Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (2): 289-295.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1972
Previous Articles Next Articles
Exercise in the prevention and treatment of knee osteoarthritis: key factors and cautions
Song Xiaoneng1, 2, Hu Linghui2, Huang Desheng3, Zhou Xuchang2, Wu Wei2
- 1Jiangnan University Sports Department, Wuxi 214122, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China; 3Wuxi Sports School, Wuxi 214122, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2019-04-02Revised:2019-04-13Accepted:2019-05-25Online:2020-01-18Published:2019-12-25 -
Contact:Wu Wei, PhD, Researcher, Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China -
About author:Song Xiaoneng, Lecturer, Jiangnan University Sports Department, Wuxi 214122, Jiangsu Province, China; Shanghai University of Sport, Shanghai 200438, China -
Supported by:the Shanghai Key Laboratory of Human Sports Capacity Development and Support (Shanghai University of Sport), No. 11DZ2261100
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Song Xiaoneng, Hu Linghui, Huang Desheng, Zhou Xuchang, Wu Wei. Exercise in the prevention and treatment of knee osteoarthritis: key factors and cautions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(2): 289-295.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks

2.1 正常与非正常膝关节 正常的膝关节不容易被长期运动所破坏,即使是强度大或者体质量大于自身标准水平,因为软骨表面能够对这些重复的载荷和运动做出适应性反应[17]。但单次冲击载荷超过25 mPa会导致膝关节退变,引起膝骨关节炎的早期症状(如:基质纤维颤动、软骨细胞簇形成、软骨下骨增厚等)[18]。而由于膝关节损伤或关节发育不良导致的非正常膝关节,可以被日常的关节使用水平而破坏。如韧带和半月板损伤后,往往破坏关节的稳定性,阻碍关节表面承受应力的自然分布,这会增加软骨表面某些部位的峰值应力,减少其他部位的峰值应力[19-20]。此外,关节疼痛和受限会导致膝关节肌肉无力,甚至关节松弛。在这种情况下,轻度膝关节损伤甚至可以改变软骨代谢和基质组成,因为软骨表面的峰值应力分布遭到破坏。在一些调查中,膝关节损伤后,经常锻炼的人比不锻炼的人更容易患膝骨关节炎,且这种进展永远不会立即或在短时间内被感觉到或看到[21]。超过80%有膝关节损伤病史的美国橄榄球运动员,他们在退役10-30年后有膝骨关节炎的迹象[22]。 冲击载荷的强度、速度和频率也会影响膝关节软骨[23]。正常的人体软骨可以承受高达25 mPa的冲击载荷而不会出现明显的断裂[18]。正常软骨可能会在以下两种情况下被破坏:一方面,当冲击载荷作用缓慢时,软骨会变形以吸收或减少载荷,但如果冲击力很快,软骨就不能充分发挥作用,此时软骨表面很容易遭到破坏[24];另一方面,重复载荷会破坏组织,损伤程度的通常随着载荷的增加和循环次数的增加而增加,见表1[25-27]。 "

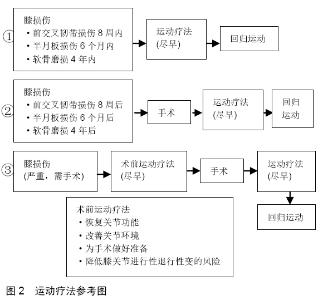
正常膝关节损伤时,关节内存在氧化应激(oxidative stress, OS)和炎症[28]。过剩的活性氧(reactive oxygen species, ROS)和炎症因子(肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素1等)激活了相关信号通路MAPKs,促进环氧合酶2和基质金属蛋白酶13等水平,从而破坏了软骨细胞和关节软骨。MAPKs信号通路中主要的3条通路参与其中,p38、JNK和ERK,具体作用详见表1[29-30]。 2.2 运动疗法对改善膝骨关节炎症状的作用 2.2.1 疼痛 膝骨关节炎的主要症状是疼痛,疼痛机制主要由于周围神经和中枢神经敏感性,膝骨关节炎导致两者传播痛觉过敏,而产生疼痛[31]。运动疗法对膝骨关节炎具有抗炎作用,这种作用有两个方面[32]:单次的运动可以产生局部抗炎作用,例如一次抗阻运动可以减轻局部疼痛的感觉[33];定期或长期的运动则可以使中枢神经适应疼痛,从而降低疼痛敏感性[34]。Marius等[35]通过KOOS评价量表的测试结果得出,运动可以提高疼痛的耐受值。 2.2.2 膝关节功能 运动疗法可以改善膝关节功能,如膝关节屈曲、伸展和步态表现。由于膝关节疼痛、僵硬、肿胀和活动受限等,患者通常不能正常行走。RYO等[36]的系统综述表明,运动锻炼可以增加行走的时间,加快步态速度,甚至可以增加总的步行距离。疼痛、关节僵硬、肿胀和活动受限等常伴随着膝骨关节炎患者,因此,膝骨关节炎患者害怕在走路的时候摔跤[37]。TOPP等[38]也研究得出,运动疗法在增加步行距离、步态速度和步行时间方面具有低到中等质量的疗效。 2.2.3 肌肉萎缩 膝骨关节炎患者肌无力、疼痛与身体功能密切相关,肌肉挛缩可引起膝关节疼痛和残疾,运动对肌肉挛缩有一定的治疗作用[39]。适量冲击载荷是维持关节软骨健康所必不可少的,仅仅是关节的运动并不足以保持关节软骨的完整性,而膝关节肌肉收缩强度是反映关节软骨质量的重要因素,主要包括股四头肌和腘绳肌。股四头肌的肌力是预防膝功能障碍的主要因素,急性关节炎和膝骨关节炎患者发生膝关节不稳时,股四头肌活动往往减少[40-42]。这几乎与关节源性肌肉抑制有关,由炎症、疼痛和肿胀引起的关节源性肌肉抑制,最终损伤相关感受器,使股四头肌活动减少[43]。腘绳肌是另一条重要的肌肉,它可以通过施加胫骨后拉力来稳定膝关节,保护前交叉韧带在高冲击落地时免受高外展张力的影响[44]。此外,腘绳肌的紧张有助于膝关节更加稳定[45]。因此,降低腘绳肌与股四头肌的强度比(腘绳肌与股四头肌共同收缩)可能增加前交叉韧带损伤的风险。相反,RUAN等[46]发现静态拉伸腿筋后,腘绳肌-股四头肌强度比降低,但高冲击落地时膝关节负荷和损伤风险没有增加,甚至膝关节外侧所受负荷降低。静态拉伸腘绳肌肌腱后,急停、跳、变向能力(增加膝损伤风险的动作)得以增强。另外一方面,膝关节肌肉还能吸收冲击,对软骨下骨和半月板作为减震器,保护覆盖软骨,肌肉萎缩则减震保护作用将随之减弱[47]。 2.3 运动疗法在膝骨关节炎中存在不足 膝关节损伤后通常会出现膝部生物力学异常,在步态早期存在“膝关节僵硬步态模式”,包括患侧膝关节伸展和屈曲角减少,即使经过一定的运动疗法,这种模式也能持续较长时间。如髋关节生物力学异常,特别是在动态下肢外翻位置,在康复计划后仍可存在,并增加膝关节损伤的风险。此时,继续使用将增加再次受伤的风险和发展为膝骨关节炎的可能性[48-49]。DEVDATTA等[50]对膝骨关节炎患者进行监督的拉伸、力量训练和短期镇痛治疗,在短期随访中都可改善症状和功能,但在1年后这些结果都略有下降。同样,在一份比较研究中,内侧半月板撕裂的手术治疗组和运动疗法组,两者第一次和最后一次膝关节评价量表评分并无差异,而在修正Lysholm膝关节评分量表中(Modified Lysholm Knee Scoring Scale),手术组的评分要高于运动疗法组[51]。可见,运动疗法在防治膝骨关节炎中,并不具有明显优势,甚至不如其他疗法。 2.4 运动疗法的策略问题 与手术、传统治疗等相比,运动治疗膝关节损伤的疗效存在一定矛盾。因此,如何选择运动疗法,必须知道一些重要的因素。 2.4.1 早期运动疗法中膝关节的角度问题 膝关节屈曲角度是一个关键因素,它会导致不同的膝关节结局,尤其是在膝关节损伤或膝关节手术后。INGRID等[52]发现在恢复训练中肌肉力量需要给予特别的关注,不同类型膝关节损伤之间存在差异。前交叉韧带损伤患者屈膝30°时,股四头肌力量存在最大不足。半月板损伤患者屈膝70°时,股四头肌力量存在最大不足。软骨损伤患者屈膝60°时,股四头肌力量存在最大不足。此外,在股四头肌等长收缩时,前交叉韧带受到最大张力为屈膝15°,在30°时也会受到大量张力,而在30°-50°的时候也会有牵拉感。但是力量训练在屈膝45°-60°时不会造成前交叉韧带拉伤,只会在膝关节全伸时拉伤前交叉韧带[53]。当半月板负重时,受到的最大压力在屈膝30°-60°之间,超过60°,压力随之减小[54]。 前交叉韧带和半月板损伤是膝损伤中较为常见的两种损伤,因此,在刚开始进行运动疗法中,务必要注意前交叉韧带和半月板受到较大张力和压力的角度。在前交叉韧带和半月板受伤的情况下,尽量在开始阶段的治疗中不要去在此角度给膝关节负重。同时也需注意各部损伤股四头肌力量最大不足的角度,在此角度适当减小负重,避免训练过程中失稳失衡造成再次损伤。 2.4.2 运动疗法介入时间 出现膝损伤后,运动疗法介入应尽早。INGRID等[52]发现,如果优于潜在手术的运动疗法得以安全操作,似乎没有必要给膝损伤患者进行早期手术。通常包括8周内损伤严重的前交叉韧带患者,6个月内半月板退行性撕裂的患者,4年内局部软骨磨损的患者。FILBAY等[55]研究中,将符合纳入标准的前交叉韧带患者分为3组,先手术后运动疗法组、先运动疗法后手术组和运动疗法组。最后,他们得到了一个令人惊讶的发现,年轻人出现急性前交叉韧带断裂并伴有半月板损伤,以及那些在早期有严重膝关节症状、疼痛和功能受限的人,在考虑手术前可受益于设计好的运动疗法。这是因为10周内的早期重建可能会增加术后持续困难的可能性,如关节内手术造成的软骨结构创伤,长期的关节炎症,甚至体质量增加,都可能是半月板、韧带和其他关节组织治疗的不理想环境。术前运动疗法可以恢复膝关节功能,改善关节内环境,为膝关节手术做好准备,使康复效果最大化,并降低膝关节进行性退行性变的风险。其平均持续时间为14周,每周2-4次[56]。 如果患者进行过膝关节手术,术后最好同样尽快进行运动疗法。LEE等[57]进行了一个加速运动疗法(accelerated rehabilitation exercise,ARE),仅在术后 2 d开始操作,每次2 h,每周5次,共计12周,训练强度主要根据患者的疼痛级别和运动计划。结果发现,加速运动疗法患者在等长肌力、大腿围、Lysolm评价量表、动平衡等方面均有显著改善。此外,加速运动疗法与普通物理治疗相比,更有效提高30°和60°的等长力量。通常膝关节术后可在3-7 d开始进行康复训练,强度、时间、频率逐渐增加,此过程中需密切关注膝疼痛角度、膝部肌肉力量及患者的主观感受[58-60]。作者的团队之前1例膝关节前交叉韧带重建后1 d开始运动疗法,12周后可回归日常生活。相关运动疗法的操作,可参考图2。"
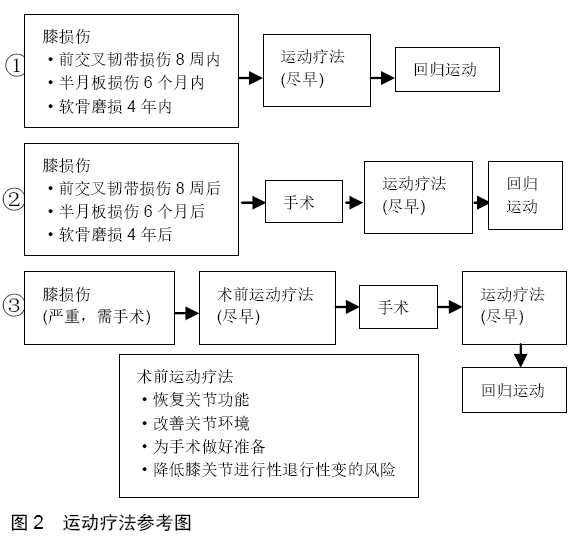

2.4.3 运动疗法治疗阶段 运动疗法治疗阶段主要分为两个阶段,早期和晚期。 早期以解决膝关节损伤为主,旨在减轻膝关节损伤、手术的疼痛、恐惧和焦虑,恢复关节活动度和膝部肌肉力量,包括关节活动松动、力量训练和神经肌肉训练。关节活动松动是早期运动疗法最为关键的部分,以膝关节屈伸为主[61]。从被动牵伸关节开始,再由患者自行操作。牵伸强度以患者忍受疼痛的酸胀感觉为主,当感觉刺痛时需立即停止。力量训练主要为抗阻训练,强度应该温和和缓慢,通常建议大约60%的最大强度[62]。神经肌肉训练是指包括动态稳定性、体位意识和协调性的运动表现训练。所有的动作都要求在运动时膝关节保持在脚和脚趾上方,同时避免过度的内偏或外偏。该强度的执行依赖于患者的反馈,必须是他们认为最大的安全角度范围内[63-64]。在运动疗法的早期,建议每个疗程在20-30 min之间[65-66]。而晚期阶段集中在准备重返运动场上,增强式训练如跑步、跳跃和敏捷性训练,可以帮助膝关节损伤患者在术后恢复运 动[67]。通常,这种运动产生的垂直地面反作用力是体质量的2-6倍,对膝关节功能恢复有积极影响。但需符合以下条件才能进行增强式训练:①主动膝关节全伸;②与健侧比,屈膝角度差异在5°内;③日常活动的疼痛评分小于2/10;④股四头肌肌力指标>60%(参考平常或健侧值);⑤术后至少12周[68-70]。此外,ERIN等[71]研究发现,负重(体质量50%)步态可以有效缓解运动治疗后和恢复运动前的“膝关节僵硬步态”,负重行走可防止肢体在动态中处于外翻位。而早期负重康复训练对关节软骨的组织学有不良影响[72],非负重运动则可减少膝关节损伤后无组织重建的创伤性骨关节炎[73],BUGBEE等[74]研究发现,非负重跑台可使大鼠膝关节的关节软骨状况更好、糖胺聚糖(增强软骨细胞抗压)水平增加、潮标(软骨发育成熟的重要标志)更具连续性。此外,BARTELS等[75]认为运动疗法中位置特异性方向变化、爆发性加速、协调技能和认知是后期的重要因素,他们展示了一个速度测试系统(Speed Court System, SCS),此系统会发出不可预测的干扰和包含以上重要因素的指令。这种训练更适合晚期的运动疗法,且有助于更科学、客观地计算回归运动的时间。 在整个运动疗法进行过程中,强度需控制在中小强度,因为膝损伤或膝手术后,关节内存在一定炎症和氧化应激。Sun等[76]发现中小强度有氧运动可减少白细胞介素1β,肿瘤坏死因子α和增加抗氧化酶的水平,可以逐渐休眠MAPKs相关信号通路(p38、JNK、ERK),从而抑制环氧合酶2和基质金属蛋白酶13的分泌。如果炎症和氧化应激情况较为严重,可选择被动运动(早期),将有利于减弱炎症和氧化应激情况[77]。一旦关节软骨被破坏,由于关节内无神经、血管和淋巴等使软骨很难被修复。因此,选择合适的运动强度非常重要,避免过度训练,加重膝关节内的炎症和氧化应激水平,而导致损伤加重。有关运动疗法策略见表2。 "

| [1] NEUMAN P, ENGLUND M, KOSTOGIANNIS I, et al. Prevalence of tibiofemoral osteoarthritis 15 years after nonoperative treatment of anterior cruciate ligament injury: a prospective cohort study. Am J Sports Med.2008;36(9):1717-1725. [2] GU X, LI C, YIN F, et al.Adipose-derived stem cells in articular cartilage regeneration: current concepts and optimization strategies. Histol Histopathol.2018;33(7):639-653. [3] YAO N, CHEN N, XU X, et al. Protective effect of Shenmai injection on knee articular cartilage of osteoarthritic rabbits and IL-1β- stimulated human chondrocytes. Exp Ther Med. 2017; 13(6):3013-3020. [4] ROOS EM, ARDEN NK. Strategies for the prevention of knee osteoarthritis. Rheumatology. 2016;12(2):92-101. [5] ZHANG W, OUYANG H, DASS CR, et al. Current research on pharmacologic and regenerative therapies for osteoarthritis.Bone Res. 2016;4:15040. [6] CHEN D, SHEN J, ZHAO W, et al. Osteoarthritis: toward a comprehensive understanding of pathological mechanism.Bone Res. 2017; 5:16044. [7] TANAKA R, OZAWA J, KITO N, et al. Effects of exercises therapy on walking ability in individuals with knee osteoarthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trails. Clin Rehabil. 2016;30(1): 36-52. [8] HALL M, HINMAN RS, WRIGLEY TV. Neuromuscular exercise post partial medial meniscectomy: randomized controlled trial. Med Sci Sports Exerc. 2015;47(8):1557-1566. [9] CHEN H, ZHENG X, HUANG H, et al. The effects of a home-based exercise intervention on elderly patients with knee osteoarthritis: a quasi-experimental study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2019; 20(1): 160. [10] RAUSCH OSTHOFF AK, JUHL CB, KNITTLE K, et al. Effects of exercise and physical activity promotion: meta-analysis informing the 2018 EULAR recommendations for physical activity in people with rheumatoid arthritis, spondyloarthritis and hip/knee osteoarthritis. RMD Open. 2018; 4(2): e000713. [11] JU CJ, ZHOU X, DONG CC, et al. Clinical observation of warm moxibustion therapy to improve quadriceps weakness after total knee arthroplasty.Zhongguo Zhen Jiu.2019;39(3): 276-279. [12] BECKWEE D, VAES P, CNUDDE M, et al. Osteoarthritis of the knee: Why does exercise work? A qualitative study of the literature. Aging Rearch Reviews. 2013;12(1): 226-236. [13] DUNCAN KJ, CHOPP-HURLEY JN, MALY MR. A systematic review to evaluate exercise for anterior cruciate ligament injuries: does this approach reduce the incidence of knee osteoarthritis. Open Access Rheumatology. 2016; 8: 1-16. [14] ACEVEDO RF, RIVERA-VEGA A, MIRANDA G, et al. Anterior cruciate ligament injury: Identification of risk factors and prevention strategies. Curr Sports Med Rep. 2014; 13(3): 186-191. [15] LIAO CD, HUANG YC, CHIU YS, et al. Effect of body mass index on knee function outcomes following continuous passive motion in patients with osteoarthritis after total knee replacement: a retrospective study. Physiotherapy. 2017;103(3): 266-275. [16] FINDLAY DM, KULIWABA JS. Bone-cartilage crosstalk: a conversation for understanding osteoarthritis. Bone Res 2016; 4: 16028. [17] BUCKWALTER JA. Sports, joint injury, and posttraumatic osteoarthritis. 2003; 33(10): 578-588. [18] REPO RU, FINLAY JB. Survival of articular cartilage after controlled impact. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1977; 59(8): 1068-1076. [19] PAPE D, HOFFMANN A, GERICH T, et al. Fractures of the knee joint in the elderly: osteosynthesis versus joint replacement. Der Orthopade. 2014; 43(4): 365-373. [20] NAKAMURA N, HORIBE S, TORITSUKA Y, et al.The location-specific healing response of damaged articular cartilage after ACL reconstruction: short-term follow-up. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2008; 16(9): 843-848. [21] FRANSEN M. Dietary weight loss and exercise for obese adults with knee osteoarthritis: modest weight loss targets, mild exercise, modest effects. Arthritis Rheum. 2004; 50(5):1366-1369. [22] RALL K, MCELROY G, KEATS TE. A study of the long term effects of football injury in the knee. Mo Med. 1984; 61: 435-438. [23] NIA HT, BOZCHALOOI IS, LI Y, et al. High-bandwidth AFM-based rheology reveals that cartilage is most sensitive to high loading rates at early stages of impairment. Biophys J. 2003; 104(7): 1529-1537. [24] BORAZJANI BH, CHEN AC, BAE WC, et al. Effect of impact on chondrocyte viability during insertion of human osteochondral grafts. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2006; 88(9):1934-1943. [25] ZIMMERMAN NB, SMITH DG, POTTENGER LA, et al. Mechanical disruption of human patellar cartilage by repetitive loading in vitro. ClinOrthop. 1988; 229: 302-307. [26] STONE AV, LITTLE KJ, GLOS DL, et al.Repetitive stresses generate osteochondral lesions in skeletally immature rabbits. Am J Sports Med. 2016; 44(11): 2957-2966. [27] GRENIER S, DONNELLY PE, GITTENS J, et al. Resurfacing damaged articular cartilage to restore compressive properties. J Biomech. 2015; 48(1):122-129. [28] YAN H, SU YX, LIN XY, et al.Zhuanggu Jianxi Decoction () limits interleukin-1 β-induced degeneration chondrocytes via the caveolin-p38 MAPK signal pathway.Chin J Integr Med. 2014;20(5): 353-359. [29] SCHULZE G, MOBASHERI A, DE P. Loss of chondrogenic potential in dedifferentiated chondrocytes correlates with deficient Shc-Erk interaction and apoptosis. Osteoarthritis and Cartilage. 2004; 12(6) : 448-458. [30] KITANAKA T, NAKANO R, KITANAKA N. JNK activation is essential for activation of MEK/ERK signaling in IL-1 beta induced COX-2 expression in synovial fibroblasts. Scientific Reports. 2017; 7: 39914. [31] ARENDT-NIELSEN L, NIE H, LAURSEN MB, et al. Sensitization in patients with painful knee osteoarthritis.Pain.2010;149(3):573-581. [32] PETERSEN AM, PEDERSEN BK.The anti-inflammatory effect ofexercise. J Appl Physiol. 2005;98:1154-1162. [33] HELMARK IC, MIKKELSEN UR, BORGLUM J, et al. Exercise increases interleukin-10 levels both intra-articularly and peri-synovially in patients with knee osteoarthritis: a randomized controlled trial. Arthritis ResTher. 2010; 12: R126. [34] KOSEK E, ROOS EM, AGEBERG E, et al. Increased pain sensitivity but normal function of exercise induced analgesia in hip and knee osteoarthritis: treatment effects of neuromuscular exercise and total joint replacement. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013; 21(9): 1299-1307. [35] MARIUS H, LOUISE K, THOMAS GN, et al. Association of exercise therapy and reduction of pain sensitivity in patients with knee osteoarthritis: A randomized controlled trial. Arhritis Care Res (Hoboken). 2014;66(12):1836-1843. [36] RYO T, JUNYA O, NOBUHIRO K, et al. Effect of exercise therapy on walking ability in individuals with knee osteoarthritis: a systematmic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Clin Rehabil. 2016;30(1):36-52. [37] SHERRINGTON C, WHITNEY JC, LORD SR, et al. Effective exercise for the prevention of falls: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2008; 56(12): 2234-2243. [38] TOPP R, SWANK AM, QUESADA PM. The effect of prehabilitation exercise on strength and functioning after total knee arthroplasty. PMR 2009;1(8):729-735. [39] DAS T, MUSTAPHA J, INDES J,et al. Technique optimization of orbital atherectomy in calcified peripheral lesions of the lower extremities: the CONFIRM series, a prospective multicenter registry. Cather CardiovascInterv. 2014; 83(1): 115-122. [40] CHANG EW, JOHNSON S, POLLARD C, et al. Landing biomechanics in anterior cruciate ligament reconstructed females who pass or fail a functional test battery. Knee. 2018; 25(6):1074-1082. [41] SANAZ S, MOHAMMAD AM, FATEMEH E. Knee muscle activity during gait in patients with anterior cruciate ligament injury: a systematic review of electromyographic studies. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2017; 25(5): 1432-1442. [42] HUANG MH, YANG RC, LE CL, et al. Preliminary results of integrated therapy for patients with knee osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2005; 53(6): 812-820. [43] BLACKBURN JT, PAMUKOFF DN, SAKR M, et al. Whole body and local muscle vibration reduce artificially induced quadriceps arthrogenic inhibition. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2014; 95(11): 2021-2028. [44] LIN CF, LIU H, GROS MT, et al. Biomechanical risk factors of non-contact ACL injuries: A stochasticbio-mechanical modeling study. J Sport Health.2012; 1: 36-42. [45] BLACKBURN JT, NORCROSS MF, PADUA DA. Influences of hamstring stiffness and strength on anterior knee joint stability. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon). 2011; 26(3): 278-283. [46] RUAN MF, ZHANG Q, WU X. Acute effects of static stretching of hamstring on performance and anterior cruciate ligament injury risk during stop-jump and cutting tasks in female athletes. J Strength Cond Res. 2017;31(5):1241-1250. [47] DECKER MJ, TORRY MR, WYLAND DJ, et al. Gender differences in lower extremity kinematics, kinetics and energy absorption during landing. ClinBiomech. 2003; 18(7): 662-669. [48] DI SL, LOGERSTEDT D, GARDINIER ES, et al. Gait patterns differ between ACL-reconstructed athletes who pass return-to-sport criteria and those who fail. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41(6):1310-1318. [49] HARTIGAN E, LAWRENCE M, NURRAY T, et al. Biomechanical profiles when towing a sled and wearing a weighted vest once cleared for sports post-ACL reconstrution. Sports Health: A multidisciplinary approach. 2016; 8(5): 456-464. [50] DEVDATTA SN, ASHOK K, LAXMAN R, et al. Role of nonoperative treatment in managing degenerative tears of the medial meniscus posterior root. J Orthopaed Traumatol. 2013; 14: 193-199. [51] RIMINGTON T, MALLIK K, EVANS D, et al. Aprospective study of the non-operative treatment of degenerative meniscus tears. Orthopedics. 2009; 32:558-564. [52] INGRID E, HEGE G, AGNETHE N, et al. Quantifying quadriceps muscle strength in patients with ACL injury, focal cartilage lesions, and degenerative meniscus tears. Orthop J Sports Med. 2016; 4(10): 2325967116667717. [53] LUQUE-SERON JA, MEDINA-PORQUERES I. Anterior cruciate ligament strain in vio. Sports Health: A multidisciplinary approach. 2016; 8(4): 451. [54] JIANG W, GAO SG, LI KH, et al. Impact of partial and complete rupture of anterior cruciate ligament on medial meniscus: A cadavaric study. Indian J Orthop. 2012; 46(5):514-519. [55] FILBAY SR, ROOS EM, FROBELL RB, et al.Delaying ACL reconstruction and treating with exercise therapy alone may alter prognostic factors for 5-year outcome: an exploratory analysis of the KANON trial.Br J Sports Med. 2017;51(22):1622-1629. [56] ALSHEWAIER S, YEOWELL G, FATOYE F. The effectiveness of pre-operative exercise physiotherapy rehabilitation on the outcomes of treatment following anterior cruciate ligament injury: a systematic review. Clin Rehabil. 2017; 31(1): 34-44. [57] LEE M, SUNG DJ, LEE J, et al. Enhanced knee joint function due to accelerated rehabilitation exercise after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction surgery in Korean male high school soccer players. J Exe Rehab. 2016; 12(1): 29-36. [58] LUQUE-SERON JA, MEDINA-PORQUERES IM. Anterior cruciate ligament strain in vivo: A systematic review. Sports Health. 2016; 8(5): 451-455. [59] GLASS R, WADDELL J, HOOGENBOOM B. The effects of open versus closed kinetic chain exercises on patients with ACL deficient or reconstructed knees: a systematic review. N Am J Sports Phys Ther. 2010; 5(2):74-84. [60] FUKUDA TY, FINGERHUT D, COIMBRA MV. Open kinetic chain exercises in a restricted range of motion after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. A randomized controlled trial. Am J Sports Med. 2013; 41(4): 788-794. [61] XU J, ZHANG J, WANG XQ, et al. Effect of joint mobilization techniques for primary total knee arthroplasty: Study protocol for a randomized controlled trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017; 96(49): e8827. [62] PELLAND L, BROSSEAU L, WELLS G, et al. Efficacy of strengthening exercises for osteoarthritis(part I): a meta-analysis. Phys Ther Rev. 2004;9:77-108. [63] RUTHERFORD DJ, HUBLEY-KOZEY CL, STANISH WD. The neuromuscular demands of altering foot progression angle during gait in asymptomatic individuals and those with knee osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil. 2010;18: 654-661. [64] SILJE S, EWA MR, MAY AR. A 12-week exercise therapy program in middle-aged patients with degenerative meniscus tears: A case series with 1-year follow-up. J Orthop Sports Phy Ther. 2012; 42(11):919-931. [65] ADAMS D, LOGERSTEDT DS, HUNTER GA, et al. Current concepts for anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction:a criterion-based rehabilitation progression.J Orthop Sports Phys Ther. 2012;42(7): 601-614. [66] JARVIS MM, GRAHAM-SMITH P, COMFORT P. A methodological approach to quantifying plyometric intensity. J Strength Cond Res. 2016; 30(9): 2522-2532. [67] NESSLER T, DENNEY L, SAMPLEY J. ACL injury prevention: What does research tell us? Curr Rev Musculoskelet Med. 2017; DOI 10.1007/s12178-017-9416-5. [68] JOY E, TAYLOR JR, NOVAK M, et al. Factors influencing the implementation of ACL injury prevention strategies by girls soccer coaches. J Strength Cond Res. 2013;27(8):2263-2269. [69] BEHRENS M, MAU-MOELLER A, BRUHN S. Effect of plyometric training on neural and mechanical properties of the knee extensor muscles. Int JSports Med. 2014;35(2):101-119. [70] CHMIELEWSKI TL, GEORGE SZ, TILLMAN SM, et al. Low-versus high-intensity plyometric exercise during rehabilitation after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction. Am J Spo Med. 2016; 44(3): 609-617. [71] ERIN H, MICHAEL L, THOMAS M, et al. Biomechanics profiles when towing a sled and wearing a weighted vest once cleared for sports post-ACL reconstruction. Sports Health. 2016; 8(5): 456-464. [72] CHANG NJ, LIN CC,SHI MY, et al. Positive effects of cell-free porous PLGA implants and early loading exercise on hyaline cartilage regeneration in rabbits. Acta Biomater. 2015; 28: 128-137. [73] CHANG NJ, SHIE MY, LEE KW, et al. Can early rehabilitation prevent post traumatic osteoarthritis in the patellofemoral joint after anterior cruciate ligament rupture? Understanding the pathological features. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(4):829. [74] BUGBEE WD, PULIDO PA, GOLDBERG T, et al. Use of an anti-gravity treadmill for early postoperative rehabilitation after total knee replacement: a pilot study to determine safety and feasibility. Ame J Orthop. 2016; 45(4): E167-173. [75] BARTELS T, PROEGER S, BREHME K, et al. The speed Court system in rehabilitation after reconstruction surgery of the anterior cruciate ligament. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2016; 136: 957-966. [76] 孙君志,王东辉,王纯,等.不同强度跑台运动对大鼠血清总抗氧化能力、超氧化物歧化酶活性及丙二醛含量的影响[J].中国临床康复, 2006,10(48):68-71. [77] 穆耶赛尔•麦麦提尼亚孜,胡毅,任云萍,等. 持续被动运动条件下骨关节炎软骨细胞Erk活性及增殖[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(42): 6265-6270. |
| [1] | Wang Jianping, Zhang Xiaohui, Yu Jinwei, Wei Shaoliang, Zhang Xinmin, Xu Xingxin, Qu Haijun. Application of knee joint motion analysis in machanism based on three-dimensional image registration and coordinate transformation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(在线): 1-5. |
| [2] | Wu Bingshuang, Wang Zhi, Tang Yi, Tang Xiaoyu, Li Qi. Anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction: from enthesis to tendon-to-bone healing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(8): 1293-1298. |
| [3] | Shao Yangyang, Zhang Junxia, Jiang Meijiao, Liu Zelong, Gao Kun, Yu Shuhan. Kinematics characteristics of lower limb joints of young men running wearing knee pads [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 832-837. |
| [4] | Zhou Jianguo, Liu Shiwei, Yuan Changhong, Bi Shengrong, Yang Guoping, Hu Weiquan, Liu Hui, Qian Rui. Total knee arthroplasty with posterior cruciate ligament retaining prosthesis in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis with knee valgus deformity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(6): 892-897. |
| [5] | Wei Xing, Liu Shufang, Mao Ning. Roles and values of blood flow restriction training in the rehabilitation of knee joint diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(5): 774-779. |
| [6] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Changes in kinematic parameters after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty and high tibial osteotomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(3): 390-396. |
| [7] | Zhao Tianyu, Jin Song, Zhang Di, Liu Xiaoxiao, Ma Jiang, Wang Ju. Baduanjin training for patellar tendinopathy in a randomized controlled trial: improving pain, muscle flexibility and lower limb balance stability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1662-1668. |
| [8] | Xu Renjie, Zhong Qiao, Liu Yubo, Yu Xiao, Yan Yongqing, Saijilafu, Yang Huilin, Chen Guangxiang. Quantitative analysis of transcriptome and proteome of knee joint synovial cells with osteopontin knockdown [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2022, 26(11): 1680-1685. |
| [9] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [10] | Zhong Hehe, Sun Pengpeng, Sang Peng, Wu Shuhong, Liu Yi. Evaluation of knee stability after simulated reconstruction of the core ligament of the posterolateral complex [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 821-825. |
| [11] | Liu Shaohua, Zhou Guanming, Chen Xicong, Xiao Keming, Cai Jian, Liu Xiaofang. Influence of anterior cruciate ligament defect on the mid-term outcome of fixed-bearing unicompartmental knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 860-865. |
| [12] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [13] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [14] | Liu Xin, Yan Feihua, Hong Kunhao. Delaying cartilage degeneration by regulating the expression of aquaporins in rats with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 668-673. |
| [15] | Xie Chongxin, Zhang Lei. Comparison of knee degeneration after anterior cruciate ligament reconstruction with or without remnant preservation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 735-740. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||