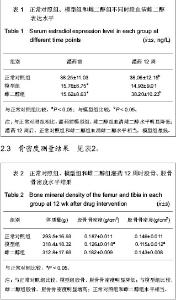
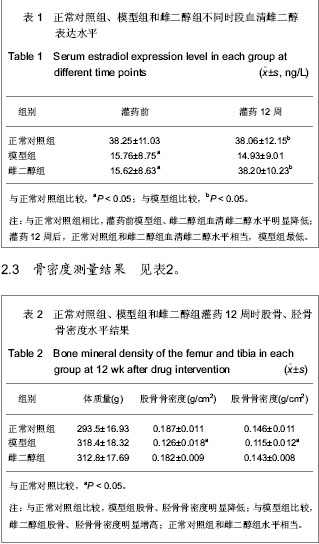
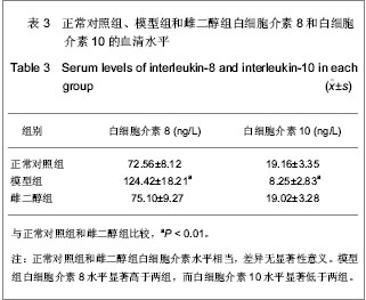
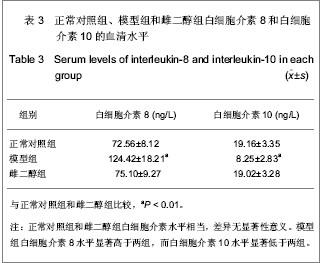
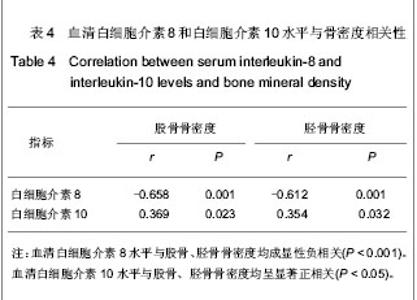
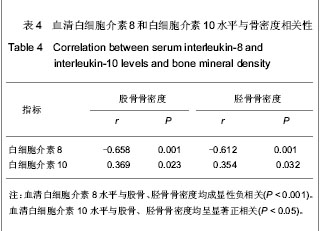
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (24): 4394-4400.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.24.004
Previous Articles Next Articles
Estrogen effects on serum interleukin-8 and interleukin-10 expression in ovariectomized rats with osteoporosis
Lu Shou-ming1, Lu Shou-liang2, Sun Tian-wei3, Zhang Hang2, Wang Qi-ming2
- 1 Xian County People’s Hospital, Cangzhou 062250, Hebei Province, China
2 Tianjin Medical University, Tianjin 300070, China
3 Department of Orthopedics, Tianjin People’s Hospital, Tianjin 300121, China
-
Received:2012-10-05Revised:2012-12-09Online:2013-06-11Published:2013-06-11 -
Contact:Sun Tian-wei, M.D., Master’s supervisor, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Tianjin People’s Hospital, Tianjin 300121, China billsuntw@163.com -
About author:Lu Shou-ming, Xian County People’s Hospital, Cangzhou 062250, Hebei Province, China caoerqingqing2009@163.com -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Tianjin, No. 12JCYBJC16800*
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lu Shou-ming, Lu Shou-liang, Sun Tian-wei, Zhang Hang, Wang Qi-ming. Estrogen effects on serum interleukin-8 and interleukin-10 expression in ovariectomized rats with osteoporosis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(24): 4394-4400.
share this article
| [1] Ding C, Parameswaran V, Udayan R,et al. Circulating levels of inflammatory markers predict change in bone mineral density and resorption in older adults: a longitudinal study. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2008;93(5):1952-1958.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18285417[2] Magaña JJ, Gómez R, Cisneros B,et al. Association of interleukin-6 gene polymorphisms with bone mineral density in Mexican women. Arch Med Res, 2008;39(6): 618-624.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18662595[3] Pino AM, Ríos S, Astudillo P,et al. Concentration of adipogenic and proinflammatory cytokines in the bone marrow supernatant fluid of osteoporotic women. J Bone Miner Res.2010;25(3):492-498.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19653807[4] Dieli-Conwright CM, Spektor TM, Rice JC,et al. Hormone therapy attenuates exercise-induced skeletal muscle damage in postmenopausal women. J Appl Physiol.2009;107(3): 853-858.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19574506[5] Wang Y, Li LZ, Zhang YL, et al. LC, a novel estrone-rhein hybrid compound, concurrently stimulates osteoprotegerin and inhibits receptor activator of NF-κB ligand (RANKL) and interleukin-6 production by human osteoblastic cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2011;337(1-2):43-51. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21291955[6] Iacovino JR.Mortality outcomes after osteoporotic fractures in men and women.J Insur Med. 2001;33(4):316-320.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11877911[7] Niu T,Rosen CJ.The insulin-like growth factor-I gene and osteoporosis:a critical appraisal. Gene. 2005;361:38-56.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16183214[8] Ali Gur, Aziz denli, Demzi Cexik, et al.The effects of Alendronate and calcitonin on cytokines in postmenopausal osteporosis:A 6-month randomized and controlled study.Yonsei Med J.2003;44(1): 99-109.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12619182[9] Williams LM, Sarma U, Willets K, et al. Expression of constitutively active STAT3 can replicate the cytokine suppressive activity of interleukin-10 in human primary macrophages. J Biol Chem.2007;282:6965-6975.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/17194701[10] Zupan J, Komadina R, Marc J. The relationship between osteoclastogenic and anti-osteoclastogenic pro-inflammatory cytokines differs in human osteoporotic and osteoarthritic bone tissues. J Biomed Sci. 2012;19(1):28.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22380539[11] Inada M, Miyaura C. Cytokines in bone diseases. Cytokine and postmenopausal osteoporosis. Clin Calcium. 2010;20 (10):1467-1472.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23055015[12] Ralston SH. Analysis of gene expression in bone biopsies by polymerase chain reaction:evidence fern hanced eytokine expression in postmenopausal osteoporosis. J Bone Miner Res.1994;9:883-885.:http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8079663[13] Gür A, Denli A, Cevik R,et al. The effects of alendronate and calcitonin on cytokines in postmenopausal osteoporosis: a 6-month randomized and controlled study. Yonsei Med J. 2003; 44:99-109.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12619182[14] Liang JX, Chen G, Lin LX, et al. Zhonghua Guzhi Shusong he Gukuangyan Jibing Zazhi. 2011;4(1):32-35.梁继兴,陈刚,林丽香,等. 绝经前、后女性骨代谢指标与白介素-1β受体拮抗剂的关系[J]. 中华骨质疏松和骨矿盐疾病杂志, 2011, 4(1):32-35.http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_zhgzsshgkyjbzz201101005.aspx[15] Li CG, Liu LH, Tang WD, et al. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 2011;31(8):1320-1322.李彩格,刘丽华,唐蔚东,等. 血清瘦素和白介素-6水平与绝经期妇女骨代谢的关系[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2011,31(8):1320-1322.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZLXZ201108016.htm[16] Sunyer T, Lewis J, Collin P, et al. Estrogen's bone-protective effects may involve differential IL-1 receptor regulation in human osteoclast-like cells. J Clin Invest.1999;103(10): 1409-1418.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10330423[17] Ajay K Malik, Sophia Khaldoyanidi, Dominick L Auci, et al.5-Androstene-3β, 7β,17β-triol (β-AET) Slows Thermal Injury Induced Osteopenia in Mice: Relation to Aging and Osteoporosis.Plos One. 2010;5(10):e13566.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21042414[18] Cvoro A, Yuan C, Paruthiyil S, et al. Cross talk between glucocorticoid and estrogen receptors occurs at a subset of proinflammatory genes. J Immunol. 2011;186(7):4354-4360.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21357268[19] Lovibond AC, Haque SJ, Chambers TJ, et al. TGF-beta-induced SOCS3 expression augments TNF-alpha-induced osteoclast formation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2003;309(4):762-767.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/13679037[20] Hong MH, Williams H, Jin CH, et al. The inhibitory effect of interleukin-10 on mouse osteoclast formation involves novel tyrosine-phosphorylated proteins. J Bone Miner Res. 2000; 15(5):911-918.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10804021[21] Owens JM, Gallagher AC, Chambers TJ. IL-10 modulates formation of osteoclasts in murine hemopoietic cultures. J Immunol. 1996;157(2):936-940.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8752948[22] Percegoni N, Ferreira AC, Rodrigues CF, et al. Profile of serum IL-1beta and IL-10 shortly after ovariectomy and estradiol replacement in rats. Horm Metab Res. 2009; 41(1):50-54.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18841529[23] Aggarwal R, Lu J, Kanji S, et al. Human umbilical cord blood-derived CD34+ cells reverse osteoporosis in NOD/SCID mice by altering osteoblastic and osteoclastic activities. PLoS One. 2012;7(6):e39365.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22724005[24] Gür A, Denli A, Nas K, et al. Possible pathogenetic role of new cytokines in postmenopausal osteoporosis and changes during calcitonin plus calcium therapy. Rheumatol Int. 2002; 22(5):194-198.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12215865[25] Chen HY, Chen WC, Hsu CM, et al. Tumor necrosis factor alpha, CYP 17, urokinase, and interleukin 10 gene polymorphisms in postmenopausal women: correlation to bone mineral density and susceptibility to osteoporosis. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol. 2005;122(1):73-78.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15927351[26] Fan L, Lin H. Zhongguo Guzhi Susong Zazhi. 2011;17(5): 435-439. 范璐,林华.不同生理时期雌激素对骨量的影响[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2011,17(5):435-439.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZGZS201105019.htm[27] Shao BY, Yu Y, Fu X, et al. Zhongguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2013;29(3):515-520.邵秉一,于洋,付欣,等. 雌激素缺乏导致的骨质疏松发病过程中骨髓间充质干细胞FasL表达降低对CD4+ T淋巴细胞凋亡的影响[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2013,29(3):515-520.http://www.cqvip.com/QK/92208X/201303/45247598.html[28] Song JJ, Luo ZJ, Liu J, et al. Zhongguo Gu yu Guanjie Zazhi. 2013;11(2):84-89.宋佳峻,罗卓荆,刘建, 等. 糖皮质激素与卵巢摘除后对大鼠骨量及骨代谢影响的对比研究[J]. 中国骨与关节杂志,2013, 11(2): 84-89.http://d.wanfangdata.com.cn/Periodical_zggzlzz201302008.aspx[29] Luo CY, Wang L, Sun C, et al. Estrogen enhances the functions of CD4(+)CD25(+)Foxp3(+) regulatory T cells that suppress osteoclast differentiation and bone resorption in vitro. Cell Mol Immunol. 2011;8(1):50-58.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/21200384[30] Reich MS,Jarvis JP,Silva MJ,et al.Genetic relationships between obesity and osteoporosis in LGXSM recombinant inbred mice.Genet Res.2008;90(4):433-434.http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/19061533[31] Liu D, Yao S, Wise GE. Effect of interleukin-10 on gene expression of osteoclastogenic regulatory molecules in the rat dental follicle. Eur J Oral Sci. 2006;114(1):42-49. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16460340[32] Zheng Q, Liang N. Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 2012;32(17): 3651-3653.郑青,梁宁. 老年性骨质疏松患者血清细胞因子水平与OPG/RANKL/RANK轴的相关性[J]. 中国老年学杂志,2012, 32(17): 3651-3653.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZLXZ201217016.htm[33] Sun Y, Yang L, Lv ZP, et al. Zhonguo Bingli Shengli Zazhi. 2011;27(4):755-758.孙影,杨丽,吕辰鹏,等. 骨碎补总黄酮对去卵巢骨质疏松模型大鼠血清中瘦素、白细胞介素6、前列腺素E_2及骨组织中β_2-肾上腺素受体的影响[J]. 中国病理生理杂志,2011,27(4): 755-758.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-ZBLS201104034.htm[34] Liu XH,Kinchenbaum A,Yao S,et al.Cross-talk between the interleu-kin-6 and prostaglandin E(2)signaling system results in enhancement ofosteoclastogenesis through effects on the osteoprotegerin/receptor activatorof nuclear factor-κB(RANK) ligand RANK system. Endocrinology. 2005;146(8):1991-1998. http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/15618359[35] Wang XL, Zhang Y, Yu WH. Linchuang Huicui. 2007;22(4): 286-287.王秀玲,张颖,于文浩. 糖骨康对糖尿病骨质疏松患者血清骨钙素、肿瘤坏死因子α、白细胞介素6含量的影响[J]. 临床荟萃, 2007,22(4):286-287.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-LCFC200704036.htm[36] LI ZW, Zhang MF, Zhao FY. Zhongguo Guzhi Shusong Zazhi. 2005;11(4):418-422.李忠武,章明放,赵凤云. 白细胞介素-1、-6mRNA在去势大鼠骨组织中的表达及其意义[J]. 中国骨质疏松杂志,2005,11(4): 418-422.http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-LCFC200704036.htm |
| [1] | Ren Rong, Li Ling-wei, Guo Qi-fa. Feasibility of implantation of a cemented femoral stem in the treatment of osteoporotic femoral neck fracture in elderly patients: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(48): 7261-7266. |
| [2] | Zhang Yan, Yang Qiu-ping, Zhao Yan, Zhao Yu-mei, Tan Hong, Du Si-cheng. Establishing a rat model of type 2 diabetes: its bone metabolism level [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(40): 6041-6047. |
| [3] | Wei Jun-qiang, Liu Li-rui, Wang Xin-yu, Yan Shi, Jin Yu, Feng Zhen. Proximal femoral nail antirotation fixation for osteoporotic intertrochanteric fracture in the elderly: characteristics of deep venous thrombosis of lower extremity [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5224-5230. |
| [4] | Zhang Yi-long, Ren Lei, Sun Zhi-jie, Wang Ya-hui, Sun He. New vertebral compression fractures after vertebroplasty: association with osteoporosis and spinal sagittal imbalances [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(35): 5263-5269. |
| [5] | Wu Jian-jun. Biocompatibility of Sextant minimally invasive pedicle screw fixation for osteoporotic vertebral fractures in the elderly [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(31): 4603-1609. |
| [6] | Ning Xu, Zhuang Yong, Liu Miao, Zhang Hao, Huang Ming-zhi. Biomechanical properties of lower anterior vertebral pedicle screw system and its effects on osteoporotic vertebral stability [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(31): 4665-4670. |
| [7] | Liu Yang, Liu Dan, Xiao Yun-xiang, Chen Hai-dan, Zhao Hong-wei. Biomechanical properties of a novel pourable cement pedicle screw and its application to osteoporotic lumbar degeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(31): 4671-4676. |
| [8] | Yu Hai-ming, Li Yi-zhong, Yao Xue-dong, Lin Jin-kuang, Pan Yuan-cheng, Zhuang Hua-feng,Wang Pei-wen. Percutaneous vertebroplasty or percutaneous kyphoplasty for Kummell’s disease with vertebral posterior wall collapse: how to treat individually? [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(26): 3856-3862. |
| [9] | Ren Zhi-shuai, Cheng Zhao-jun, Sun He-jun, Sun Zhen-hui, Cui Zi-jian, Zhang Li-long, Lin Yong-zhi, Zhang Ren-zan, Peng Bing, Zhang Xue-li. Osteoporosis-related factors in patients with knee osteoarthritis before total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2016, 20(22): 3212-3218. |
| [10] | Qiu Xiao-feng, Liu Xue-mei. Fiber post versus metal post in repairing the maxillary premolars [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(8): 1245-1249. |
| [11] | Liang Hai-bo, Su Wei, Luo Shi-xing. Relationship of serum estradiol levels with age and lesion severity in women with knee osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(46): 7533-7537. |
| [12] | Huang Cheng-long, Xiao Jin-gang. Osteogenic differentiation of adipose-derived stem cells on a composite scaffold in the repair of osteoporotic bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(41): 6696-6702. |
| [13] | Liang Jing, Zhou Qi, Wei Li, Hu Fang-qiong, Wang Jun. Specific gene expression of osteoclasts under different oxygen tension [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(29): 4695-4700. |
| [14] | Fang Chao, Xie Jia-bing, Xu Zhu-jun, Ding Guo-zheng, Yang Min, Wang Zheng-yu, Zhou Mao-sheng. Proximal femoral nail antirotation-Asia for trochanteric femoral fractures: the first choice for the elderly patients [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(22): 3469-3474. |
| [15] | Huang Xiao-nan. Percutaneous vertebroplasty for treatment of osteoporotic vertebral fractures: high-viscosity versus low-viscosity bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2014, 18(16): 2461-2467. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||