Life Sci. 2001;70(1):49-56. [25] Woerdenbag HJ, Moskal TA, Pras N,et al. Cytotoxicity of artemisinin-related endoperoxides to Ehrlich ascites tumor cells. J Nat Prod. 1993;56(6):849-856.[26] 宁殿玺,徐在海,滕翕和.青蒿酯钠静脉注射对犬的亚急性毒性[J].中国药理学与毒理学杂志,1987,1(1):135-136.[27] Dayan AD. Neurotoxicity and artemisinin compounds do the observations in animals justify limitation of clinical use. Med Trop (Mars). 1998;58(3 Suppl):32-37.[28] Gorczynski RM, Alexander C, Bessler W,et al. An alteration in the levels of populations of CD4+ Treg is in part responsible for altered cytokine production by cells of aged mice which follows injection with a fetal liver extract. Immunol Lett. 2007; 109(2):101-112. [29] Gorczynski RM, Alexander C, Bessler W,et al.An alteration in the levels of populations of CD4+ Treg is in part responsible for altered cytokine production by cells of aged mice which follows injection with a fetal liver extract.Immunol Lett. 2007; 109(2):101-112.[30] 周平,高玉祥.青蒿琥酯对小鼠免疫功能的影响[J].蚌埠医学院学报,1996,21(1):5-8.[31] Khan NU, Fildes JE, Al-Aloul M, et al. Increased serum concentrations of Th1 chemokines are associated with acute rejection following heart transplantation.J Heart Lung Transplantation. 2007;26(2):194.[32] Nakashima H. Membranous nephropathy is developed under Th2 environment in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Med Hypotheses. 2007;69(4):787-791. [33] 金慧玲,高玉祥.青蒿琥酯对豚鼠表皮郎格罕细胞的影响[J].蚌埠医学院学报,1993,18(4) :225-227.[34] 张利群,窦肇华.大鼠小肠移植急性排斥反应中IL-2表达的研究[J].临沂医学专科学校学报,2004,26(3):161-162.[35] Dekel B, Böcher WO, Marcus H,et al. Acute cellular rejection of human renal tissue by adoptive transfer of allogeneic human peripheral blood mononuclear cells into chimeric rats: sequential gene expression of cytokines, chemokines and cytolytic effector molecules, and their regulation by CTLA-4-Ig. Int Immunol. 1999;11(10):1673-1683.[36] Steiger JU, Nickerson PW, Hermle M,et al. Interferon-gamma receptor signaling is not required in the effector phase of the alloimmune response. Transplantation. 1998;65(12): 1649-1652.[37] 周平,高玉祥.青蒿琥酯对NK细胞活性及ADCC 活性的影响[J].蚌埠医学院学报,1995,20(6):363-365.[38] Newell KA, He G, Guo Z,et al. Cutting edge: blockade of the CD28/B7 costimulatory pathway inhibits intestinal allograft rejection mediated by CD4+ but not CD8+ T cells.J Immunol. 1999;163(5):2358-2362.[39] Valujskikh A, Heeger PS. CD4+ T cells responsive through the indirect pathway can mediate skin graft rejection in the absence of interferon-gamma.Transplantation. 2000;69(5): 1016-1019.[40] Su GL, Walgenbach KJ, Heeckt PH,et al. Increased expression of interferon-gamma in a rat model of chronic intestinal allograft rejection.Transplantation. 1996; 62(2): 242-248.[41] 莫正魁,李立,王建忠.青蒿素对小鼠迟发型超敏反应的免疫抑制作用[J].昆明医学院学报, 2005,26(4): 55-59.[42] 林培英,张丹,肖柳英,等.青蒿素、青蒿酯和蒿甲醚对抑制性T细胞的作用[J].广州医药,1998,29(1):37-39.[43] 余其斌,金慧玲.青蒿琥酯治疗系统性红斑狼疮30例临床观察[J]. 蚌埠医学院学报,1996,21(3):173-174.[44] 金慧玲,肖玉周,高玉祥,等.青蒿琥酯对大鼠皮肤移植排斥反应的影响[J].蚌埠医学院学报,1997,22(3):152-153.[45] Takeuchi T, Lowry RP, Konieczny B. Heart allografts in murine systems. The differential activation of Th2-like effector cells in peripheral tolerance. Transplantation. 1992; 53(6):1281-1294.[46] Dallman MJ, Larsen CP, Morris PJ. Cytokine gene transcription in vascularised organ grafts: analysis using semiquantitative polymerase chain reaction. J Exp Med. 1991;174(2):493-496.[47] Hitoshi Nakashima. Membranous nephropathy is developed under Th2 environment in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Medical Hypotheses, 2007, 30: 231-235.[48] 郭尧,吴玲娟,徐潘生,等.大白鼠长期服用青蒿琥酯的安全性评估[J].中国血吸虫病防治杂志,2000,12(1):27-29.[49] 张俊才.健康人对青蒿琥酯片的耐受性和不良反应[J].新药与临床,1992,11(2):70-72.[50] 刘旭.抗疟药青蒿琥酯的研究[J].药学进展,1999,23:47-50.[51] 陈重阳,袁模军,唐国权.青蒿琥酯对小鼠实验性肝损伤的保护作用[J].中国药理学通报,1990,6(6):382. |