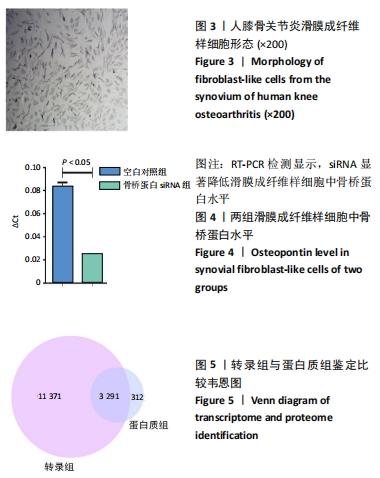
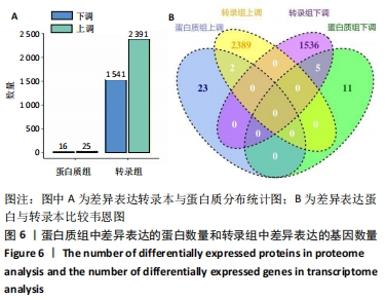
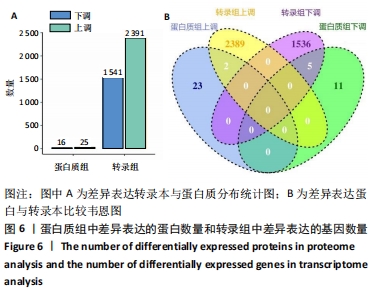
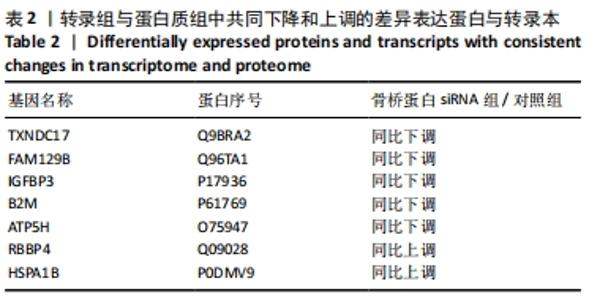
[1] ISHIGURO N, KOJIMA T, POOLE AR. Mechanism of cartilage destruction in osteoarthritis. Nagoya J Med Sci. 2002;65(3-4):73-84.
[2] CHEN D, SHEN J, ZHAO W, et al. Osteoarthritis: toward a comprehensive understanding of pathological mechanism. Bone Res. 2017;5:16044.
[3] TATEIWA D, YOSHIKAWA H, KAITO T. Cartilage and Bone Destruction in Arthritis: Pathogenesis and Treatment Strategy: A Literature Review. Cells. 2019;8(8):818.
[4] BENITO MJ, VEALE DJ, FITZGERALD O, et al. Synovial tissue inflammation in early and late osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. 2005;64(9):1263-1267.
[5] PULLIG O, WESELOH G, GAUER S, et al. Osteopontin is expressed by adult human osteoarthritic chondrocytes: protein and mRNA analysis of normal and osteoarthritic cartilage. Matrix Biol. 2000;19(3):245-255.
[6] HASEGAWA M, SEGAWA T, MAEDA M, et al. Thrombin-cleaved osteopontin levels in synovial fluid correlate with disease severity of knee osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol. 2011;38(1):129-134.
[7] HONSAWEK S, TANAVALEE A, SAKDINAKIATTIKOON M, et al. Correlation of plasma and synovial fluid osteopontin with disease severity in knee osteoarthritis. Clin Biochem. 2009;42(9):808-812.
[8] MARTIN I, JAKOB M, SCHÄFER D, et al. Quantitative analysis of gene expression in human articular cartilage from normal and osteoarthritic joints. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2001;9(2):112-118.
[9] ELBASHIR SM, HARBORTH J, LENDECKEL W, et al. Duplexes of 21-nucleotide RNAs mediate RNA interference in cultured mammalian cells. Nature. 2001;411(6836):494-498.
[10] BERENBAUM F. Osteoarthritis as an inflammatory disease (osteoarthritis is not osteoarthrosis!). Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2013;21(1):16-21.
[11] FELSON DT, NEOGI T. Osteoarthritis: is it a disease of cartilage or of bone? Arthritis Rheum. 2004;50(2):341-344.
[12] KAPOOR M, MARTEL-PELLETIER J, LAJEUNESSE D, et al. Role of proinflammatory cytokines in the pathophysiology of osteoarthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 2011;7(1):33-42.
[13] DE LANGE-BROKAAR BJ, IOAN-FACSINAY A, VAN OSCH GJ, et al. Synovial inflammation, immune cells and their cytokines in osteoarthritis: a review. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2012;20(12):1484-1499.
[14] SCANZELLO CR, GOLDRING SR. The role of synovitis in osteoarthritis pathogenesis. Bone. 2012;51(2):249-257.
[15] LIU-BRYAN R. Synovium and the innate inflammatory network in osteoarthritis progression. Curr Rheumatol Rep. 2013;15(5):323.
[16] LOEUILLE D, CHARY-VALCKENAERE I, CHAMPIGNEULLE J, et al. Macroscopic and microscopic features of synovial membrane inflammation in the osteoarthritic knee: correlating magnetic resonance imaging findings with disease severity. Arthritis Rheum. 2005;52(11):3492-3501.
[17] BENJAMIN M, MCGONAGLE D. Histopathologic changes at “synovio-entheseal complexes” suggesting a novel mechanism for synovitis in osteoarthritis and spondylarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2007;56(11): 3601-3609.
[18] MORADI B, ROSSHIRT N, TRIPEL E, et al. Unicompartmental and bicompartmental knee osteoarthritis show different patterns of mononuclear cell infiltration and cytokine release in the affected joints. Clin Exp Immunol. 2015;180(1):143-154.
[19] XU G, NIE H, LI N, et al. Role of osteopontin in amplification and perpetuation of rheumatoid synovitis. J Clin Invest. 2005;115(4):1060-1067.
[20] SHAKIBAEI M, SEIFARTH C, JOHN T, et al. Igf-I extends the chondrogenic potential of human articular chondrocytes in vitro: molecular association between Sox9 and Erk1/2. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;72(11):1382-1395.
[21] YOKOTA T, SHIMOKAWA H, SHIBATA S, et al. Insulin-like growth factor I regulates apoptosis in condylar cartilage. J Dent Res. 2008;87(2):159-163.
[22] MCCARTHY TL, CENTRELLA M. Local IGF-I expression and bone formation. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2001;11(4):213-219.
[23] MCQUEENEY K, DEALY CN. Roles of insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) and IGF-I binding protein-2 (IGFBP2) and -5 (IGFBP5) in developing chick limbs. Growth Horm IGF Res. 2001;11(6):346-363.
[24] MORALES TI. The insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in uncultured human cartilage: increases in insulin-like growth factor binding protein 3 during osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2002;46(9): 2358-2367.
[25] IWANAGA H, MATSUMOTO T, ENOMOTO H, et al. Enhanced expression of insulin-like growth factor-binding proteins in human osteoarthritic cartilage detected by immunohistochemistry and in situ hybridization. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2005;13(5):439-448.
|