Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research
Previous Articles Next Articles
The top cited articles on bioartificial liver in Web of Science
Zhang Fan1, Lao Xue-jun2, Jiang Jian-wei3, Cao Ming-rong2
- 1First Department of General Surgery, Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical College, Guangzhou 510700, Guangdong Province, China; 2Second Department of General Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China; 3Department of Biochemistry, Medical College, Jinan University, Guangzhou 510632, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2013-04-18Revised:2013-06-13Online:2013-07-30Published:2013-07-30 -
Contact:Lao Xue-jun, Associate chief physician, Second Department of General Surgery, First Affiliated Hospital of Jinan University, Guangzhou 510630, Guangdong Province, China Foxlxj2k@126.com -
About author:Zhang Fan★, Master, Attending Physician, First Department of General Surgery, Fifth Affiliated Hospital of Guangzhou Medical College, Guangzhou 510700, Guangdong Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Fan, Lao Xue-jun, Jiang Jian-wei, Cao Ming-rong. The top cited articles on bioartificial liver in Web of Science [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.31.023.
share this article

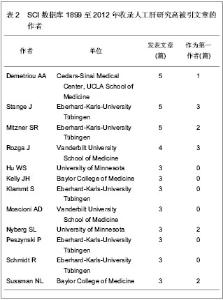
2.1 SCI数据库1899至2012年收录人工肝研究高被引文章分析 2.1.1 SCI数据库1899至2012年收录人工肝研究高被引文章的研究领域 SCI数据库1899至2012年共收录4 144篇人工肝研究文献,其中包括3 182篇研究原著,962篇综述,会议论文,勘误等类型稿件。其中,2 814篇文章被引用次数大于1次,78篇文章被引超过100次。通过阅读摘要和全文,共有33篇文献纳入本文分析,其中,11篇稿件与肝细胞培养相关[16-26],7篇稿件关于人工肝装置安全性的动物实验[27-33],5篇为生物型人工肝治疗肝衰竭的研究[34-38],4篇为人工肝分子吸附再循环系统研究[39-42],6篇其他研究[43-48]。 2.1.2 SCI数据库1899至2012年收录人工肝研究高被引文章的前5位国家分析 从文献总量的国家分布来看,33篇人工肝研究高被引文章来自11个国家,其中,美国的研究文献篇数最多,为24篇,占总文献量的70.59%,说明美国在人工肝研究中占据领先地位;德国以6篇文献位居第2位,占总文献量的17.65%;日本,荷兰及英国各发表了3篇高被引的文章,位居第3位。 2.1.3 SCI数据库1899至2012年收录人工肝研究高被引文章的来源机构 见表1。"

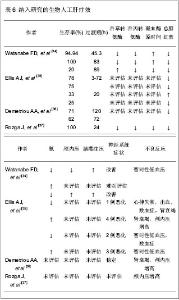
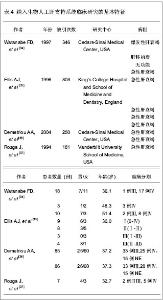
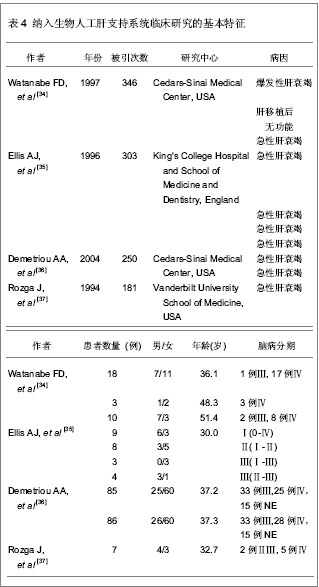
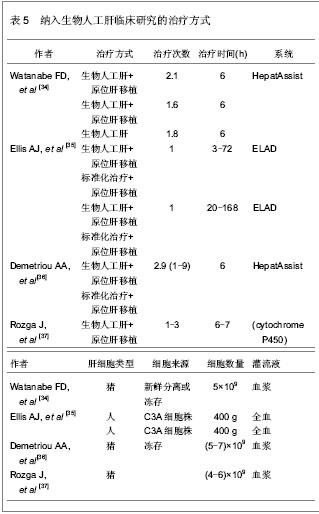
大多数作者通过描述临床和生化指标、肝移植过渡期、存活率和不良反应事件,用来评估人工肝的治疗效果。一般来说,上述指标均有不同程度改善,包括转氨酶、血氨、总胆红素、凝血酶原时间、颅内压和脑灌注压。其中肝移植过渡期从3 h到8 d不等。需要注意的是,2项随机对照试验结果并不那么乐观。Ellis等[35]报道了生物人工肝联合原位肝移植治疗组与单纯原位肝移植手术组在生存期方面统计并无明显差异。Demetriou等[36]报道了在使用HepatAssist系统治疗的患者中,只有对因过量摄入对乙酰氨基酚引起急性肝衰竭这一亚组的患者,他们的生存率才有明显改善。另外,4篇文章均报道生物人工肝系统发生了不良反应,其中暂时性低血压最为常见。人工肝治疗效果,见表6。"

| [1] Russell PS. Understanding resource use in liver transplantation. JAMA. 1999;281(15):1431-1432.[2] Allen JW, Hassanein T, Bhatia SN. Advances in bioartifcial liver devices. Hepatology. 2001;34(3):447-455.[3] Harper AM, Rosendale JD. The UNOS OPTN waiting list and donor registry: 1988-1996. Clin Transpl.1996:69-90. [4] Fishman JA, Rubin RH. Infection in organ-transplant recipients. N Engl J Med. 1998;338:1741-1751. [5] Kimoto S, Sugiura M, Sakamoto K, et al. The artificial liver. Arch De Vecchi Anat Patol. 1960;31:229-239. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/14409107。[6] Davenport A, Will EJ, Davison AM. Continuous vs. intermittent forms of haemofiltration and/or dialysis in the management of acute renal failure in patients with defective cerebral autoregulation at risk of cerebral oedema. Contrib Nephrol. 1991;93:225-233.[7] O’Grady JG, Gimson AES, O’Brien CJ, Pucknell A, Hughes RD, Williams R. Controlled trials of charcoal haemoperfusion and prognostic factors in fulminant hepatic failure. Gastroenterology. 1988;94(5 Pt 1):1186-1192.[8] Riordan SM, Williams R. Extracorporeal support and hepatocyte transplantation in acute liver failure and cirrhosis. Journal of Gastroenterology and Hepatology 1999;14:757-770.[9] Ding YT, Xu QX, Qiu YD, et al. Molecular adsorbent recycling system in treating patients with acute liver failure: a bridge to liver transplantation. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 2004;3:508-510.[10] Eguchi S, Kawazoe Y, Sugiyama N, et al. Effects of recombinant human hepatocyte growth factor on the proliferation and function of porcine hepatocytes. ASAIO Journal. 2000;46(1):56-59.[11] Stockmann HB, Hiemstra CA, Marquet RL, Ijzermans JN. Extracorporeal perfusion for the treatment of acute liver failure.Annals of Surgery 2000;231:460-470.[12] Moed HF: New developments in the use of citation analysis in research evaluation. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2009; 57:13-18.[13] Adam D: The counting house. Nature. 2002;415 (6873): 726-729.[14] Hennessey K, Afshar K, Macneily AE. The top 100 cited articles in urology. Can Urol Assoc J. 2009;3:293-302.[15] Rosenberg AL, Tripathi RS, Blum J. The most influential articles in critical care medicine. J Crit Care. 2010;25: 157-170.[16] Powers MJ, Domansky K, Kaazempur-Mofrad MR, et al. A microfabricated array bioreactor for perfused 3D liver culture. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2002;78(3):257-269.[17] Wang XH, Li DP, Wang WJ, et al. Crosslinked collagen/chitosan matrix for artificial livers. Biomaterials. 2003;24(19):3213-3220. [18] Berthiaume F, Moghe PV, Toner M, et al. Effect of extracellular matrix topology on cell structure, function, and physiological responsiveness: hepatocytes cultured in a sandwich configuration. FASEB J. 1996;10(13):1471-1484.[19] Tilles AW, Baskaran H, Roy P, et al. Effects of oxygenation and flow on the viability and function of rat hepatocytes cocultured in a microchannel flat-plate bioreactor. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2001;73(5):379-389.[20] Suzuki A, Zheng Y, Kondo R, et al. Flow-cytometric separation and enrichment of hepatic progenitor cells in the developing mouse liver. Hepatology. 2000;32(6):1230-1239.[21] Powers MJ, Janigian DM, Wack KE, et al. Functional behavior of primary rat liver cells in a three-dimensional perfused microarray bioreactor. Tissue Eng. 2002;8(3):499-513.[22] Leclerc E, Sakai Y, Fujii T. Microfluidic PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane) bioreactor for large-scale culture of hepatocytes. Biotechnol Prog. 2004;20(3):750-755.[23] Fukuda J, Khademhosseini A, Yeo Y, et al. Micromolding of photocrosslinkable chitosan hydrogel for spheroid microarray and co-cultures. Biomaterials. 2006;27(30):5259-5267[24] Schwartz RE, Reyes M, Koodie L, et al. Multipotent adult progenitor cells from bone marrow differentiate into functional hepatocyte-like cells. J Clin Invest. 2002;109(10):1291-1302[25] Nyberg SL, Remmel RP, Mann HJ, et al. Primary hepatocytes outperform Hep G2 cells as the source of biotransformation functions in a bioartificial liver. Ann Surg. 1994;220(1):59-67.[26] Bhatia SN, Balis UJ, Yarmush ML, et al. Probing heterotypic cell interactions: hepatocyte function in microfabricated co-cultures. J Biomater Sci Polym Ed. 1998;9(11):1137-1160.[27] Wolf CF, Munkelt BE. Bilirubin conjugation by an artificial liver composed of cultured cells and synthetic capillaries. Trans Am Soc Artif Intern Organs. 1975;21:16-27.[28] Rozga J, Williams F, Ro MS, et al. Development of a bioartificial liver: properties and function of a hollow-fiber module inoculated with liver cells. Hepatology. 1993; 17(2): 258-265.[29] Rozga J, Holzman MD, Ro MS, et al. Development of a hybrid bioartificial liver. Ann Surg. 1993;217(5):502-509; discussion 509-511.[30] Nyberg SL, Shatford RA, Peshwa MV, et al. Evaluation of a hepatocyte-entrapment hollow fiber bioreactor: a potential bioartificial liver. Biotechnol Bioeng. 1993;41(2):194-203.[31] Flendrig LM, la Soe JW, Jörning GG, et al. In vitro evaluation of a novel bioreactor based on an integral oxygenator and a spirally wound nonwoven polyester matrix for hepatocyte culture as small aggregates. J Hepatol. 1997;26(6): 1379-1392.[32] Sussman NL, Chong MG, Koussayer T, et al. Reversal of fulminant hepatic failure using an extracorporeal liver assist device. Hepatology. 1992;16(1):60-65.[33] Soto-Gutiérrez A, Kobayashi N, Rivas-Carrillo JD, et al. Reversal of mouse hepatic failure using an implanted liver-assist device containing ES cell-derived hepatocytes. Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24(11):1412-1419.[34] Watanabe FD, Mullon CJ, Hewitt WR, et al. Clinical experience with a bioartificial liver in the treatment of severe liver failure. A phase I clinical trial. Ann Surg. 1997;225(5):484-491; discussion 491-494.[35] Ellis AJ, Hughes RD, Wendon JA, et al. Pilot-controlled trial of the extracorporeal liver assist device in acute liver failure. Hepatology. 1996;24(6):1446-1451.[36] Demetriou AA, Brown RS Jr, Busuttil RW, et al. Prospective, randomized, multicenter, controlled trial of a bioartificial liver in treating acute liver failure. Ann Surg. 2004;239(5):660-667; discussion 667-670.[37] Rozga J, Podesta L, LePage E, et al. A bioartificial liver to treat severe acute liver failure. Ann Surg. 1994;219(5): 538-544; discussion 544-546.[38] Sussman NL, Gislason GT, Conlin CA, et al. The Hepatix extracorporeal liver assist device: initial clinical experience. Artif Organs. 1994;18(5):390-396.[39] Strom SC, Fisher RA, Thompson MT, et al. Hepatocyte transplantation as a bridge to orthotopic liver transplantation in terminal liver failure. Transplantation. 1997;63(4):559-569.[40] Mitzner SR, Stange J, Klammt S, et al. Improvement of hepatorenal syndrome with extracorporeal albumin dialysis MARS: results of a prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial. Liver Transpl. 2000;6(3):277-286.[41] Stange J, Mitzner SR, Risler T, Erley CM, Lauchart W, Goehl H, et al. Molecular adsorbent recycling system (MARS): clinical results of a new membrane-based blood purifcation system for bioartifcial liver support. Artifcial Organs 1999; 23(4):319-330.[42] Sorkine P, Ben Abraham R, Szold O, et al. Role of the molecular adsorbent recycling system (MARS) in the treatment of patients with acute exacerbation of chronic liver failure. Crit Care Med. 2001;29(7):1332-1336.[43] Sen S, Davies NA, Mookerjee RP, et al. Pathophysiological effects of albumin dialysis in acute-on-chronic liver failure: a randomized controlled study. Liver Transpl. 2004;10(9): 1109-1119.[44] Pitkin Z, Mullon C. Evidence of absence of porcine endogenous retrovirus (PERV) infection in patients treated with a bioartificial liver support system. Artif Organs. 1999;23(9):829-833.[45] Mitzner SR, Stange J, Klammt S, et al. Extracorporeal detoxification using the molecular adsorbent recirculating system for critically ill patients with liver failure. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2001;12 Suppl 17:S75-82.[46] Stange J, Hassanein TI, Mehta R, et al. The molecular adsorbents recycling system as a liver support system based on albumin dialysis: a summary of preclinical investigations, prospective, randomized, controlled clinical trial, and clinical experience from 19 centers. Artif Organs. 2002;26(2):103-110.[47] Stange J, Mitzner S. A carrier-mediated transport of toxins in a hybrid membrane. Safety barrier between a patients blood and a bioartificial liver. Int J Artif Organs. 1996;19(11): 677-691.[48] Matsumura KN, Guevara GR, Huston H, et al. Hybrid bioartificial liver in hepatic failure: preliminary clinical report. Surgery. 1987;101(1):99-103.[49] Wang XH, Li DP, Wang WJ, et al. Crosslinked collagen/chitosan matrix for artificial livers. Biomaterials. 2003;24(19):3213-3220. |
| [1] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [2] | Yang Xin, Jin Zhe, Feng Xu, Lu Bing. The current situation of knowledge and attitudes towards organ, eye tissue, body donation of residents in Shenyang [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 779-784. |
| [3] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [4] | Ren Wenbo, Liao Yuanpeng. Visualization analysis of traumatic osteoarthritis research hotspots and content based on CiteSpace [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(21): 3374-3381. |
| [5] | Wei Jinqiang, Huang Dengcheng, Cao Xuewei, Zhou Jianwei, Sun He, Li Zehui. Analysis of researches on TCM treatments for cartilage diseases in recent 20 years by mapping knowledge domains [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3202-3209. |
| [6] | Zhang Kai, Zhang Xiaobo, Shi Jintao, Wang Keping, Zhou Haiyu. Mesenchymal stem cells for treatment of intervertebral disc degeneration: a bibliometric and visualization analysis based on Web of Science database [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3031-3038. |
| [7] | Huang Zeling, Shi Shanni, He Junjun, Gao Hongjian, Ge Haiya, Hong Zhenqiang. Meta-analysis of safety and effectiveness of proximal fibular osteotomy and high tibial osteotomy in the treatment of knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(18): 2945-2952. |
| [8] | Huang Na, Liu Jiayue, Huang Yingjie, Wen Junmao, Wang Haibin, Zhang Qingwen, Zhou Chi . Bibliometric and visualized analysis of research on osteonecrosis of the femoral head from the Web of Science in the last 5 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2711-2718. |
| [9] | Wen Shuaibo, Han Jie, Wu Yukun. Bibliometric and visual analysis of literature on cartilage repair in the Web of Science in recent 15 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(17): 2657-2663. |
| [10] | Song Yahan, Wu Yunxia, Fan Daoyang. Knowledge mapping of three-dimensional printing in biomedical field based on VOSviewer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(15): 2385-2393. |
| [11] | Wu Cunshu, Zhan Xiaoxuan, Zhao Siyi, Huang Fan, Zhang Yue, Qiu Mingwang, Xia Jingxian, Lu Xiaobo. Gait training for spinal cord injury based on radar plotting: an overview of systematic reviews [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(14): 2287-2296. |
| [12] | Wang Shao, Yuan Dajiang, Li Yanyan, Li Xiaoya. Dexmedetomidine combined with local anesthetic for brachial plexus block: a systematic review and meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(12): 1951-1958. |
| [13] | Liu Yali, Wang Huan, Yan Qiong, Wang Gang, Hou Boru, Wang Dengfeng, Ma Bin, Ren Haijun. Therapeutic effect of stem cells in chronic temporal lobe epilepsy: a systematic review of animal studies [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 152-158. |
| [14] | Deng Jinman, Fang Guanjun, Wang Yu, Ding Shaobo. Efficacy and characteristics of parecoxib and celecoxib in the treatment of pain after orthopedic surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(9): 1471-1476. |
| [15] | Chen Juan, Zhang Ting, Wu Yidan, Lu Yan, Ouyang Zhaolian. China’s strengths in basic research in the main subfields of tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(8): 1267-1271. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||