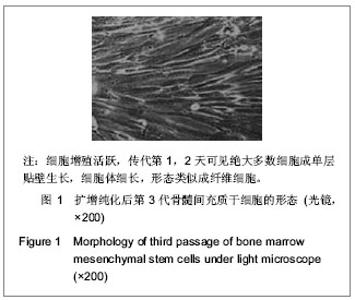
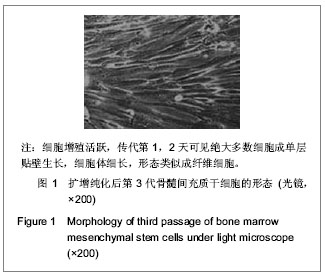
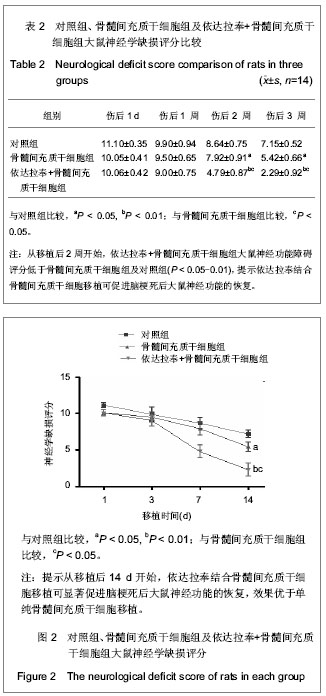
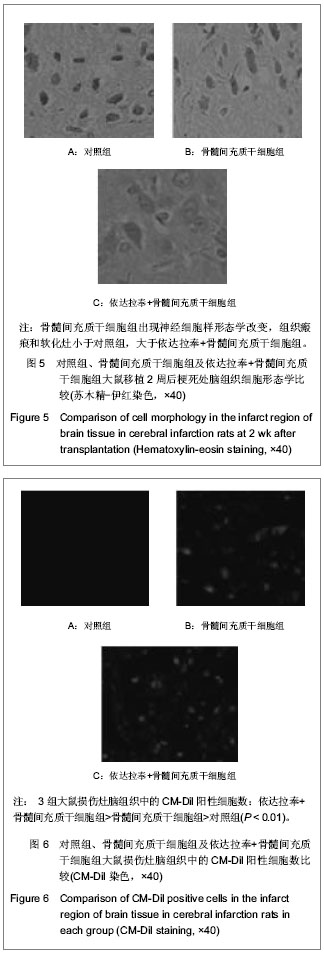
| [1] Liu J,Zhu H, Lin Y, et al. Human mesenchymal stem cell transplantation protects against cerebral ischemic injury and upregulates interleukin10 expression in Macaca fascicularis. Brain Res. 2010;1334:65-72.[2] Zhang TY. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(14):2557-2561.张婷勇.骨髓间充质干细胞移植并用单唾液酸神经节苷脂治疗大鼠脑梗死[J]. 中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(14): 2557-2561. [3] Zhang HL,Wu XM. Zhonghua Naoxueguanbing Zazhi. 2010; 4(4):40-45.张洪连,吴晓牧.骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗脑梗死及存在问题[J].中华脑血管病杂志,2010,4(4):300-307. [4] Wen J, Feng X. Patterns of Nogo-A, NgR, and RhoA expression in the brain tissues of rats with focal cerebral infarction. Transl Res. 2009;154(1):40-48. [5] Zhou GQ, Jin Y, Zhang P. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(45):8416-8420.周国庆,金怡,张鹏.沉默RhoA基因对骨髓间充质干细胞静脉移植治疗脑梗死大鼠的作用[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,14(45):8416-8420. [6] Peng Y, Zhang QM, You H, et al. Growth-associated protein 43 and neural cell adhesion molecule expression follow-ing bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cell transplantation in a rat model of ischemic brain injury. Neural Regen Res. 2010;5(13):975-980.[7] Wang XS, Li HF, Zhao Y, et al. Radix Astragali-induced differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells. Neural Regen Res. 2009;4(7):497-502. [8] Lei L, Zhou RX. Migration and differentiation of bone marrow-derived multipotent adult progenitor cells through tail vein injection in a rat model of cerebral ischemia. Neural Regen Res. 2009;4(2):118-122.[9] Chu K, Kim M, Park KI, et al. Human neural stem cells improve sensorimotor deficits in the adult rat brain with experimental focal ischemia. Brain Res. 2004;1016(2): 145-153. [10] Li CL ,Li XB,Dong RG,et al. Shenjing Jibing yu Jingshen Weisheng. 2011;11(5):478-481.李传玲,李晓宾,董瑞国,等.亚低温联合β-七叶皂甙钠对实验性脑出血后AQP4表达及脑水肿的影响[J].神经疾病与精神卫生, 2011,11(5):478-481. [11] Ji FT,Cao MH,Liang JJ,et al. Zhongguo Yaolixue Tongbao. 2011;27(4):524-527.纪风涛,曹铭辉,梁建军, 等.姜黄素预处理对大鼠脑缺血/再灌注损伤后AQP-4及脑水肿的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2011,27(4): 524-527. [12] Lu HB,Dong RG,Li XB,et al.Zuzhong yu Shenjing Jibing. 2011;18(6):348-352.鹿寒冰,董瑞国,李晓宾,等.大鼠实验性脑梗死后AQP4表达与MRI变化的相关性研究[J].卒中与神经疾病,2011,18(6): 348-352. [13] Wang SL, Wang YT, Jiang Y,et al.Zhongguo Shenjing Zaisheng Yanjiu. 2011;6(13):1005-1009.王士雷,王艳婷,江岩,等.预防性应用克罗卡林对大鼠脑缺血后AQP-4和血脑屏障通透性的影响[J].中国神经再生研究,2011, 6(13):1005-1009. [14] Li Y, Cui XN,Chen ZT, et al. Zhongguo Shiyan Fangjixue Zazhi. 2011;17(19):153-156.李妍,崔向宁,陈泽涛, 等.活血化瘀中药对脑出血大鼠脑组织 含水量及AQP4表达的影响[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2011,17(19): 153-156.[15] Ouyang XH, Jia J, Liu ZW. Sichuan Yixue. 2012;33(4): 676-678.欧阳锡华,贾军,刘政委.脑外伤患者AQP4的表达及其与临床预后的关系[J].四川医学,2012,33(4):676-678.[16] Yang ZX, Li ZZ. Ningxia Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2012;34(6): 600-603,540.杨振兴,李宗正.小剂量地塞米松对创伤性脑水肿AQP4的影响[J].宁夏医科大学学报,2012,34(6):600-603,540. [17] Shao BP, Yu HS, Wang JL. Dongwu Yixue Jinzhan. 2012; 33(1):87-91.邵宝平,余华晟,王建林.AQP9在脑疾病中的研究进展[J].动物医学进展,2012, 33(1):87-91. [18] Wang FX, Zhang J, Wang C, et al. Heilongjiang Yiyao Kexue. 2012;35(4):1-2.王复新,张洁,王辰,等.尼莫地平对早期脑出血大鼠AQP4 mRNA、MMP-9mRNA表达的影响[J].黑龙江医药科学,2012, 35(4):1-2. [19] Zhang B, Sun SQ, Gan SW, et al. Zhongguo Linchuang Jiepouxue Zazhi. 2012;30(3):329-332.张波,孙善全,甘胜伟,等.两种脑出血动物模型的AQP4表达与磁共振成像的比较研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2012,30(3): 329-332.[20] Wang HH, Lu H, Ding JY, et al. Zhongfeng yu Shenjing Jibing Zazhi. 2012;29(6):534-537.王海合,卢红,丁继岩,等.β-七叶皂苷钠对大鼠局灶性脑缺血再灌注后AQP4蛋白表达的影响[J].中风与神经疾病杂志,2012, 29(6):534-537.[21] Lin CH, Zheng WL, Yang J, et al. Zhongguo Yiyao Zhinan. 2012;10(15):441-442.林重辉,郑文玲,杨军,等.乌司他丁对大鼠缺血性脑水肿脑组织AQP4表达的影响[J].中国医药指南,2012,10(15):441-442.[22] Cui XN, Yin L, Wang YL. Zhongguo Kangfu Lilun yu Shijian. 2005;11(9):719-721.崔向宁,尹岭,王玉来.水通道蛋白4在大鼠创伤性脑水肿中的作用机制[J].中国康复理论与实践,2005,11(9):719-721.[23] Laing RJ, Jakubowski J, Laing RW. Middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Which method works best?Stroke. 1993;24(2):294-297.[24] Zhao XM, Liu YG. Xinxiang Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2012;29(8): 571-574.赵小妹,刘永刚.骨髓间充质干细胞与上清液治疗大鼠脑梗死的疗效[J].新乡医学院学报,2012,29(8):571-574.[25] Li Y, Chen J, Chen XG, et al. Human marrow stromal cell therapyfor troke in rat: Neurotrophins and functional recovery. Neurology.2002;59(4):514-523.[26] Tan H, He XY, Li XG. Zhongguo Yaofang. 2007;18(29): 2296-2297.谭华,何晓英,李小刚.依达拉奉治疗急性脑出血的临床疗效及对自由基含量的影响[J].中国药房,2007,18(29):2296-2297. [27] Liu XD, Zhang LJ, Zhao LJ. Sichuan Yixue. 2012;33(3): 431-433.刘信东,张利娟,赵丽君.依达拉奉治疗大面积脑梗死的临床疗效观察[J].四川医学,2012,33(3):431-433.[28] Zhang M, Zhang Y, Lv H, et al. Zhongguo Yiyuan Yongyao Pingjia yu Fenxi. 2012;12(3):249-251.张敏,张月,吕辉,等.依达拉奉注射液联合苦碟子注射液治疗急性脑梗死的疗效观察[J].中国医院用药评价与分析,2012,12(3): 249-251.[29] Ye GL. Zhongguo Yiyuan Yongyao Pingjia yu Fenxi. 2010; 10(4):335-336.叶冠龙.低分子肝素钙与依达拉奉联合治疗对进展性脑梗死的疗效及血清一氧化氮的影响[J].中国医院用药评价与分析, 2010,10(4):335-336.[30] Zhao B, Liu B, Zhang YQ. Tianjian Yiyao. 2012;40(5):483-485.赵彬,刘斌,张玉芹.依达拉奉对脑出血大鼠血肿周围组织Caspase-3和Pdcd-5蛋白表达的影响[J].天津医药,2012, 40(5): 483-485.[31] Wu QY, Xu S,Ding XS. Xiandai Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi. 2011; 20(10):1185-1188.吴秋义,徐庶,丁新生.依达拉奉联合奥扎格雷钠对大鼠缺血再灌注损伤后的脑保护作用[J].现代中西医结合杂志,2011,20(10): 1185-1188. [32] Kim SS, Yoo SW, Park TS, et al. Neural induction withneurogenin1 increases the therapeutic effects of mesenchymalstem cells in the ischemic brain. Stem Cells. 2008;26(9): 2217-2228. |