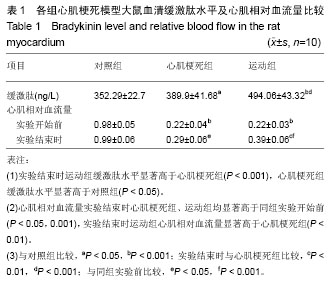
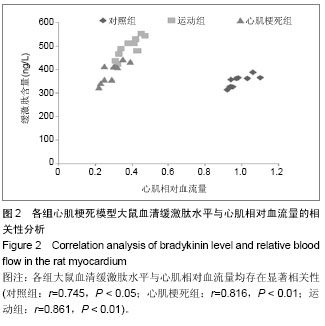
| [1] 张蕾,王莉,吴世政.激肽释放酶-激肽系统在中枢神经系统的研究进展[J].陕西医学杂志, 2008,37(8):1073-1074.[2] 官玉红,李仁立.缓激肽与心血管疾病[J].心血管病学进展, 2005, 26(S1): 39-42. [3] 江双双,柏友萍,孙俊,等.减肥运动处方对青春后期体质量超标和肥胖学生心脏动力学参数的影响.中国校医,2013,27(1):46-50.[4] 傅聪,姚玉宇,马根山,等.血管内皮细胞生长因子和血浆组织激肽释放酶与冠状动脉狭窄的相关性研究[J].南京医科大学学报, 2012,32(9):1241-1245.[5] Ripa RS,Jorgensen E, Baldazzi F,et al. The influence of genotype on vascular endothelial growth factor and regulation of myocardial collateral blood flow in patient with acute and chronic coronary heart disease. Scand J Clin Lab Invest.2009; 69(6):722-728.[6] 黄芳,杨晶金,王雪玲,等. VEGF和bFGF在大鼠压疮模型中的表达及其意义[J].中国病理生理杂志,2012,28(8):1504-1506.[7] 何佳,丁凤菲,刘敏珍. VEGF/VEGFR 在脑缺血再灌注损伤中的神经保护作用[J]. 神经损伤与功能重建, 2013, 8(3): 177-180.[8] Meneton P, Bloch-Faure M, Hagege AA,et al. Cardiovascular abnormalities with normal blood pressure in tissue kallikrein-deficient mice.Proc Natl AcadSci USA. 2001; 98(5): 634 -2639.[9] 王学文,徐善慧,张宁坤,等. 改良冠脉结扎法提高大鼠心梗模型存活率方法探讨[J].山西医科大学学报,2011,42(11):931-934.[10] 娄淑杰.不同强度运动对幼龄大鼠海马组织BDNF及NMDA R1mRNA表达的影响[J].第二军医大学学报,2007,28(8): 916-918. [11] Shen M, Gao J, Li J. Effect of ischaemic exercise training of a normal limb on angiogenesis of a pathological ischaemic limb in rabbits. Clin Sci (Lond). 2009;117(5):201-208.[12] DeJong AT, Wmnack CJ, Perrine JA. et al. Hemostatic responses to resistance training in patients with coronary artery disease. J Cardiopulm Rehabil. 2006; 26: 80- 83.[13] Yoshinaga K, Beanlands RS, Dekemp RA, et al. Effect of exercise training on myocardial blood flow in patients with stable coronary artery disease. Am Heart J. 2006; 151(6): 1324.e11-18.[14] Sandri M, Adams V, Gielen S, et al. Effects of Exercise and Ischemia on Mobilization and Functional Activation of Blood-Derived Progenitor Cells in Patients with Ischemic Syndromes: Results of 3 Randomized Studies. Circulation. 2005; 111: 3391-3399.[15] 车琳,张亚楠. 老年心血管疾病运动康复研究进展[J]. 实用老年医学,2013,27(3):180-183.[16] 赵皓,张海侠,姜谧. 运动疗法在心脏瓣膜术后的应用[J].中国老年学杂志,2013, 33(17):4335-4336.[17] 李广鹤,车琳.冠心病患者抗阻运动康复进展[J].实用老年医学, 2013,27(3):184-188.[18] 郑昆, 杨原, 薄海. 运动训练对急性心肌梗死后心室重构及心肌细胞凋亡的影响[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2011,20(1):16-19.[19] 宋凯,丁宁伟.低氧运动对大鼠血清VEGF含量及心肌VEGF 基因和蛋白表达的影响[J].南京体育学院学报:自然科学版,2011, 11(6):23-27.[20] 吴冬鸣,唐燕,韩艺,等.大鼠心肌缺血再灌注后不同时间点心脏及肝脏中HIF-1、VEGF的表达[J].南京医科大学学报:自然科学版,2012,32(8):1047-1051.[21] 章斌,许智惠,陶正贤.血管内皮生长因子165通过抑制钙敏感性受体减少缺血/再灌注心肌细胞凋亡[J].中国临床药理学与治疗学, 2011,16(1):26-32.[22] 杨波, 任晓丽, 张钧.有氧运动对高蛋氨酸饮食大鼠血浆NO、ET和NO /ET系统的影响[J].中国应用生理学杂志,2011,27(2): 221-224.[23] 张琳,邓树勋,郝选明.运动与心肌细胞凋亡的线粒体机制[J].体育学刊,2010,17(3):92-98.[24] 蒋磊,周振茂,夏美燕.运动对大鼠心肌细胞与一氧化氮合酶的影响[J].西北农林科技大学学报:自然科学版,2013,41(6):8-12.[25] 李军勇,伊力哈木托合提.运动对细胞凋亡的影响[J].现代生物医学进展,2011,11(3):593-597.[26] 王晓红,赵晓霞,李文玉,等. 激肽释放酶对脑梗死患者血管内皮生长因子的影响[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志,2009, 29(9): 794-796.[27] 袁刚,王涛, 赵春霞,等.人组织激肽释放酶基因对2型糖尿病大鼠血压的影响及机制[J].中国病理生理杂志,2006, 22(7):1289- 1294.[28] 汪道文.人组织激肽释放酶[J].岭南心血管病杂志(第13届中国南方国际心血管病学术会议专刊),2011:16-17.[29] 赵晓霞,宋春伶.激肽释放酶F激肽系统促进脑缺血后血管新生的机制[J]. 中风与神经疾病杂志,2011,28(9):859-861.[30] Parenti A, Morbidelli L, Ledda F, et al. The bradykinin/B1 receptor promotes angiogenesis by up--regulation of endogenous FGF-2 in endothelium via the nitric oxide synthase pathway. FASEB J. 2001; 15:1487-1489.[31] Knox AJ, Cort ett L, Stocks J, et al. Human airway smooth muscle cells secrete vascular endothelial growth factor:up-regulation by bradykinin via a protein kinase C and prostanoid-dependent mechanism. FASEBJ. 2001;15(13): 2480-2488.[32] Xia CF,Yin H,Borlongan CV,et al. Kallikrein gene transfer protects against ischemic stroke by promoting glial cell migration and inhibting apoptosis. Hypertension. 2004;43: 453-459.[33] Rashid MH, Inoue M, Koudo S, et al. Novel expression of vanilloid receptor 1 on capsaicin- insensitive fiber s accounts for the analgesic effect of capsaicin cream in neuropathic pain. J Pharma col Exp Ther. 2003;304(3) : 940-948.[34] 李飞,贾国良,李伟,等. 缓激肽与心肌延迟相缺血预适应的实验研究[J].第四军医大学报, 2000, 21(3): 317-319.[35] Yang XM, KriegT, Cui L, et al. NECA and bradykinin at reperfusion reduce infarction in rabbit hearts by signaling through PI3K, ERK, and NO. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2004;36(3) : 411-421.[36] 汪涛,康毅,娄建石.激肽释放酶-激肽系统的心血管领域研究进展[J]. 中国药理学与毒理学杂志,2003,12(6):466-470. [37] 王瑾,张炜芳,高嵩丹,等.内源性缓激肽对血管紧张素I诱导乳鼠心肌细胞肥大的影响[J]. 中华临床医师杂志:电子版,2011,5(2): 403-407.[38] Czokalo-Plichta M, Skibinska E, Kosiorek P, et al. Kallikrein-kinin system activation and its interactions with other plasma haemostatic components in the coronary artery. Rocz Akad Med Bialymst. 2001;46:209-224. [39] 邱峰,励建安,陆晓,等.心肌缺血和有氧运动训练诱导VEGF表达时间规律的实验研究[J].中国康复医学杂志, 2008,23(3): 193-197.[40] 焦喜便.递增负荷运动通过NO信号通路降低高血压机制的探讨[J]. 河南大学学报:自然科学版,2013,43(2):176-180. |