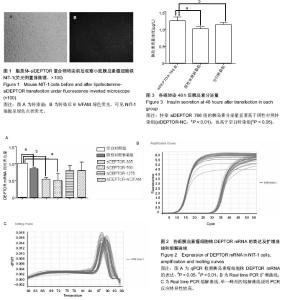
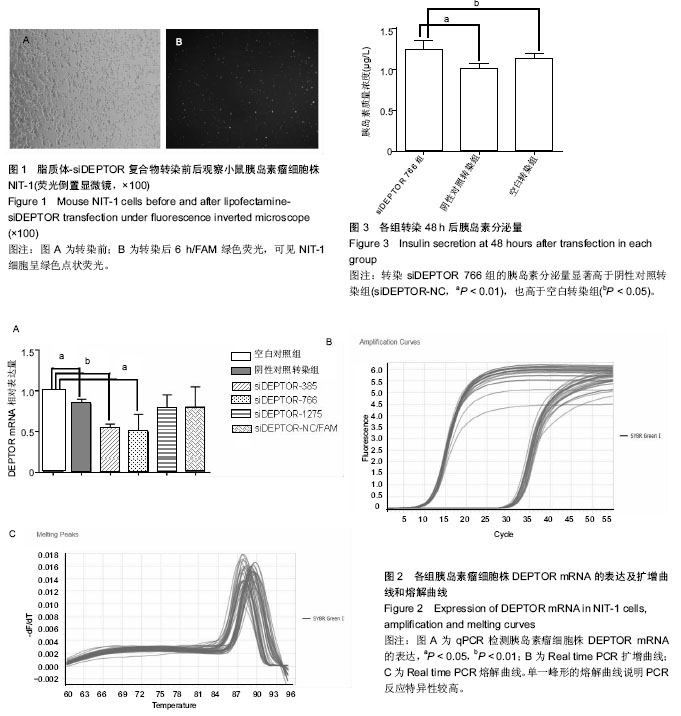
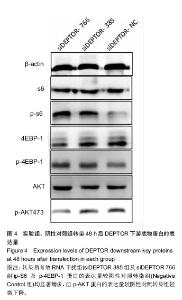
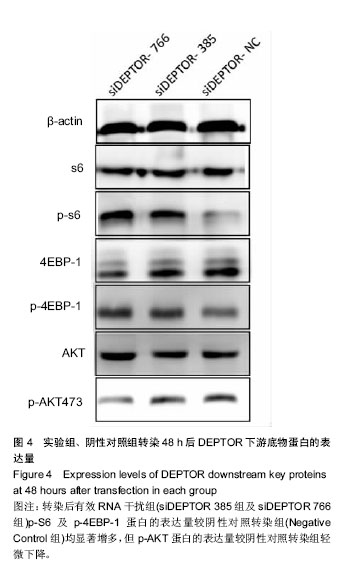
| [1] IDF Diabetes Atlas eighth edition. 2017, International Diabetes Federation.[2] Yang W, Lu J, Weng J,et al.Prevalence of diabetes among men and women in China. N Engl J Med.2010. 362(12): 1090-1101.[3] Dinesh Shah A, Langenberg C, Rapsomaniki E, et al.Type 2 diabetes and incidence of cardiovascular diseases: a cohort study in 1.9 million people. Lancet Diabetes Endocrinol.2015; 3(2):105-113.[4] Yagihashi S, Inaba W, Mizukami H. Dynamic pathology of islet endocrine cells in type 2 diabetes: beta-Cell growth, death, regeneration and their clinical implications.J Diabetes Investig. 2016;7(2):155-165.[5] Peterson TR, Laplante M, Thoreen CC, et al.DEPTOR is an mTOR inhibitor frequently overexpressed in multiple myeloma cells and required for their survival.Cell.2009;137(5):873-886.[6] Zhang HR, Chen JM, Zeng ZY, et al.Knockdown of DEPTOR inhibits cell proliferation and increases chemosensitivity to melphalan in human multiple myeloma RPMI-8226 cells via inhibiting PI3K/AKT activity. J Int Med Res.2013;41(3): 584-595.[7] Proud CG. Dynamic balancing: DEPTOR tips the scales. J Mol Cell Biol.2009;1(2): 61-63.[8] Lai EY, Chen ZG, Zhou X, et al.DEPTOR expression negatively correlates with mTORC1 activity and tumor progression in colorectal cancer. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2014;15(11):4589-4594.[9] Meng ZX, Li S, Wang L, Ko HJ, et al.Baf60c drives glycolytic metabolism in the muscle and improves systemic glucose homeostasis through Deptor-mediated Akt activation. Nat Med.2013;19(5):640-645.[10] Bernal-Mizrachi E, Kulkarni RN, Scott DK, et al.Human beta-cell proliferation and intracellular signaling part 2: still driving in the dark without a road map. Diabetes.2014;63(3): 819-831.[11] Vergès B, Cariou B. mTOR inhibitors and diabetes. Diabetes Res Clin Pract.2015;110(2):101-108.[12] Ardestani A, Lupse B, Kido Y, et al.mTORC1 Signaling: A Double-Edged Sword in Diabetic β Cells. Cell Metab. 2018; 27(2):314-331.[13] Gu Y, Lindner J, Kumar A, et al.Rictor/mTORC2 is essential for maintaining a balance between beta-cell proliferation and cell size. Diabetes.2011;60(3):827-837.[14] Rachdi L, Balcazar N, Osorio-Duque F, et al.Disruption of Tsc2 in pancreatic beta cells induces beta cell mass expansion and improved glucose tolerance in a TORC1- dependent manner. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A.2008;105(27): 9250-9255.[15] Pirollo KF, Chang EH.Targeted delivery of small interfering RNA: approaching effective cancer therapies. Cancer Res. 2008;68(5): 1247-1250.[16] 袁松,孙会敏,丁丽霞.脂质体物理化学稳定性研究进展[J].中国药事, 2011,25(4):384-388.[17] 张旭,丁会芹,王冰,等.脂质体介导RNAi的研究[J]. 生物医学工程学杂志, 2012,29(4):722-726.[18] 许戈阳,刘芬婷,沈哲民,等. mTOR信号通路在糖代谢中作用[J]. 生理科学进展, 2015,46(2): 94-98.[19] Cota D. Mammalian target of rapamycin complex 1 (mTORC1) signaling in energy balance and obesity. Physiol Behav. 2009;97(5): 520-524.[20] Le Bacquer O, Petroulakis E, Paglialunga S, et al.Elevated sensitivity to diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance in mice lacking 4E-BP1 and 4E-BP2. J Clin Invest.2007; 117(2): 387-396.[21] Demidenko ZN, Shtutman M, Blagosklonny MV. Blagosklonny, Pharmacologic inhibition of MEK and PI-3K converges on the mTOR/S6 pathway to decelerate cellular senescence. Cell Cycle.2009;8(12):1896-900.[22] Fritsche L, Neukamm SS, Lehmann R, et al.Insulin-induced serine phosphorylation of IRS-2 via ERK1/2 and mTOR: studies on the function of Ser675 and Ser907.Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab.2011;300(5):E824-836.[23] Jacinto E, Loewith R, Schmidt A, et al.Mammalian TOR complex 2 controls the actin cytoskeleton and is rapamycin insensitive. Nat Cell Biol.2004;6(11): 1122-1128.[24] Elghazi L, Balcazar N, Blandino-Rosano M, et al.Decreased IRS signaling impairs beta-cell cycle progression and survival in transgenic mice overexpressing S6K in beta-cells. Diabetes. 2010;59(10): 2390-2399.[25] Briaud I, Dickson LM, Lingohr MK,et al.Insulin receptor substrate-2 proteasomal degradation mediated by a mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR)-induced negative feedback down-regulates protein kinase B-mediated signaling pathway in beta-cells. J Biol Chem.2005;280(3): 2282-2293.[26] Efeyan A, Sabatini DM. mTOR and cancer: many loops in one pathway.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2010;22(2): 169-176.[27] Copps KD, White MF.egulation of insulin sensitivity by serine/threonine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate proteins IRS1 and IRS2. Diabetologia.2012; 55(10): 2565-2582.[28] Chau GC,Im DU,Kang TM,et al.mTOR controls ChREBP transcriptional activity and pancreatic beta cell survival under diabetic stress. J Cell Biol.2017;216(7): 2091-2105.[29] Koyanagi M,Asahara S,Matsuda T,et al.Ablation of TSC2 enhances insulin secretion by increasing the number of mitochondria through activation of mTORC1. PLoS One. 2011;6(8):e23238.[30] Gurevitch D,Boura-Halfon S,Isaac R,et al.Elimination of negative feedback control mechanisms along the insulin signaling pathway improves beta-cell function under stress. Diabetes, 2010;59(9):2188-2197. |