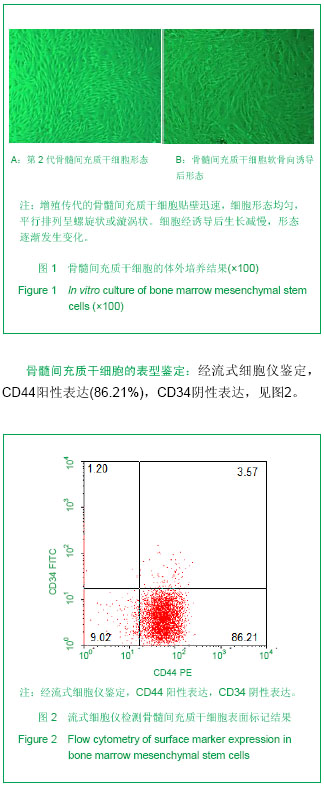
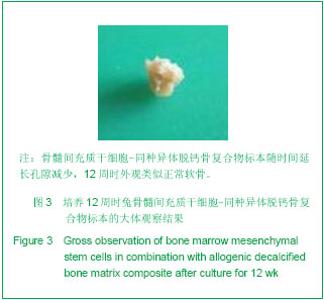
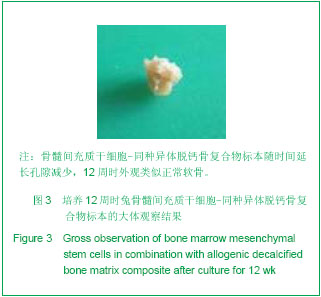
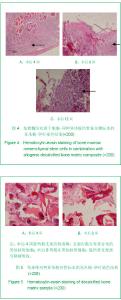
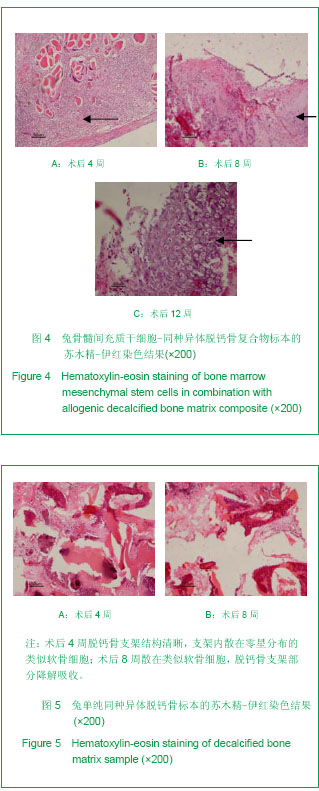
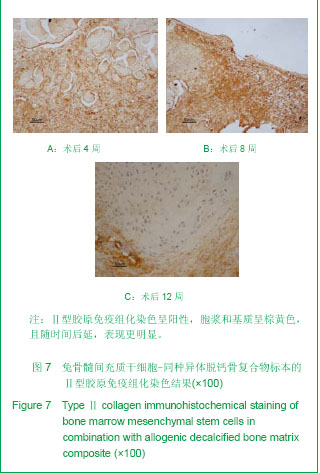
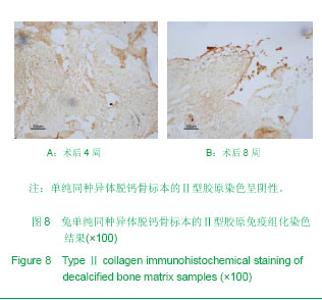
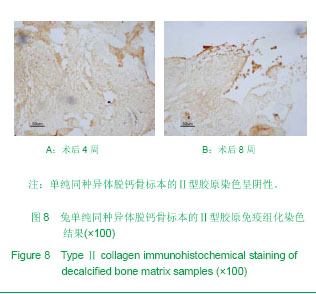
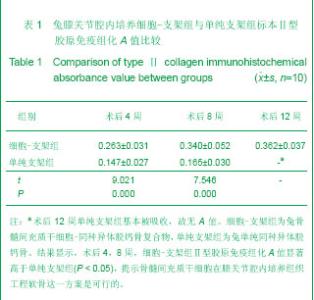
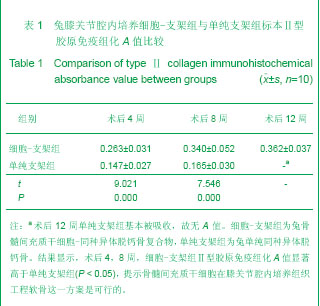
| [1] Hunziker EB. Articular cartilage repair: are the intrinsic biological constraints undermining this process insuperable? Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 1999;7: 15-28.[2] van der Kraan PM, Buma P, van Kuppevelt T, et al. Interaction of chondrocytes, extracellular matrix and growth factors: relevance for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Osteoarthritis Cartilage. 2002;10: 631-637.[3] Shi SS, Xu ST. Beijing: People’s Military Medical Press.2002: 129.时述山, 胥少汀. 实用骨与软骨移植[M]. 北京: 人民军医出版社, 2002: 129.[4] Buckwalter JA, Mankin HJ. Articular cartilage: degeneration and osteoarthritis repair, regeneration and transplantation. Instr Course Lect. 1998;47: 487-504.[5] 中华人民共和国科学技术部. 关于善待实验动物的指导性意见. 2006-09-30.http://www.most.gov.cn/fggw/zfwj/zfwj2006/200609/t20060930_54389.htm[6] Otto WR, Rao J. Tomorrow's skeleton staff: mesenchymal stem cells and the repair of bone and cartilage. Cell Prolif. 2004; 37: 97-110. [7] Agha-Hosseini F, Jahani MA, Jahani M, et al. In vitro isolation of stem cells derived from human dental pulp. Clin Transplant. 2010;24: E23-28.[8] Gimble JM, Guilak F, Nuttall ME, et al. In vitro differentiation potential of mesenchymal stem cells. Transfus Med Hemoth. 2008;35: 228-238. [9] Kassem M. Mesenchymal stem cells: biological characteristics and potential clinical applications. Cloning Stem Cells. 2004;6: 369-374. [10] Carlo Stella C, Gianni MA. Biology and clinical applications of marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2005;53: 162-164. [11] Bernardo ME, Locatelli F, Fibber WE. Mesenchymal stromal cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2009;1176: 101-117.[12] Bilodeau K, Mantovani D. Bioreactors for tissue engineering: focus on mechanical constraints. A comparative review. Tissue Eng. 2006;12: 2367-2383.[13] Aggarwal S, Pittenger MF. Human mesenchymal stem cells modulate allogeneic immune cell responses. Blood. 2005;105: 1815-1822. [14] Ramasamy R, Tong CK, Seow HF, et al. The immunosuppressive effects of human bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells target T cell proliferation but not its effector function. Cell Immunol. 2008;251: 131-136.[15] Qin J, Zhao ZL. Xiandai Mianyixue. 2010;30(6): 515-519.秦静, 赵振林. 骨髓间充质干细胞的免疫原性特点及其免疫调节能力[J]. 现代免疫学, 2010, 30(6): 515-519.[16] Wang XG, Deng CY, Qi H, et al. Xiandai Mianyixue. 2009; 29(2): 106-110.王新根, 邓春艳, 齐晖, 等. 骨髓间充质干细胞对同种异体T淋巴细胞不同亚群功能的影响[J]. 现代免疫学, 2009, 29(2): 106-110.[17] Burg KJ, Porter S, Kellam JF. Biomaterial developments for bone tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2000; 21: 2347-2359. [18] Johnstone B, Hering TM, Caplan AI, et al. In vitro. chondrogenesis of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells. Exp Cell Res. 1998;238: 265-272. [19] Worster AA, Nixon AJ, Brower-Toland BD, et al. Effect of transforming growth factor beta1 on chondrogenic differentiation of cultured equine mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Vet Res. 2000;61: 1003-1010.[20] Barry F, Boynton RE, Liu B, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow: differentiation-dependent gene expression of matrix components. Exp Cell Res. 2001;268: 189-200. [21] Ebisawa K, Hata K, Okada K, et al. Ultrasound enhances transforming growth factor beta-mediated chondrocyte differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. Tissue Eng. 2004;10: 921-929.[22] Van den Berg WB, Van der Kraan PM, Scharstuhl A, et al. Growth factors and cartilage repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2001; 391 Suppl:S244-250.[23] Uebersax L, Merkle HP, Meinel L. Insulin-like growth factor I releasing silk fibroin scaffolds induce chondrogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells. J Control Release. 2008;127: 12-21. [24] Bosnakovski D, Mizuno M, Kim G, et al. Chondrogenic differentiation of bovine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in different hydrogels: influence of collagen type II extracellular matrix on MSC chondrogenesis. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2006;93: 1152-1163.[25] Guilak F, Fermor B, Keefe FJ, et al. The role of biomechanics and inflammation in cartilage injury and repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res. 2004;423: 17-26.[26] Hardingham T, Tew S, Murdoch A. Tissue engineering: chondrocytes and cartilage. Arthritis Res. 2002;4 Suppl 3: S63-68. [27] Smith RL, Lin J, Trindade MC, et al. Time-dependent effects of intermittent hydrostatic pressure on articular chondrocyte type II collagen and aggrecan mRNA expression. J Rehabil Res Dev. 2000;37: 153-161.[28] Fan WM, Cai J. Zhonghua Shiyan Waike. 2006;23(8): 977-979.范卫明, 蔡俊. 周期性压力对组织工程软骨的影响及其作用机制[J]. 中华实验外科, 2006, 23(8): 977-979.[29] Lv CW, Hu YY, Cui YM, et al. Shengwu Yixue Gongcheng yu Linchuang. 2008;12(4): 271-274.吕昌伟, 胡蕴玉, 崔玉明, 等. 三维立体空间动态培养及骨髓间充质干细胞软骨向分化的研究[J]. 生物医学工程与临床, 2008, 12(4): 271-274.[30] Hegewald AA, Ringe J, Bartel J, et al. Hyaluronic acid and autologous synovial fluid induce chondrogenic differentiation of equine mesenchymal stem cells: a preliminary study. Tissue Cell. 2004;36: 431-438. |