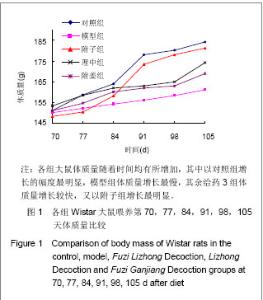
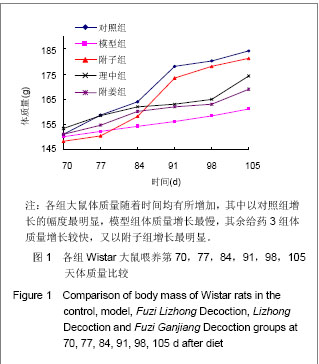
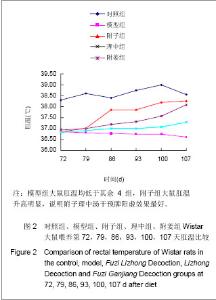
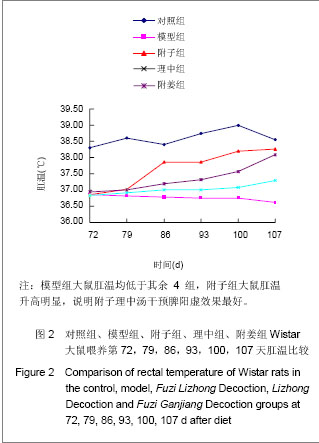
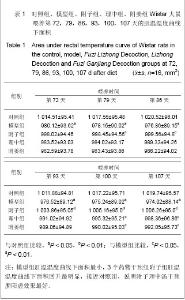
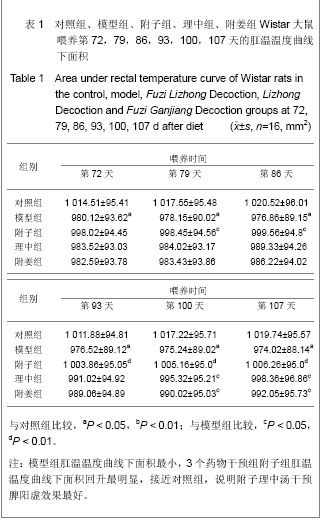
| [1] Xiang MR. Zhongguo Zhongyi Jichu Yixue Zazhi. 1999;5(4): 40-41.向茂然. 素体“脾阳虚” 人论治规律初探[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,1999,5(4):40-41.[2] Yang X,Yang WS,Wang Y,et al. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi. 2008;23(3):244-246.杨雪,杨文思,王勇,等.脾阳虚证中阳虚症状群的实验评价[J].中华中医药杂志,2008,23(3):244-246.[3] Yang X,Yang WS,Wang Y,et al. Zhongguo Zhongyi Jichu Yixue Zazhi. 2008;14(4):271-272.杨雪,杨文思,王勇,等.脾阳虚消化不良症状群客观评价的实验研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志,2008,14(4):271-272.[4] Smith RE, Horwitz BA.Brown fat and thermogenesis.Physiol Rev. 1969;49(2):330-425.[5] Nicholls DG, Locke RM.Thermogenic mechanisms in brown fat.Physiol Rev. 1984;64(1):1-64.[6] Verghese S, Maria CF, Mullaseri AS,et al. Aspergillus endocarditis presenting as femoral artery embolism. Mycoses. 2004;47(5-6):252-256.[7] Wan G. Shijie Kexue Jishu:Zhongyiyao Xiandaihua. 2009; 11(1):1-2.万钢.推动中医药现代化、国际化是中华民族的历史责任——在"南沙中药标准化与国际化研讨会"上的发言[J].世界科学技术:中医药现代化,2009,11(1):1-2.[8] Fu JH,Fu Y,Liu JX. Zhongguo Zhongyiyao Xinxi Zazhi. 2006; 13(1):52-54.付建华,付宇,刘建勋.“组分中药学”假说的构想[J].中国中医药信息杂志,2006,13(1):52-54.[9] Sun XG,Lv ZP. Zhongyao Yaoli yu Linchuang. 2011;27(3): 120-122.孙学刚,吕志平.方剂组学:一种基于方剂提取物质控的中医药转化医学研究策略[J].中药药理与临床,2011,27(3):120-122.[10] Tang HQ,Zhang WT,Wang Y,et al. Zhongguo Zhongyi Jichu Yixue Zazhi. 2010;16(12):1136-1137.唐汉庆,张文通,王勇,等. 脾阳虚证大鼠胃生长素改变的实验研究[J].中国中医基础医学杂志, 2010,16(12):1136-1137.[11] Zhang WT,Tang HQ,Lu AN,et al. Zhonghua Zhongyiyao Zazhi. 2011;26(3):490-494.张文通,唐汉庆,卢阿娜,等.附子理中丸对脾阳虚证大鼠骨骼肌肌球蛋白ATP酶活性的影响[J]. 中华中医药杂志,2011,26(3): 490-494.[12] Tang HQ,Zhang WT,Lu AN,et al. Zhongguo Yaoshi. 2010; 13(12):1691-1694.唐汉庆,张文通,卢阿娜,等.附子理中丸对脾阳虚证大鼠骨骼肌能荷影响的实验研究[J]. 中国药师,2010,13(12):1691-1694.[13] Zhang WT,Tang HQ,Lu AN,et al. Shijie Huaren Xiaohua Zazhi. 2010;18(35):3782-3786.张文通,唐汉庆,卢阿娜,等.附子理中丸对脾阳虚证大鼠肝脏能荷的下调机制[J]. 世界华人消化杂志,2010,18(35):3782-3786.[14] Wu YQ,Tang HQ,Wu CS,et al. Zhongguo Shiyan Fangjixue Zazhi. 2011;17(14):206-210.吴云起,唐汉庆,吴翠松,等.脾阳虚证大鼠棕色脂肪组织和解偶联蛋白1关联性的研究[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2011,17(14): 206-210.[15] Tang HQ,Wei Y. Hainan Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2010;16(3):285- 288.唐汉庆,韦祎. 脾阳虚模型小鼠产热障碍机制及附子理中汤的干预作用[J]. 海南医学院学报,2010,16(3):285-288.[16] Zhang WT,Tang HQ,Wang Y,et al. Zhongguo Yaoshi. 2010; 13(7): 918-921.张文通,唐汉庆,王勇,等.附子理中丸增强脾阳虚证大鼠适应性产热[J].中国药师, 2010,13(7):918-921.[17] Tang HQ. Liaoning Zhongyi Zazhi. 2010,37(suppl):248-249.唐汉庆. AQP2和AQP4在脾阳虚证动物中的表达及附子理中汤干预效应的生理机制[J]. 辽宁中医杂志,2010,37(增刊): 248-249.[18] Tang HQ. Liaoning Zhongyi Zazhi. 2010;37(10):1881-1883.唐汉庆.李东垣升脾阳诸法运用钩玄[J].辽宁中医杂志,2010, 37(10): 1881-1883.[19] Madden CJ, Morrison SF. Endogenous activation of spinal 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) receptors contributes to the thermoregulatory activation of brown adipose tissue. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2010;298(3):R776-783.[20] Zhao X, Wang Y, Yang S,et al. Underlying Mechanism of Aconitum Lizhong Acting on Experimental Hypothermia with Indigestion in Rats: Role of Ghrelin. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012;2012:542461. |