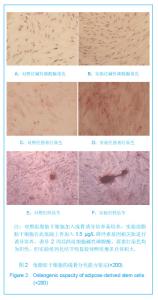
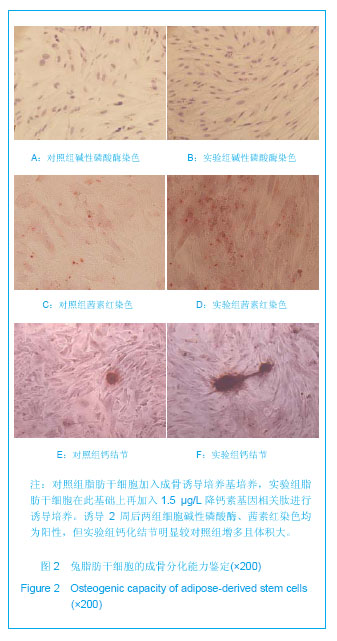
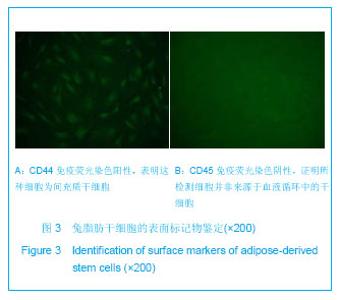
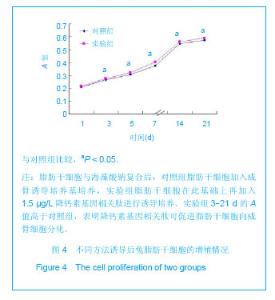
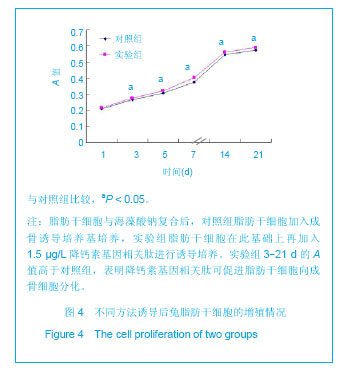
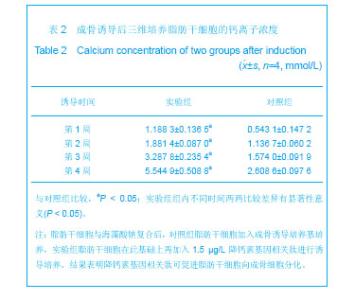
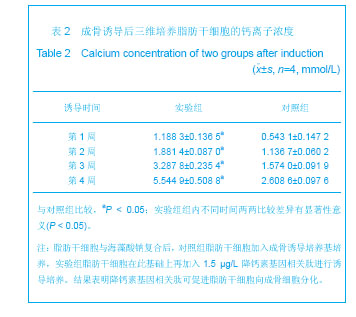
| [1] Shinbara H,Okubo M,Kimura K,et al.Participation of calcitonin gene related peptide release -d via axon reflex in the local increase in muscle blood flow following manual acupuncture. Acupunct Med.2013;31(1):81-87.
[2] 窦常胜,叶彩宏,张士发,等.先天性心脏病合并肺动脉高压患儿血浆内皮素、降钙素基因相关肽的临床研究[J].临床儿科杂志, 2010, 28(7):621-623.
[3] Porseva VV,Strelkov AA,Shikin VV,et al.Age-related changes in sensory neurons containin-g calcitonin gene-related peptide under conditions of afferentation deficit in rats. Ontogenez.2012;43(6):405-412.
[4] Hukkanen M,Konttinen YT,Santavirta S,et al.Rapid proliferation of calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunoreactive nerves during healing of rat tibial fracture suggests neural involvement in bone growth and remodelling.Neuroscience.1993;54(4):969-979.
[5] Aoki M,Tamai K,Saotome K.Substance P-and calcitonin gene-related peptide-immunofluorescent nerves in the repair of experimental bone defects.Int Orthopaeds.2004;18(5): 317-324.
[6] Li J,Kreicbergs A,Bergstrom J,et al.Site-specific CGRP innervation coincides with bone formation during fracture healing and modeling:A study in rat angulated tibia.J Orthop Res.2007;25(9):1204-1212.
[7] Hayashi Y,Ohtori S,Yamashita M,et al.Direct single injection of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibitor does not affect calcitonin gene-related peptide expression in dorsal root ganglion neurons innervating punctured discs in rats.Spine (Phila Pa 1976).2009;34(26):2843-2847.
[8] Onuoha GN.Circulating sensory peptide levels within 24h of human bone fracture.Peptides.2011;22(7):1107-1110.
[9] 孙晓新,张柳,刘志奎,等.骨折愈合过程中降钙素基因相关肽表达与脑损伤的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(2):263-267.
[10] Ekelund A,Ahmed M,Bjurholm A,et al. Neuropeptides in heterotopic bone induced by bone matrix in immunosuppressed rats.C1in Orthop Relat Res.1997; 13(345):229-238.
[11] 张远金,周赤兵,段军,等.降钙素基因相关肽神经生长因子与失神经支配兔骨折愈合[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(41):7675-7677.
[12] 李志宏,周振华,谢菊英,等.坐骨神经和股神经离断后肢固定对大鼠降钙素基因相关肽水平及骨密度的影响[J].中国康复医学, 2009, 24(12):1112-1115.
[13] 姚建华,时述山,李亚非,等.脊髓损伤大鼠胫骨骨痂中降钙素基因相关肽的改变[J].中华实验外科杂志,2010,17(4):342-343.
[14] Granholm S,Lundberg P,Lerner UH.Expression of the calcitonin receptor,calcitonin receptor-like receptor,and receptor activity modifying proteins during osteoclast differentiation.J Cell Biochem.2008;104(3):920-933.
[15] 中华人民共和国科学技术部.关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.
[16] Zuk PA,Zhu M,Ashjian P,et al.Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells.Mol Biol Cell.2002;13(12): 4279-4295.
[17] Zuk PA,Zhu M,Mizuno H,et al.Multilineage cells from human adipose tissue: implications for cell-based therapies.Tissue Eng.2001;7(2):211-228.
[18] Pilchard HL,Richerd WM,Klitzman B,et al.Adult adipose-derived stem cells attachment to biomaterials. Biomaterials. 2007;28(6):936-946.
[19] Rodriguez AM,Elabd C,Amri EZ,at al.The human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells.Biochimie.2005; 87(1):125-128.
[20] Yu H,VandeVord PJ,Mao L,et al.Improved tissue-engineered bone regeneration by endothelial cell mediated vascularization. Biomaterials.2009;30(4):508-517.
[21] 卢向东,郭庆华,刘强. 转基因干细胞构建组织工程骨的初步实验研究[J].中华显微外科杂志,2010,33(2):143-147.
[22] 闫峰,杨卫良,杨威.生物材料修复股骨缺损及其性能评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(16):2963-2966.
[23] 张建新,徐展望,常峰.组织工程化人工骨修复骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2009,17(16):1258-1261.
[24] Tobita M,Orbay H,Mizuno H.Adipose-derived stem cells: current findings and future perspectives.Discov Med. 2011; 11(57):160-170.
[25] 张东,杨克,马忠石,等.藻酸盐三维细胞培养在骨组织工程中应用的研究进展[J].生物技术通报,2007,23(6):62-66.
[26] Rosenfeld MG,Mermod JJ,Amara SG,et al.Production of a novel neuropeptide encoded by the calcitonin gene via tissue-specific RNA processing.Nature. 1983;304(5922): 129-135.
[27] Morris HR,Panico M,Etienne T,et al.Isolation and characterization of human calcitonin gene-related peptide. Nature.1984;308(5961):746-748.
[28] Barwell J,Wheatley M,Conner AC,et al.The activation of the CGRP receptor. Biochem Soc Trans.2013;41(1):180-184.
[29] Wang L,Shi X,Zhao R,et al.Calcitonin-gene-related peptide stimulates stromal cell osteogenic differentiation and inhibits RANKL induced NF-kappaB activation, osteoclastogenesis and bone resorption.Bone.2010;46(5): 1369-1379.
[30] Huebner AK,Keller J,Catala-Lehnen P,et al.The role of calcitonin and alpha-calcitonin gene-related peptide in bone formation.Arch Biochem Biophys.2008;473(2):210-217.
[31] Jimenez-Andrade JM,Mantyh WG,Bloom AP,et al.A phenotypically restricted set of primary afferent nerve fibers innervate the bone versus skin:therapeutic opportunity for treating skeletal pain. Bone.2010;46(2):306-313.
[32] Naot D,Cornish J.The role of peptides and receptors of the calcitonin family in the regulation of bone metabolism. Bone. 2008;43(5):813-818. |