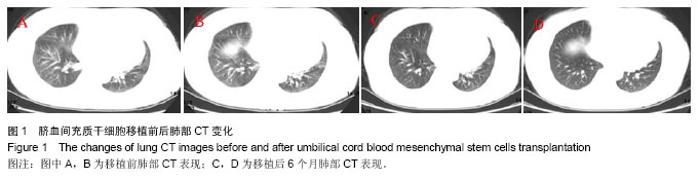
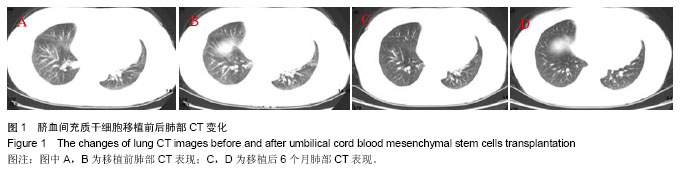
| [1] 陈光辉,牛丰南.炎症性肌病[A]// 李作汉,张平.神经肌肉疾病的临床与病理[M]. 北京:人民卫生出版社,2007:162-192 .
[2] Dalakas MC. Polymyositis, dermatomyositis and inclusion-body myositis. N Engl J Med. 1991;325(21): 1487-1498.
[3] Mastaglia FL, Phillips BA. Idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: epidemiology, classification, and diagnostic criteria. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2002;28(4):723-741.
[4] Reed AM, Ernste F. The inflammatory milieu in idiopathic inflammatory myositis. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2009;11(4): 295-301.
[5] McGuckin CP, Forraz N, Allouard Q, et al. Umbilical cord blood stem cells can expand hematopoietic and neuroglial progenitors in vitro. Exp Cell Res. 2004;295(2):350-359.
[6] Lu FZ, Fujino M, Kitazawa Y, et al. Characterization and gene transfer in mesenchymal stem cells derived from human umbilical-cord blood. J Lab Clin Med. 2005;146(5):271-278.
[7] Hao L, Gao L, Chen XH, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived stromal cells prevent graft-versus-host disease in mice following haplo-identical stem cell transplantation. Cytotherapy. 2011;13(1):83-91.
[8] Bohan A, Peter JB. Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1975;292(7):344-347.
[9] Hughes AL, Nei M. Evolution of the major histocompatibility complex: independent origin of nonclassical class I genes in different groups of mammals. Mol Biol Evol. 1989;6(6):559-579.
[10] Miller FW, Rider LG, Chung YL, et al. Proposed preliminary core set measures for disease outcome assessment in adult and juvenile idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2001;40(11):1262-1273.
[11] Erices A, Conget P, Minguell JJ. Mesenchymal progenitor cells in human umbilical cord blood. Br J Haematol. 2000; 109(1):235-242.
[12] 陈欢雪,王晓非.间充质干细胞移植治疗4种风湿性疾病:10年资料分析[J].中国组织工程研究, 2014, 18(14):2263-2268.
[13] Yang GX, Pan LP, Zhou QY, et al. Therapeutic effects of umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cells transplantation on systemic lupus erythematosus. Sichuan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2014;45(2):338-341, 350.
[14] 陈爱明,刘青,钱伯源,等. 皮肌炎/多发性肌炎患者白介素4、干扰素γ、转化生长因子β 1的检测[J].中华皮肤科杂志,2003,36(9): 505-506.
[15] Hagiwara E, Adams EM, Plotz PH, et al. Abnormal numbers of cytokine producing cells in patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 1996;14(5):485-491.
[16] 赵殿元,唐丽,贺福初.Th17细胞在自身免疫性疾病中的作用[J].现代免疫学,2009,29(4):341-243.
[17] 梅杨,高静,潘发明,等. 强直性脊柱炎患者Th17/Treg相关细胞因子的研究[J]. 安徽医科大学学报, 2011, 46(3):269-272.
[18] Sarkar S, Fox DA. Targeting IL-17 and Th17 cells in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin North Am. 2010;36(2): 345-366.
[19] Iwakura Y, Ishigame H. The IL-23/IL-17 axis in inflammation. J Clin Invest. 2006;116(5):1218-1222.
[20] Voo KS, Wang YH, Santori FR, et al. Identification of IL-17-producing FOXP3+ regulatory T cells in humans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(12):4793-4798.
[21] Morgan ME, Flierman R, van Duivenvoorde LM, et al. Effective treatment of collagen-induced arthritis by adoptive transfer of CD25+ regulatory T cells. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 52(7):2212-2221.
[22] Cai L, Yin JP, Starovasnik MA, et al. Pathways by which interleukin 17 induces articular cartilage breakdown in vitro and in vivo. Cytokine. 2001;16(1):10-21.
[23] 韩文娟,张红鸭,康娟,等. 多发性肌炎肌组织中Th17细胞的浸润[J].现代生物医学进展,2012,12(7):1277-1279.
[24] Arsura EL, Greenberg AS. Adverse impact of interstitial pulmonary fibrosis on prognosis in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 1988;18(1):29-37.
[25] Chen YJ, Wu CY, Shen JL. Predicting factors of interstitial lung disease in dermatomyositis and polymyositis. Acta Derm Venereol. 2007;87(1):33-38.
[26] Airio A, Kautiainen H, Hakala M. Prognosis and mortality of polymyositis and dermatomyositis patients. Clin Rheumatol. 2006;25(2):234-239.
[27] Ponyi A, Constantin T, Balogh Z, et al. Disease course, frequency of relapses and survival of 73 patients with juvenile or adult dermatomyositis. Clin Exp Rheumatol. 2005;23(1): 50-56.
[28] Bonella F, Costabel U. Biomarkers in connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 2014;35(2):181-200.
[29] 王黎明,王立华,李铭,等. 脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗类风湿性关节炎患者Th1/Th2、Treg的变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014, 18(45):7279-7284.
[30] 王丹丹,张华勇,冯学冰,等.脐带间充质干细胞移植治疗系统性红斑狼疮的临床分析[J].中华风湿病学杂志,2010,14(2):76-79.
[31] 祁秋干,纪娜,史强,等.脐血间充质干细胞移植治疗严重性系统性红斑狼疮的临床疗效初探[J].中华细胞与干细胞杂志,2014, 4(3):153-157. |