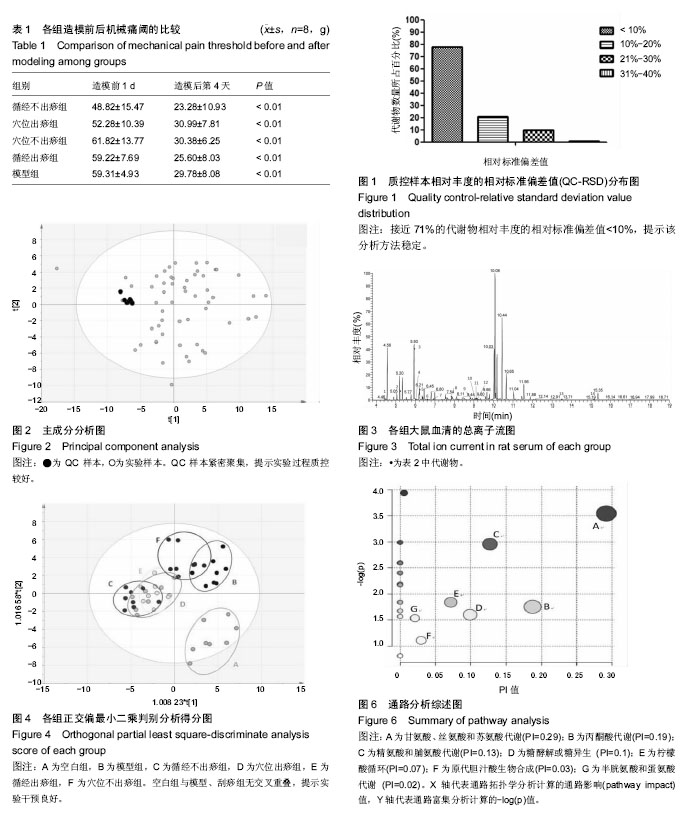
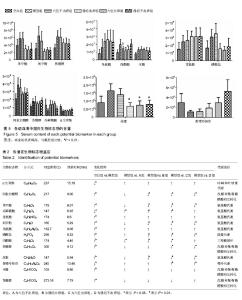
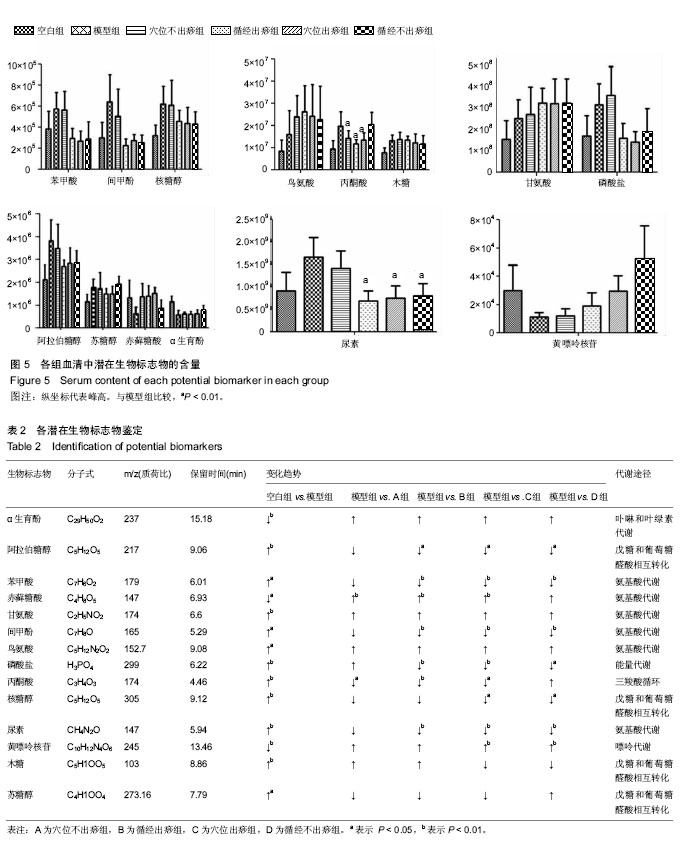
| [1] 许建文,胡兵,尹利军.腰椎间盘突出症蛋白质组学变化与中医证型的相关性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(41):7763-7766.[2] 周仲英.中医内科学[M].北京:中国中医药出版社,2003.[3] 陈华,姜荣荣.刮痧疗法治疗腰椎间盘突出症理论探讨[J].长春中医药大学学报,2013,29(4):643-645.[4] 姜荣荣,徐桂华,陈华,等.从文献计量学角度探刮痧治疗的优势病种[J].中医学报,2014,29(5):756-758.[5] 李洁,徐桂华,姜荣荣,等.刮痧法治疗腰椎间盘突出症临床疗效观察[J].辽宁中医药大学学报,2013,15(5):176-178.[6] 张鸿嫣.基于差异蛋白质组学研究刮痧干预腰椎间盘突出症的效应机制[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2017.[7] 杨敏.基于血清蛋白质组学技术研究刮痧干预腰椎间盘突出症的效应机制[D]. 南京:南京中医药大学,2017.[8] 杨延泽,邓毅,杨秀娟等.代谢组学在中医药领域应用现状[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2018,25(1):132-135.[9] 陈志敏,胡昌江,郑午,等.代谢组学在中药炮制机制研究中的应用概述[J].中华中医药学刊,2018,36(2):275-279.[10] Taylor J, Buckingham MJ, Sadler PJ. Application of metabolomics to plant genotype discrimination using statistics and machine learning. Bioinforrnatics. 2002;18(suppl 2):241-248. [11] Qiu Y, Su M, Liu Y, et al. Application of ethyl chloroformate derivatization for gas chromatography-mass spectrometrybased metabonomic profi ling. Analytica Chimica Acta. 2007;583(2):277-283. [12] Shamji MF, Allen KD, So S, et al. Gait abnormalities and inflammatory cytokines in an autologous nucleus pulposus model of radiculopathy. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34(7):648-654. [13] 赵丽云,姜会梨,任秀君,等.针刺对腰椎间盘突出症大鼠模型痛行为和脊神经根组织形态学的影响[J].北京中医药大学学报, 2014,37(8):551-555, 578.[14] 许广喜.刺络放血结合针刺治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J].当代医学,2011, 17(17):158-159.[15] 杨红,王光义,陈晓霞.通阳刮痧疗法对腰椎间盘突出大鼠炎性细胞因子及机体免疫功能的影响[J].中国老年学杂志,2018,38(10):2477-2479.[16] 倪慧君,程为玉.刮痧疗法治疗腰椎间盘突出症的临床观察[J].湖北中医杂志,2016,38(9):44-45.[17] 陈华,徐桂华,姜荣荣,等.刮痧对腰椎间盘突出症大鼠血清IgG及椎间盘组织病理改变的影响[J].南京中医药大学学报, 2014,30(5):450-453.[18] 张鸿嫣,杨敏,徐桂华,等.刮痧对腰椎间盘突出症模型大鼠神经损伤的保护作用[J].南京中医药大学学报,2016,32(6):553-556.[19] 王莹莹,杨莉,杨金生,等.刮痧治疗腰肌劳损疗效评价及影响因素研究[J].南京中医药大学学报,2013,29(5):422-425.[20] 范俊驰,何承建,白书臣.刮痧结合硬膜外封闭治疗腰椎间盘突出症108例临床观察[J].湖南中医杂志,2014,30(10):71-73.[21] 姜荣荣.刮痧治疗腰椎间盘突出症大鼠作用机制的实验研究[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2013.[22] 谭明生,齐英娜,姜良海,等.球囊导管构建大鼠督脉瘀阻型上颈脊髓损伤模型的研究[J].中医正骨,2016,28(12):1-5.[23] 朱玉璞,裴培,刘璐,等.电针对硝酸甘油偏头痛大鼠模型行为学观察[J].北京中医药,2017,36(4):317-320.[24] 张鸿嫣,杨敏,岳容兆,等.刮痧对腰椎间盘突出症模型大鼠背根神经节炎性细胞因子和血清疼痛物质的影响[J].时珍国医国药,2017,28(2):500-503.[25] Kind T, Wohlgemuth G, Lee DY, et al. FiehnLib: mass spectral and retention index libraries for metabolomics based on quadrupole and time-of-flight gas Chromatography/mass spectrometry. Anal Chem. 2009, 81(24):10038-10048. [26] 安文博,姜劲挺,张伦广,等.复方倍他米松局部注射后自体髓核移植模型大鼠脊髓及背根神经节中P物质和降钙素基因相关肽变化[J].中国组织工程研究,2014,18(49):7955-7960.[27] 顾思岚.基于高通量测序和代谢组学的艰难梭菌感染患者肠道微生态研究[D].杭州:浙江大学,2016.[28] 陈鹏,陈富超,吴玥,等.鞣花酸对D-型半乳糖致衰老大鼠干预的尿液代谢组学生物标志物的筛选及代谢通路分析[J].中国医院药学杂志, 2018, 38(9):1-8.[29] 常相伟,王博然,王彤,等.基于UPLC-Q-TOF/MS的植物代谢组学技术鉴别林下山参的生长年限[J].中国中药杂志, 2016,41(19):3609-3614.[30] Kuhn KS, Muscaritoli M, Wischmeyer P, et al. Glutamine as indispensable nutrient in oncology: experimental and clinical evidence. Eur J Nutr. 2010;49(04):197-210. [31] Perego MC, Caloni F, Cortinovis C, et al. Influence of a Roundup formulation on glyphosate effects on steroidogenesis and proliferation of bovine granulosa cells in vitro. Chemosphere. 2017;188(4):274-279. [32] 沈淑洁,水素芳,肖炳坤,等.基于1H-NMR及LC-MS技术研究金铃子散对炎症大鼠模型调节机制的影响[J].中国中药杂志, 2017,42(2):363-369.[33] Wang Q, van Hoecke M, Tang XN, et al. Pyruvate protects against experimental stroke via an anti-inflammatory mechanism. Neurobiol Dis. 2009;36 (1):223-231. [34] 林志龙.丙酮酸盐对大鼠小肠缺血再灌注引起的肠屏障损伤的保护作用及机制的研究[D].石家庄:河北医科大学,2013.[35] 张星华,杜小正,王金海,等.糖酵解途径与类风湿关节炎发病的关系[J].广东医学,2015,36(15):2430-2432.[36] 任晓磊.基于代谢组学的慢性支气管炎发病机理及岩白菜素作用机制研究[D].北京:北京中医药大学,2016.[37] Zhang P, Zhu W, Wang D, et al. A combined NMR- and HPLC-MS/MS- based metabolomics to evaluate the metabolic perturbations and subacute toxic effects of endosulfan on mice. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2017;24(23):18870-18880. [38] 戴子一.基于1HNMR平台探讨揉髌手法对兔膝关节骨关节炎模型血清代谢组学的影响[D].南宁:广西中医药大学,2017.[39] 华永丽.当归挥发油干预大鼠LPS炎症模型的相关代谢物及代谢通路分析[D].兰州:甘肃农业大学,2014.[40] 蒋立锐.精氨酸在代谢中的作用[J].生理科学进展, 1982,13(2):170-172.[41] Keynan O, Mirovsky Y, Dekel S, et al. Safety and Efficacy of Dietary Agmatine Sulfate in Lumbar Disc-associated Radiculopathy. An Open-label, Dose-escalating Study Followed by a Randomized, Double-blind, Placebo-controlled Trial. Pain Med. 2010;11(3): 356-368. [42] Bakshi N, Morris CR. The role of the arginine metabolome in pain: implications for sickle cell disease. J Pain Res. 2016;30(9):167-175. |