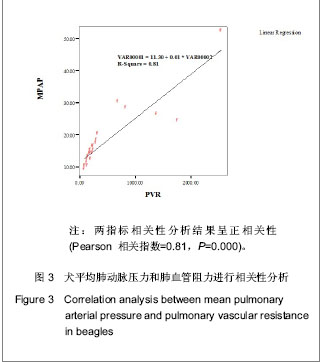
| [1] Mattocks AR, Jukes R, Brown J. Simple procedures for preparing putative toxic metabolites of pyrrolizidine alkaloids. Toxicon.1989;27:561-567.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/2749755 [2] Tang J, Wang ZT, Zhang M, et al. Release and identification of monocrotaline acid from dehydromonocrotaline . J China Pharma Univer.2003;34:499-502http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Tang+J%2C+Wang+ZT%2C+Zhang+M [3] Humbert M, Morrell NW, Archer SL,et al.Cellular and molecular pathobiology of pulmonary arterial hypertension.J Am Coll Cardiol.2004;43:13-24.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15194174 [4] Sun B,Liu WL.Zhongguo Yixue Kexueyuan Xuebao. 1984; 6:466.孙波,刘文利.右心导管测定大鼠肺动脉压的实验方法[J].中国医学科学院学报,1984,6:466.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZYKX198406061.htm [5] Dumitrascu R, Koebrich S, Dony E, et al.Characterization of a murine model of monocrotaline pyrrole-induced acute lung injury, BMC Pulm Med.2008;25:10http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=Characterization+of+a+murine+model+of+monocrotaline+pyrrole-induced+acute+lung+injury [6] Gu Y,Wang ZP,Lu JJ,et al.Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2003;19(10):1416-1417.顾勇,王治平,鲁建军,等.野百合碱所致肺动脉高压大鼠模型中碱性成纤维细胞生长因子、内皮素- 1及其受体的表达和外源性NO的作用[J].中国病理生理杂志,2003,19(10):1416-1417.http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92208X/200310/8481563.html [7] Ohar JA, Pyle JA, Waller KS, et al. A rabbit model of pulmonary hypertension induced by the synthetic platelet-activating factor acetylglyceryl ether phosphorylcholine, Am Rev Respir Dis.1990;141:104-110.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=A+rabbit+model+of+pulmonary+hypertension+induced+by+the+synthetic+platelet-activating+factor+acetylglyceryl+ether+phosphorylcholine [8] Wang W,Zhang YQ,Wu SM,et al.Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2006;22(3):612-615.王伟, 张宜乾, 吴树明,等.兔高动力性肺动脉高压模型的建立[J].中国病理生理杂志,2006,22(3):612-615.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZBLS200603047.htm [9] Carlos AC, Junior D, Mark T, et al.Low-dose intravenous nitrite improves hemodynamics in a canine model of acute pulmonary thromboembolism.Free Radical Biology & Medicine. 2006;41: 1764-1770.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17157179 [10] Gust R, Schuster DP.Vascular remodeling in experimentally induced subacute canine pulmonary hypertension. Exp Lung Res.2001;27:1-12.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11202060 [11] Zhao YH, Su ZK, Zhang HB, et al. Establishment of a canine model of pulmonary hypertension with dehydromonocrotaline. Chin J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2005;21:346-348.http://www.39kf.com/focus/lc/hx/2006-05-25-207249.shtml[12] Gruenewald M, Renner J, Meybohm P, et al. Reliability of continuous cardiac output measurement during intra-abdominal hypertension relies on repeated calibrations: an experimental animal study. Crit Care. 2008;12:132.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18957114 [13] Cariou A, Monchi M, Dhainaut JF, et al. Continuous cardiac output and mixed venous oxygen saturation monitoring.J Crit Care.1998;13:198-213.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9869547[14] Thrush D, Downs J, Robert A.Continuous Thermodilution Cardiac Output:Agreement With Fick and Bolus Thermodilution Methods. J Cardiothor Vasc An.1995;9: 399-404http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/7579109 [15] Boyle M, Jacobs S, Torda TA, et al. Amssessment of the agreement between cardiac output measured by bolus themodilution and continuous methods with particular reference to the effect of heart rhythm. Aus Cri Care.1997; 10:5-11. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9180438 [16] Girgis RE, Li D, Zhan X, et al.Attenuation of chronic hypoxic pulmonary hypertension by simvastatin,Am J Physiol Heart Circ.2003;285: 938-945.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12750068 [17] Heath D.The rat is a poor animal model for the study of human pulmonary hypertension.Cardioscience. 1992;3:1-5.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/?term=The+rat+is+a+poor+animal+model+for+the+study+of+human+pulmonary+hypertension.Cardioscience |