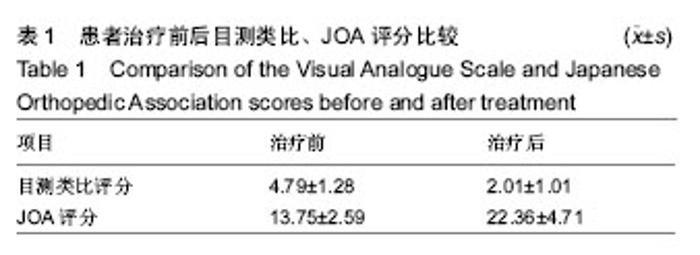
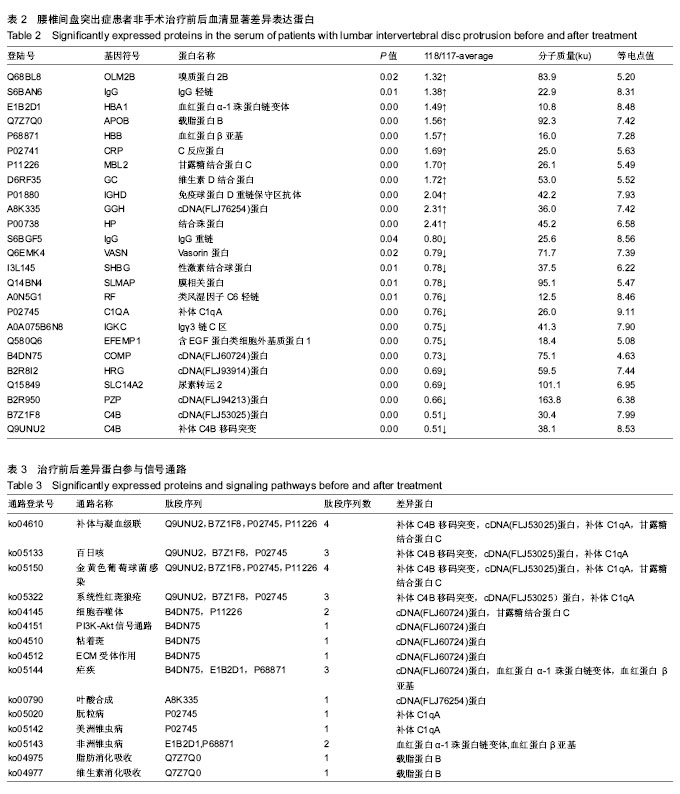
| [1] 杨豪,王建儒,郑召民.椎间盘源性腰痛发病机制的研究进展[J].中华医学杂志,2013,93(19):1514-1516.[2] 赵学军,左玲,傅志俭,等.经皮椎间孔镜下髓核摘除术治疗腰椎间盘突出症[J].中国疼痛医学杂志,2013,19(1):8-12.[3] 胡有谷.腰椎间盘突出症[M].3版.北京:人民卫生出版社,2005.[4] 中华医学会.临床诊疗指南.骨科分册[M].北京:人民卫生出版社, 2009.[5] 国家中医药管理局.中医病证诊断疗效标准[M].北京:中国医药科技出版社,2012:214215.[6] Unwin RD, Griffiths JR,Whetton AD.Simultaneous analysis of relative protein expression levels across multiple samples using iTRAQ isobaric tags with 2D nano LC-MS/MS. Nat Protoc. 2010; 5(9):1574.[7] Atlas SJ, Keller RB, Wu YA, et al. Long-term outcomes of surgical and nonsurgical management of sciatica secondary to a lumbar disc herniation: 10 year results from the Maine Lumbar Spine Study. Spine.2005;30(8):927-935. [8] 刘阁,逄越,刘欣,等.C1q蛋白家族的结构、分布、分类和功能[J].遗传, 2013,35(9):1072-1080.[9] 张霞辉.补体C1q对Aβ1-40纤维诱导的BV-2小胶质细胞炎性反应的影响[D].南方医科大学,2011.[10] Tanga FY,Nutile-McMenemy N,DeLeo JA.Tanga.The CNS role of Toll-like receptor 4 in innate neuroimmunity and painful neuropathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2005;102(16):5856-5861. [11] 王新梅,杨莹,薛霞.神经病理性疼痛的小胶质细胞机制[J].科技创新导报, 2012,19:233-234.[12] ROPPER AH, Zafonte RD. Sciatica. N Engl J Med.2015;372(13): 1240-1248.[13] 刘振刚,卢一生,施建东,等.腰椎间盘突出症和椎间盘源性疼痛的免疫病理学研究[J].颈腰痛杂志,2016,37(4):272-275.[14] 钱国祥.软骨低聚基质蛋白在退变腰椎间盘终板组织中的表达变化[D].大理学院,2013.[15] 马壮.软骨低聚基质蛋白在退变腰椎间盘纤维环中的表达变化[D].大理学院,2013.[16] 陈帅,赵凤东,张建锋,等.12个新椎间盘分子标志物在人退变髓核组织中的评估[A]. 浙江省医学会骨科学分会.2014年浙江省骨科学学术年会论文汇编[C].浙江省医学会骨科学分会,2014:2.[17] Hoff P, Buttgereit F, Burmester GR, et al. Osteoarthritissynovial fluid activates pro-inflammatory cytokines in primaryhuman chondrocytes. Int Orthop.2013;37:145-151.[18] 关鹏,尹利军,许建文,等.腰椎间盘突出症活血化瘀治疗的目标蛋白筛选及鉴定[J].中国全科医学,2016,19(32):3950-3955.[19] 张永臣.龙虎交战针法对腰椎间盘突出症患者IgG、IgM和补体C_3的影响[J].针灸临床杂志,2008,24(11):4-5.[20] 孙志岭,徐骁,王玲,等.强直性脊柱炎湿热痹阻证血清差异蛋白组学研究[J].南京中医药大学学报,2015,31(5):412-415.[21] 黄涛,付勤,张铁峰,等.不同退变程度腰椎间盘组织中一氧化氮和超氧化物歧化酶含量的变化及其意义[J].中国医科大学学报, 2005, 34(5):93-94.[22] Olmarker KM, Rydevik B, Holm S. Edema formation in spinal nerverootsinducedbyexperimental, graded compression. An experimental study on the pig cauda equina with special reference todifferencesineffectsbetweenrapidandslow onset of compression. Spine(Phila Pa 1976).1989;14(6):569-573. [23] Oyedemi SO, Bradley G, Afolayan AJ. In-vitro and-vivo antioxidant activities of aqueous extract of Strychnos henningsii Gilg.African Journal of Pharmacy & Pharmacology, 2010,4(2):70-78.[24] Funk CD, Cyrus T. 12/15-lipoxygenase, oxidative modification of LDL and atherogenesis[J]. Trends Cardiovasc Med. 2001;11: 116-124.[25] Li H, Wang QJ, Zhu DN, et al. Reinioside C, a triterpene saponin of Polygala aureocauda Dunn, exerts hypolipidemic effect on hyperlipidemic mice.Phytother Res. 2008;22:159-164.[26] Amom Z, Zakaria Z, Mohamed J, et al. Lipid lowering effect of antioxidant alpha-lipoic Acid in experimental atherosclerosis. J Clin Biochem Nutr.2008;43:88-94.[27] 瞿群威,朱少铭,吴群,等.CT引导下不同方法注射臭氧对腰椎间盘突出患者SOD、LPO影响[J].生物医学工程与临床, 2013,17(2): 143-146.[28] 谭克平,刘光国,姚旭,等.针药结合对腰椎间盘突出症患者血清细胞因子、MDA、SOD及血浆血栓素β2水平的影响[J].中华中医药学刊, 2016,34(6):1523-1526.[29] 陈坚样,陆文杰,陈仲夷,等.腰痹通联合西药治疗腰椎间盘突出症疗效观察[J].中华中医药学刊,2015,33(7):1771-1773.[30] 全吉淑,尹学哲,沈明化,等.大豆异黄酮和皂甙抗脂蛋白氧化作用的研究[J].食品科学,2003,11:121-123.[31] Hardison RC, Chui DHK,Giardine B, et al. Hb Var: a relational database of humanhemoglobin variants and thalassemia mutation at the globin gene server. Hum Mutat. 2002;19(3):225-232.[32] 莫桂玲,胡朝晖,张玲,等.我国罕见异常血红蛋白突变型[β43(CD2)Glu→Lys]分析[J].国际检验医学杂志, 2010,31(9): 918-921.[33] 腰椎间盘突出症的康复治疗(专家共识讨论稿)[A].浙江省医学会物理医学与康复学分会.2014年浙江省物理医学与康复学学术年会论文汇编[C].浙江省医学会物理医学与康复学分会, 2014:3.[34] 单振兴.强直性脊柱炎血清骨化标志物的筛选与验证[D].济南大学, 2011.[35] 刘路路,郭伟,卫杰,等.腰椎间盘突出症患者血常规变化特征及意义[J].山东医药,2016,(25):87-89.[36] 姚女兆,唐杰,王文军. NF-κB和AQP-3在椎间盘退变中的表达及其可能作用的初步探讨[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2014,(25):30-34.[37] 董锡亮,赵宏斌,杨燕琼,等.肿瘤坏死因子α和白介素1β在突出椎间盘组织中的表达及意义[J].中国全科医学, 2013,16(42):4276-4278.[38] 王峰,崔玉蓬.腰椎间盘突出症患者椎间盘组织炎性因子、TGF-β_1、PGE_2表达及意义[J].山东医药, 2016,56(32):56-58.[39] 王飞.血清细胞因子与腰椎间盘突出疼痛的关系研究[J].中国医药指南, 2016,14(2):67.[40] 周光辉,薛爱国,梁逸仙,等.电针联合COX-2抑制剂治疗腰椎间盘突出症的疗效评价及对IL-6和IL-8表达的影响[J].针灸临床杂志, 2016, 32(10):38-40.[41] 何智映,黄笑妍,甄晓洲,等.叶酸对低氧诱导THP-1细胞产生炎症介质的影响[J].中国热带医学,2016,16(3):212-215,220. |