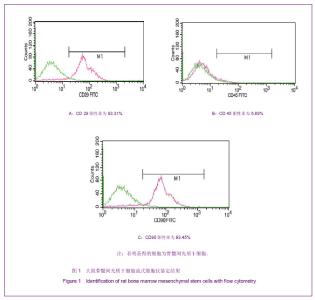
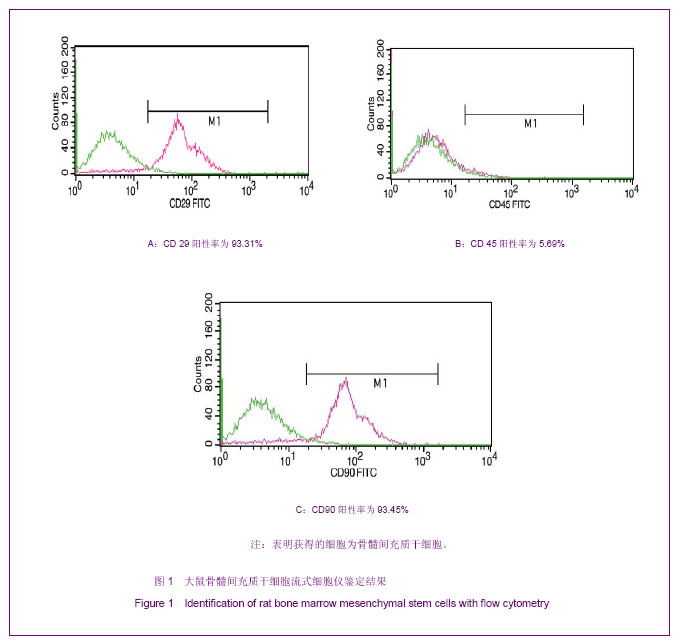
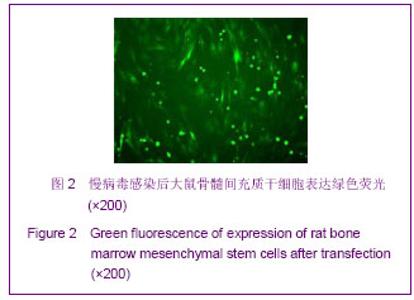
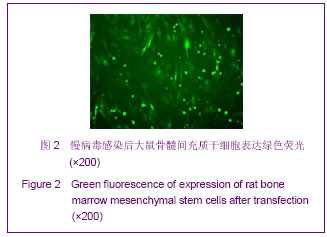
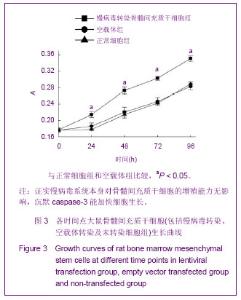
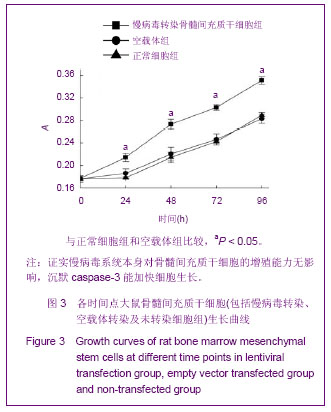
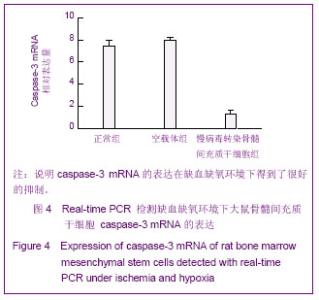
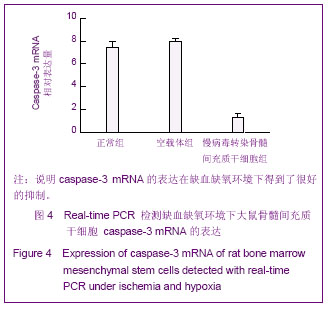
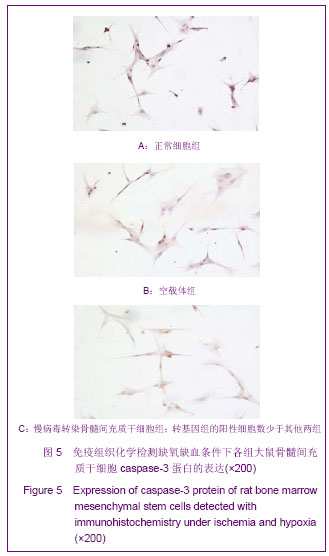
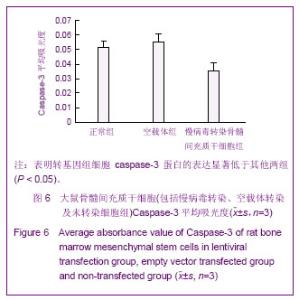
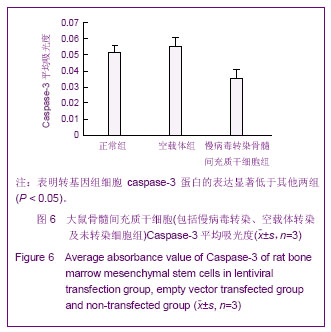
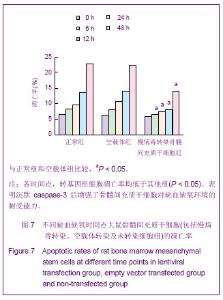
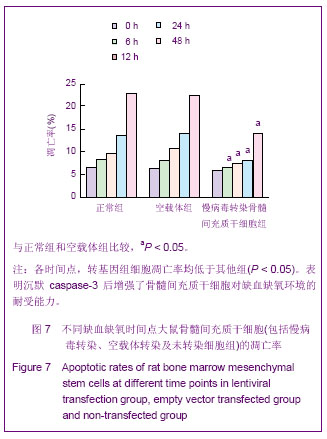
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2013, Vol. 17 ›› Issue (14): 2480-2487.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013.14.002
Previous Articles Next Articles
Silencing caspase-3 gene effects on the proliferation and apoptosis of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells
Liu Jia-liang1, Hua Ping1, Yang Song-ran2, Tao Jun1, Jiang Hui-qi1, Wang Meng1, Yang Yan-qi1
- 1 Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China
2 Department of Neurology, Guangzhou First Municipal People’s Hospital, Guangzhou 510180, Guangdong Province, China
-
Received:2012-09-14Revised:2012-11-19Online:2013-04-02Published:2013-04-02 -
Contact:Hua Ping, Doctor, Associate professor, Associate chief physician, Master’s supervisor, Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China huaping88@sina.com -
About author:Liu Jia-liang★, Studying for master’s degree, Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Sun Yat-sen Memorial Hospital, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou 510120, Guangdong Province, China jervis1986@sina.com -
Supported by:Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province, No. 7001619; the Science and Technology Planning Program of Guangdong Province, No. 2007B050200011
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liu Jia-liang, Hua Ping, Yang Song-ran, Tao Jun, Jiang Hui-qi, Wang Meng, Yang Yan-qi. Silencing caspase-3 gene effects on the proliferation and apoptosis of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2013, 17(14): 2480-2487.
share this article
| [1] Hu X, Yu SP, Fraser JL, et al.Transplantation of hypoxia-preconditioned mesenchymal stem cells improves infarcted heart function via enhanced survival of implanted cells and angiogenesis.J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg.2008; 135(4): 799-808.[2] Jameel MN, Li Q, Mansoor A, et al. Long-term functional improvement and gene expression changes after bone marrow-derived multipotent progenitor cell transplantation in myocardial infarction. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.2010; 298(5):H1348-H1356.[3] Mardikar HM, Deshpande NV, Admane P. Recent advances in the management of acute myocardial infarction. J Assoc Physicians India.2011;59 Suppl:31-36.[4] Beitnes JO, Hopp E, Lunde K, et al. Long-term results after intracoronary injection of autologous mononuclear bone marrow cells in acute myocardial infarction: the ASTAMI randomised, controlled study Heart.2009; 95(24):1983-1989.[5] Yue YY,Zhang Y,Zhang YQ.Zhongguo Yiliao Qianyan.2011; (6): 25-26.岳原亦,张扬,张一奇. Caspase家族与细胞凋亡[J].中国医疗前沿,2011, (6):25-26.[6] Deng W,Chen QW,Wang L,et al.Jichu Yixue yu Linchuang. 2012;32(4):390-395.邓玮,陈庆伟,王丽,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对缺血心肌的血管新生及增殖-凋亡的影响[J].基础医学与临床,2012,32(4):390-395. [7] Li WY,Wang Y,Sun P,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Huaxue yu Xibao Huaxue Zazhi. 2011;20(6):554-558.李文媛,王莹,孙平,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠脑缺血再灌注损伤Livin和Caspase-3表达的影响[J].中国组织化学与细胞化学杂志,2011,20(6):554-558. [8] Li MX,Li Z,Zou LH,et al.Zhongguo Laonianxue Zazhi. 2011; 31(16):3117-3119.李梅笑,李卓,邹立华,等.Caspase-3在骨髓间充质干细胞回输脑缺血再灌注模型大鼠脑组织中的表达[J].中国老年学杂志,2011, 31(16):3117-3119. [9] Li DJ,Jia QZ,Chen YB,et al.Zhongguo Shiyan Zhenduanxue. 2011;15(7):1044-1047.李东君,贾全章,陈玉丙,等.骨髓间充质干细胞抑制Wistar大鼠脊髓损伤区神经元凋亡的实验研究[J].中国实验诊断学,2011, 15(7): 1044-1047. [10] Tan X,Wang DB,Wei H,et al.Shiyong Linchuang Yiyao Zazhi. 2010, 14 (11):1-4.谭晓,王迪斌,卫慧,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对大鼠急性心肌梗死后心功能及bcl-2和caspase-3 mRNA表达水平的影响[J].实用临床医药杂志,2010, 14 (11):1-4.[11] Liang ZY,Qin SY,Jiang HH,et al.Chongqing Yixue. 2010; 39(20):2721-2723.梁梓宇,覃山羽,姜海行,等.骨髓间充质干细胞诱导肝纤维化大鼠肝星状细胞凋亡和Caspase-3表达[J].重庆医学,2010, 39(20): 2721-2723. [12] Li JS,Liu JX,Tian YS,et al.Zhongxiyi Jiehe Xuebao. 2009;7(9): 860-867.李建生,刘敬霞,田玉收,等.脑脉通联合骨髓干细胞动员对脑缺血大鼠神经细胞凋亡相关蛋白Fas、FasL及caspase-3表达的影响[J].中西医结合学报,2009,7(9): 860-867. [13] Wang ZL,Fan HJ,Pang CJ,et al.Zhongguo Yike Daxue Xuebao. 2009;38(11): 834-837.王宗立,范红杰,庞超健,等.骨髓间充质干细胞移植对缺血再灌注大鼠脑神经细胞凋亡及survivin、caspase-3蛋白表达的影响[J].中国医科大学学报,2009,38(11): 834-837. [14] Zheng HH,Feng NP,Liang SL,et al.Zhongguo Bijiao Yixue Zazhi. 2009;19(4): 27-30,51.郑海洪,冯念苹,梁松岚,等.骨髓间质干细胞移植对大鼠脑缺血再灌注凋亡蛋白Caspase-3的影响[J].中国比较医学杂志,2009, 19(4): 27-30,51. [15] Li J,Wang W,Wang ZR.Zhongyiyao Dabao. 2007;13(2): 9-11.李静,王文,王宗仁.芪丹通脉片联合骨髓间充质干细胞修复损伤内皮细胞Caspase-3、c-IPI-1和c-IPI-2的表达[J].中医药导报, 2007,13(2): 9-11. [16] Feng JJ,Yang SH,Sun L,et al.Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2006;14(11):849-851,866.冯建军,杨述华,孙立,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外诱导失巢凋亡过程中半胱氨酸蛋白酶-3的作用[J].中国矫形外科杂志,2006, 14(11):849-851,866.[17] Liu LB,Hua P,Yang SR,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu. 2012;16(19):3551-3555.刘立宝,华平,杨淞然,等. RNA干扰抑制骨髓间充质干细胞中caspase-3基因的表达[J]. 中国组织工程研究,2012,16(19): 3551-3555.[18] Caplan AI. Why are MSCs therapeutic? New data: new insight. J Pathol.2009;217(2):318-324.[19] Beitnes JO, Lunde K, Brinchmann JE, et al. Stem cells for cardiac repair in acute myocardial infarction. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther.2011;9(8):1015-1025.[20] Hamedi-Asl P, Halabian R, Bahmani P, et al. Adenovirus- mediated expression of the HO-1 protein within MSCs decreased cytotoxicity and inhibited apoptosis induced by oxidative stresses. Cell Stress Chaperones.2012; 17(2): 181-190.[21] Pereira MJ, Carvalho IF, Karp JM, et al. Sensing the cardiac environment: exploiting cues for regeneration. J Cardiovasc Transl Res.2011;4(5):616-630.[22] Lu HH, Li YF, Sheng ZQ, et al. Preconditioning of stem cells for the treatment of myocardial infarction. Chin Med J (Engl). 2012;125(2):378-384.[23] Zhang H, Hou JF, Shen Y, et al. Low level laser irradiation precondition to create friendly milieu of infarcted myocardium and enhance early survival of transplanted bone marrow cells. J Cell Mol Med.2010;14(7):1975-1987.[24] Cho YH, Cha MJ, Song BW, et al. Enhancement of MSC adhesion and therapeutic efficiency in ischemic heart using lentivirus delivery with periostin. Biomaterials.2012;33(5): 1376-1385.[25] Afanasiev SA, Falaleeva LP, Rebrova TU, et al. Effect of stress-proteins on survival of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells after intramyocardial transplantation against the background of postinfarction heart remodeling. Bull Exp Biol Med.2008;146(1):111-115.[26] Haider KH, Ashraf M. Preconditioning approach in stem cell therapy for the treatment of infarcted heart. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci.2012;111:323-356.[27] Li W, Ma N, Ong LL, et al. Bcl-2 engineered MSCs inhibited apoptosis and improved heart function. Stem Cells.2007; 25(8):2118-2127.[28] Yin Q,Jin P,Liu X,et al.SDF-1alpha inhibits hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells through PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways. Mol Biol Rep.2011;38(1):9-16.[29] Yang YJ, Qian HY, Huang J, et al. Atorvastatin treatment improves survival and effects of implanted mesenchymal stem cells in post-infarct swine hearts. Eur Heart J.2008; 29(12):1578-1590.[30] Burnett JC, Rossi JJ. RNA-based therapeutics: current progress and future prospects. Chem Biol.2012;19(1):60-71.[31] Yu XJ,Shao XM,Fang JQ.Shiyong Zhongyiyao Zazhi. 2011; 27(1):71-72.喻晓静,邵晓梅,方剑乔.细胞凋亡信号传导通路研究进展[J]. 实用中医药杂志,2011,27(1):71-72. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [3] | Ji Zhixiang, Lan Changgong. Polymorphism of urate transporter in gout and its correlation with gout treatment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1290-1298. |
| [4] | Li Jiacheng, Liang Xuezhen, Liu Jinbao, Xu Bo, Li Gang. Differential mRNA expression profile and competitive endogenous RNA regulatory network in osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1212-1217. |
| [5] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [6] | Tan Jingyu, Liu Haiwen. Genome-wide identification, classification and phylogenetic analysis of Fasciclin gene family for osteoblast specific factor 2 [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1243-1248. |
| [7] | Zhang Xiumei, Zhai Yunkai, Zhao Jie, Zhao Meng. Research hotspots of organoid models in recent 10 years: a search in domestic and foreign databases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1249-1255. |
| [8] | Wang Zhengdong, Huang Na, Chen Jingxian, Zheng Zuobing, Hu Xinyu, Li Mei, Su Xiao, Su Xuesen, Yan Nan. Inhibitory effects of sodium butyrate on microglial activation and expression of inflammatory factors induced by fluorosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1075-1080. |
| [9] | Wang Xianyao, Guan Yalin, Liu Zhongshan. Strategies for improving the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the treatment of nonhealing wounds [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1081-1087. |
| [10] | Wan Ran, Shi Xu, Liu Jingsong, Wang Yansong. Research progress in the treatment of spinal cord injury with mesenchymal stem cell secretome [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1088-1095. |
| [11] | Liao Chengcheng, An Jiaxing, Tan Zhangxue, Wang Qian, Liu Jianguo. Therapeutic target and application prospects of oral squamous cell carcinoma stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1096-1103. |
| [12] | Xie Wenjia, Xia Tianjiao, Zhou Qingyun, Liu Yujia, Gu Xiaoping. Role of microglia-mediated neuronal injury in neurodegenerative diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1109-1115. |
| [13] | Li Shanshan, Guo Xiaoxiao, You Ran, Yang Xiufen, Zhao Lu, Chen Xi, Wang Yanling. Photoreceptor cell replacement therapy for retinal degeneration diseases [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1116-1121. |
| [14] | Jiao Hui, Zhang Yining, Song Yuqing, Lin Yu, Wang Xiuli. Advances in research and application of breast cancer organoids [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1122-1128. |
| [15] | Wang Shiqi, Zhang Jinsheng. Effects of Chinese medicine on proliferation, differentiation and aging of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells regulating ischemia-hypoxia microenvironment [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1129-1134. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||