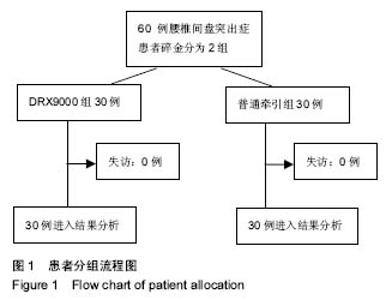
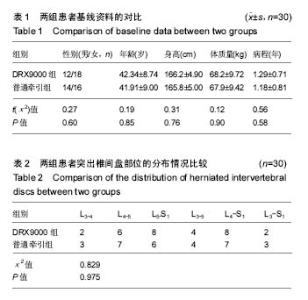
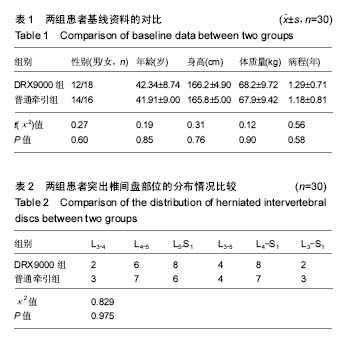
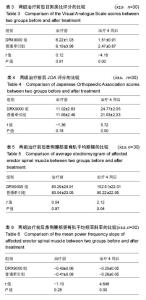
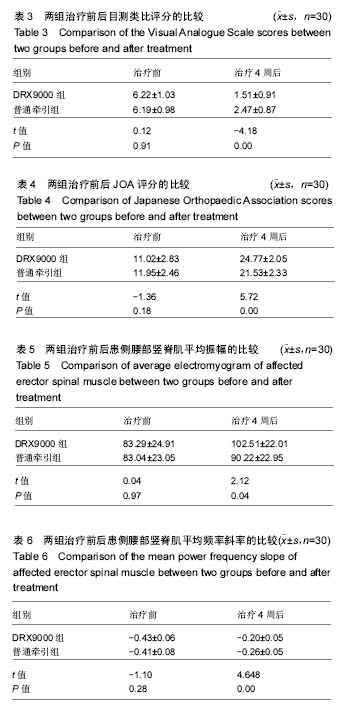
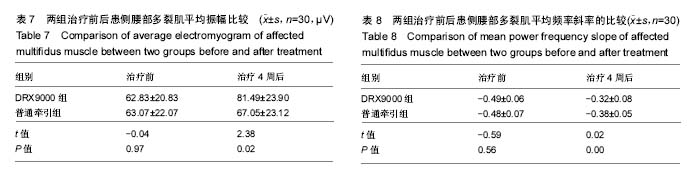
| [1] 周谋望,岳寿伟,何成奇,等.“腰椎间盘突出症的康复治疗”中国专家共识[J].中国康复医学杂志,2017,32(2): 129-135.[2] 林培川.通督调神针刺法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学博士学位论文,2017.[3] Hoy DG, Smith E, Gross M, et al. The global burden of musculoskeletal conditions for 2010: an overview of methods. Ann Rheum Dis.2014; 73(6):982-989.[4] Dahm KT, Brurberg KG, Jamtvedt G, et al. Advice to rest in bed versus advice to stay active for acute low-back pain and sciatica. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.2010: CD007612.[5] Roelofs PD, Deyo RA, Koes BW, et al. Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drugs for low back pain. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2008: CD000396.[6] Aleksiev AR. Ten- year follow- up of strengthening versus flexibility exercises with or without abdominal bracing in recurrent low back pain. Spine. 2014; 39:997[7] Patti A, Bianco A, Paoli A, et al. Effects of Pilates exercise programs in people with chronic low back pain: a systematic review. Medicine.2015; 94:e383[8] McMorland G, Suter E, Casha S, et al. Manipulation or microdiskectomy for sciatica? A prospective randomized clinical study. J Manipulative Physiol Ther. 2010; 33(8):576-584.[9] 殷稚飞,沈滢,蒋学勇,等.持续牵引与间歇牵引治疗腰椎间盘突出症的疗效观察[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2014,(9):730-731.[10] French SD, Cameron M, Walker BF, et al. Superficial heat or cold for low back pain[J]. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.2006:CD004750[11] Spijker-Huiges A, Vermeulen K, Winters JC, et al. Costs and cost-effectiveness of epidural steroids for acute lumbosacral radicular syndrome in general practice: an economic evaluation alongside a pragmatic randomized control trial. Spine. 2014;39:2007.[12] Lamb SE, Hansen Z, Lall R, et al. Group cognitive behavioural treatment for low-back pain in primary care: a randomised controlled trial and cost- effectiveness analysis.Lancet.2010; 375:916.[13] Yang HS, Yoo WG. The effects of stretching with lumbar traction on VAS and Oswestry Scales of patients with lumbar 4–5 herniated intervertebral disc. J Phys Ther Sci.2014;26(7): 1049-1050.[14] 袁光洪. SDS与普通牵引对腰椎间盘突出症的疗效对比及表面肌电分析[D].重庆:重庆医科大学硕士学位论文,2016.[15] 冯宪煊.非手术脊柱减压系统DRX9000治疗腰突症临床研究 [D].上海:上海交通大学博士学位论文,2014.[16] 高晓平.非手术脊柱减压治疗技术[J].颈腰痛杂志,2012,33(1): 48-51. [17] 冯宪煊,白跃宏. 非手术脊柱减压系统DRX9000的相关研究进展[J].颈腰痛杂志,2013, 34(6): 511-513.[18] 吴智钢,白倩,王鑫,等.骶管滴注联合物理治疗对驻陕某部官兵腰椎间盘突出症的疗效观察.医学信息, 2017,30(6):46-48.[19] 卫杰.表面肌电图与腰椎间盘突出症临床表现和疗效的相关性研究[D].北京:中国中医科学院硕士学位论文,2007.[20] 李建华.表面肌电图的康复临床评估应用进展[J].实用医院临床杂志,2014, 11(5):4-6.[21] 吴文,黄国志,刘湘江.表面肌电图用于腰椎间盘突出症疗效评定的研究[J].中华物理医学与康复杂志,2002,24(9):551-553.[22] 凌雁,张娜,朱志华.非手术脊柱减压系统牵引对慢性颈痛患者颈部肌肉表面肌电信号的影响[J].中国医药导报,2015,12(26):99-102,106.[23] Jensen MP, Karoly P, Braver S. The measurement of clinical pain intensity: a comparison of six methods. Pain. 1986;27(1):117-126.[24] Beurskens AJ, de Vet HC, Koke AJ. Measuring the functional status of patients with low back pain: assessment of the quality of four disease-specific questionnaires. Spine.1995; 20:1017-1028.[25] 黄江湖,尹晓明,林飞跃,等.非手术脊柱减压治疗腰椎间盘突出症的效果分析[J].中国当代医药,2014,21(32):41-42,45.[26] 姜永志.非手术脊柱减压治疗腰椎间盘突出症的效果分析[J].中国卫生标准管理,2015,6(4):218.[27] 刘士伟.非手术脊柱减压治疗腰椎间盘突出症效果观察[J].河南外科学杂志,2016,22(1):91-92.[28] 谭志远.非手术脊柱减压疗法治疗腰椎间盘突出的应用研究[J].临床医药文献电子杂志,2015,2(10):1842.[29] 黄睿,郗姗姗,雷鸿.SDS9800脊柱非手术减压系统治疗腰椎间盘源性疼痛47例总结[J].湖南中医杂志,2015,31(10):62-63.[30] 余旭辉,林雪琴,周惠尔.非手术脊柱减压系统治疗多节段腰间盘突出症临床效果观察[J].山西医药杂志, 2016,45(18):2172-2175.[31] Demirel A, Yorubulut M, Ergun N. Regression of lumbar disc herniation by physiotherapy. Does non-surgical spinal decompression therapy make a difference? Double-blind randomized controlled trial. J Back Musculoskelet Rehabil. 2017;30(5):1015-1022.[32] Apfel C, Cakmakkaya O, Martin W, et al. Restoration of disk height through non-surgical spinal decompression is associated with decreased discogenic low back pain: a retrospective cohort study .BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2010; 11:155.[33] Richmond C, Florio F, Wilhelm JM, et al. Magnetic resonance imaging findings after treatment with a non-surgical spinal decompression system (DRX9000TM)-case report. US Musculoskeletal Review, 2007:50-52.[34] Pergolizzi J, Yochum T, Florio F, et al. Management of discogenic low-back pain with a non-surgical decompression system (DRX9000TM)-case report. US Musculoskeletal Review.2008:14-15.[35] Pergolizzi J, Richmond C, Auster M, et al. Non-surgical spinal decompression (DRX9000TM) for the treatment of chronic low-back pain-a case report. European Musculoskeletal Review. 2008:58-60.[36] 顾非,房敏.等速测试表面肌电图在推拿治疗腰椎间盘突出症临床研究中的应用[J].时珍国医国药,2010,21(12):3225-3227.[37] 梁宇,卢铁元,马景全.手法按摩结合运动疗法指导治疗腰椎间盘突出症的疗效观察[J].颈腰痛杂志,2014,(1):69-70.[38] 蔚二文.表面肌电图评价腰椎间盘突出症的临床应用[J].中国医学工程, 2014,22(9):150-152. |