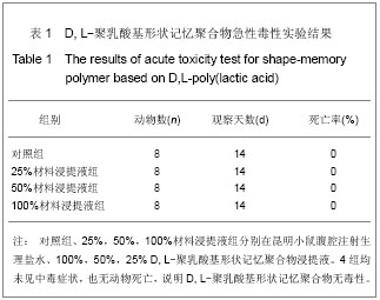
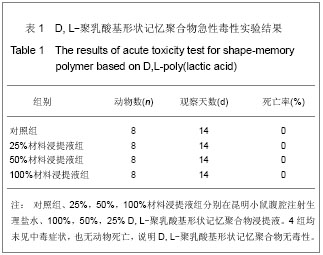
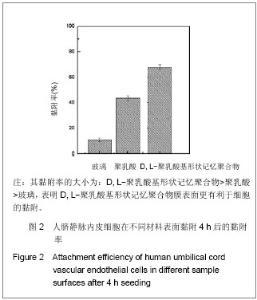
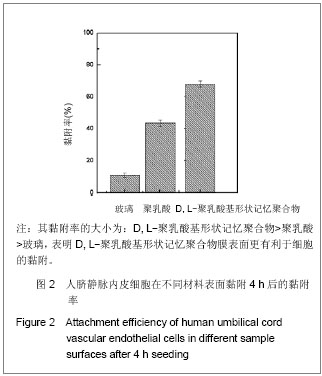
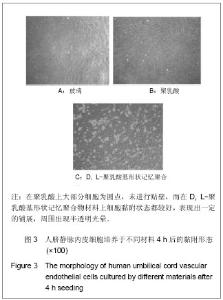
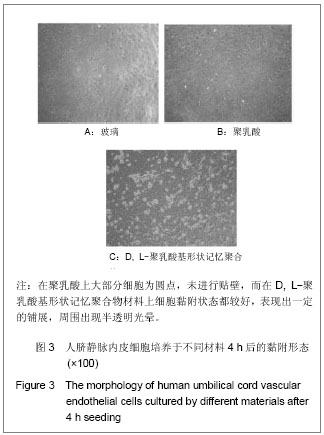
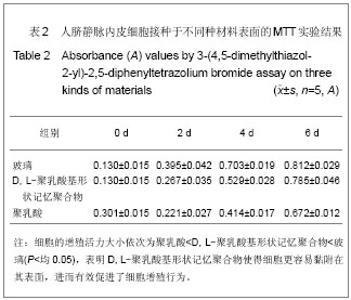
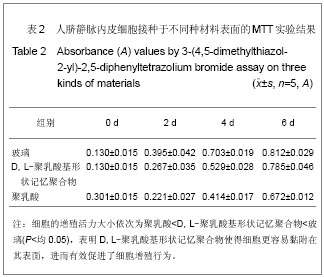
| [1] 奚廷斐.医疗器械生物学评价[J].中国医疗器械信息,1999,5(3): 4.
[2] GB/T16886.12-2003.医疗器械生物学评价第12部分:样品制备与参照样品.
[3] GB/T16886.10-2000.医疗器械生物学评价第10部分:刺激与致敏试验.
[4] GB/T16886.11-1997.医疗器械生物学评价第11部分:全身毒性试验.
[5] 胡平.组织工程用外科植入物——高分子材料的加工、改性及应用[J].中国医疗器械信息,2006,12(7):13-21.
[6] Wu K,Zhao Y,Liu BH,et al.RRR-a-tocopheryl succinate inhibits human gastric cancer SGC-7901 cell growth by inducing apoptosis and DNA synthesis arrest. World J Gastroenteml.2002;8(1):26-30.
[7] Andrade LS,Santos DB,Castro DB,et al.Absence of antimutagenicity of Cochlospermum regium (Mart. and Schr.) Pilger 1924 by micronucleus test in mice. Braz J Biol.2008; 68(1):141-147.
[8] Oliveira-Martins CR,Grisolia CK.Determination of micronucleus frequency by acridine orange fluorescent staining in peripheral blood reticulocytes of mice treated topically with different lubricant oils and cyclophosphamide. Genet Mol Res.2007;6(3): 566-574.
[9] 王雪梅,黄绪亮,赵克森.一种新型医用功能敷料的全身和细胞毒性反应[J].医疗卫生装备,1998,5(1): 6-8.
[10] 张梅霞,姚瑶,李妙,等.四种新型仿生骨组织工程支架材料生物安全性评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(19): 3641-3644.
[11] Harmand MF,Bordenave L,Bareille R,et al.In vitro study of biodegradation of a Co-Cr alloy using a human cell culture model.J Biomater Sci Polym Ed.1995;6(9): 809-814.
[12] Lee JH,Jung HW,Kang IK,et al.Cell behaviour on polymer surfaces with different functional groups.Biomaterials.1994; 15(9): 705-711.
[13] 郝和平.医疗器械生物学评价标准实施指南[M].北京: 中国标准出版社,2000: 102,285-295,334-347.
[14] 王雪梅,黄绪亮,赵克森.一种新型医用功能敷料的全身和细胞毒性反应[J].医疗卫生装备,1998,5(1): 6-8.
[15] Chauhan LK,Kumar M,Paul BN,et al.Cytogenetic effects of commercial formulations of deltamethrin and/or isoproturon on human peripheral lymphocytes and mouse bone marrow cells.Environ Mol Mutagen.2007;48(8): 636-636.
[16] Bonassi S,Fenech M,Lando C,et al.Human Micronucleus Project: International Database Comparision for Results. Environ Mole Mutagen.2001;37(1): 31-35.
[17] 卢玲,游文玮,王迎军,等.生物活性玻璃的表面修饰及其细胞相容性[J].复合材料学报,2011,28(1):114-118.
[18] 周庆翰,林娟.天然氨基酸生物材料的自组装与细胞相容性研究[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2012,29(5):898-908.
[19] 黄江鸿,王大平,刘建全,等.新型聚乳酸复合纳米羟基磷灰石人工骨的细胞相容性[J].实用骨科杂志,2012,18(4):323-326.
[20] 李春民,董建德,谷涌泉,等.ε-己内酯/L-丙交酯聚合物组织工程血管支架材料的生物相容性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2010, 24(8):988-992.
[21] 魏丽,李德超,王静,等.聚乳酸-壳聚糖纤维/羟基磷灰石-硅酸钙复合支架材料的细胞相容性[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2010,14(8):1397-1401.
[22] 陈达,计剑,沈家骢.功能化聚乳酸微球改性聚乳酸膜片表面及其细胞相容性[J].高分子学报,2004,48(6):826-829.
[23] 周辉,梁瑜.多种生物材料细胞生物相容性及其安全性的系统评价[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009,13(38):7559-7562. |