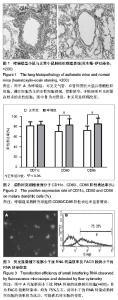
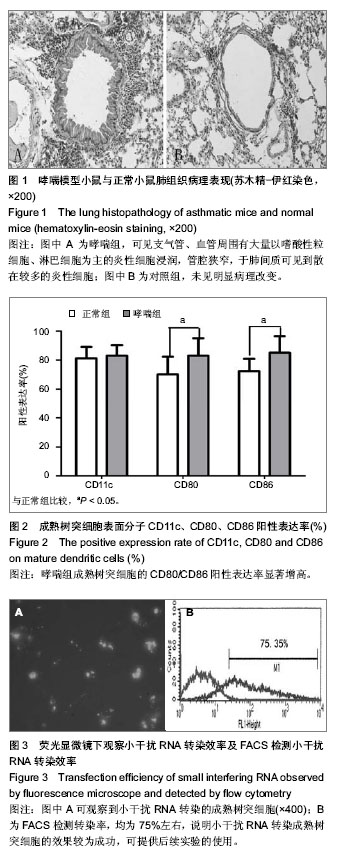
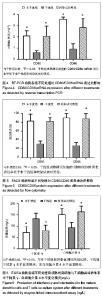
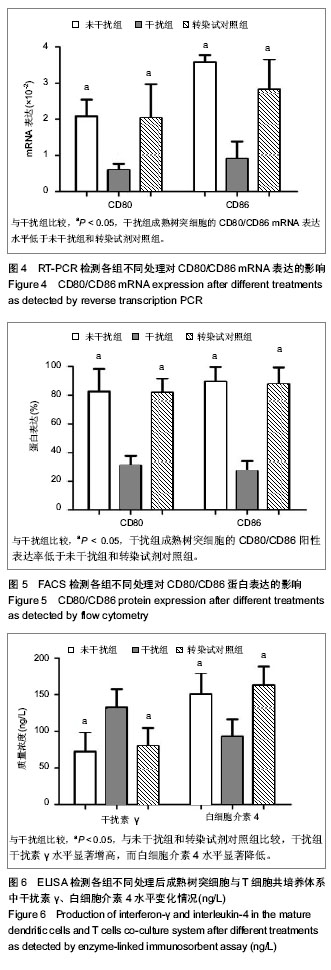
| [1] Markey KA, Koyama M, Kuns RD, et al. Immune insufficiency during GVHD is due to defective antigen presentation within dendritic cell subsets. Blood. 2012; 119(24):5918-5930.[2] Holgate ST. Innate and adaptive immune responses in asthma. Nat Med. 2012;18(5):673-683.[3] Larche M, Robinson DS, Kay AB. The role of T lymphocytes in the pathogenesis of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2003; 111(3):450-63, 464.[4] Lim TS, Goh JK, Mortellaro A, et al. CD80 and CD86 differentially regulate mechanical interactions of T-cells with antigen-presenting dendritic cells and B-cells. PLoS One. 2012;7(9):e45185.[5] Gu X, Xiang J, Yao Y, et al. Effects of RNA interference on CD80 and CD86 expression in bone marrow-derived murine dendritic cells. Scand J Immunol. 2006;64(6): 588-594.[6] Fanta CH. Asthma. N Engl J Med. 2009;360(10):1002-1014.[7] Lambrecht BN, Hammad H. Lung dendritic cells in respiratory viral infection and asthma: from protection to immunopathology. Annu Rev Immunol. 2012;30:243-270.[8] Wenzel SE. Asthma phenotypes: the evolution from clinical to molecular approaches. Nat Med. 2012;18(5):716-725.[9] Hansel TT, Johnston SL, Openshaw PJ. Microbes and mucosal immune responses in asthma. Lancet. 2013;381 (9869):861-873.[10] Goyvaerts C, Dingemans J, De Groeve K, et al. Targeting of human antigen-presenting cell subsets. J Virol. 2013; 87(20): 11304-11308.[11] Reis ESC. Dendritic cells in a mature age. Nat Rev Immunol. 2006;6(6):476-483.[12] Gill MA. The role of dendritic cells in asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012;129(4):889-901.[13] 施举红,林耀广,李太生.树突细胞在抗原呈递和支气管哮喘发病机制中的作用[J].中华结核和呼吸杂志, 2005,28(1):22-27.[14] Wong CK, Lun SW, Ko FW, et al. Increased expression of plasma and cell surface co-stimulatory molecules CTLA-4, CD28 and CD86 in adult patients with allergic asthma. Clin Exp Immunol. 2005;141(1):122-129.[15] Bellou A, Finn PW. Costimulation: critical pathways in the immunologic regulation of asthma. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2005;5(2):149-154.[16] van Rijt LS, Vos N, Willart M, et al. Essential role of dendritic cell CD80/CD86 costimulation in the induction, but not reactivation, of TH2 effector responses in a mouse model of asthma. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2004;114(1):166-173.[17] Chen YQ, Shi HZ. CD28/CTLA-4--CD80/CD86 and ICOS--B7RP-1 costimulatory pathway in bronchial asthma. Allergy. 2006;61(1):15-26.[18] Bieber T, Novak N, Herrmann N, et al. Role of dendritic cells in atopic dermatitis: an update. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2011;41(3):254-258.[19] Hespel C, Moser M. Role of inflammatory dendritic cells in innate and adaptive immunity. Eur J Immunol. 2012;42(10): 2535-2543.[20] Novak N. An update on the role of human dendritic cells in patients with atopic dermatitis. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2012; 129(4):879-886.[21] Lombardi V, Singh AK, Akbari O. The role of costimulatory molecules in allergic disease and asthma. Int Arch Allergy Immunol. 2010;151(3):179-189.[22] Zhang Y, Zhou X, Zhou B. DC-derived TSLP promotes Th2 polarization in LPS-primed allergic airway inflammation. Eur J Immunol. 2012;42(7):1735-1743.[23] Crosby JR, Guha M, Tung D, et al. Inhaled CD86 antisense oligonucleotide suppresses pulmonary inflammation and airway hyper-responsiveness in allergic mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2007;321(3):938-946.[24] Fire A, Xu S, Montgomery MK, et al. Potent and specific genetic interference by double-stranded RNA in Caenorhabditis elegans. Nature. 1998;391(6669):806-811.[25] Ghafouri-Fard S, Ghafouri-Fard S. siRNA and cancer immunotherapy. Immunotherapy. 2012;4(9):907-917.[26] Gavrilov K, Saltzman WM. Therapeutic siRNA: principles, challenges, and strategies. Yale J Biol Med. 2012;85(2): 187-200.[27] 闫文娟,徐树军,谢苗苗,等.外源性单磷酸鸟苷环二聚体对变形链球菌基因表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究, 2012,16(8): 1451-1454.[28] Lee CC, Huang HY, Chiang BL. Lentiviral-mediated interleukin-4 and interleukin-13 RNA interference decrease airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. Hum Gene Ther. 2011;22(5):577-586.[29] Li Y, Sun M, Cheng H, et al. Silencing IL-23 expression by a small hairpin RNA protects against asthma in mice. Exp Mol Med. 2011;43(4):197-204.[30] Woska JJ, Gillespie ME. Small-interfering RNA-mediated identification and regulation of the ternary SNARE complex mediating RBL-2H3 mast cell degranulation. Scand J Immunol. 2011;73(1):8-17.[31] Lu XX, McCoy KS, Xu JL, et al. Small interfering RNA targeting T-cell Ig mucin-3 decreases allergic airway inflammation and hyperresponsiveness. Inflammation. 2013;36(3):582-591.[32] Darcan-Nicolaisen Y, Meinicke H, Fels G, et al. Small interfering RNA against transcription factor STAT6 inhibits allergic airway inflammation and hyperreactivity in mice. J Immunol. 2009;182(12):7501-7508.[33] Moriwaki A, Inoue H, Nakano T, et al. T cell treatment with small interfering RNA for suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 modulates allergic airway responses in a murine model of asthma. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011;44(4):448-455.[34] 陈家军,孙宗全,董念国,等.RNA干扰抑制MyD88表达对小鼠骨髓树突状细胞生物学活性的影响[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志. 2007;23(3):193-196.[35] Yang M, Rangasamy D, Matthaei KI, et al. Inhibition of arginase I activity by RNA interference attenuates IL-13-induced airways hyperresponsiveness. J Immunol. 2006;177(8):5595-5603.[36] Mao H, Wen FQ, Liu CT, et al.Effect of interleukin-5 receptor-alpha short hairpin RNA-expressing vector on bone marrow eosinophilopoiesis in asthmatic mice. Adv Ther. 2006; 23(6):938-956.[37] 郑永华,陆晶晶,郭忠良,等. RNA干扰靶向抑制酪氨酸蛋白激酶对哮喘小鼠树突状细胞功能的影响[J].中国呼吸与危重监护杂志,2009,8(5):487-491.[38] 李建国,颛孙永勋,冉丕鑫,等.骨髓间充质干细胞对哮喘小鼠CD4+CD25+调节性T细胞及气道炎症的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(47):9302-9205. |