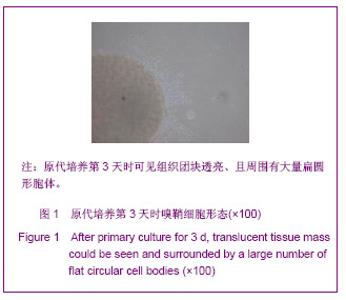
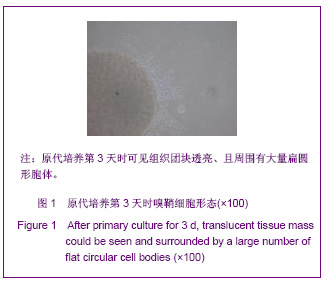
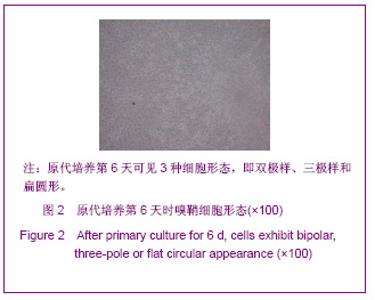
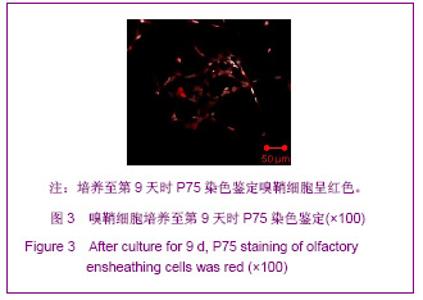
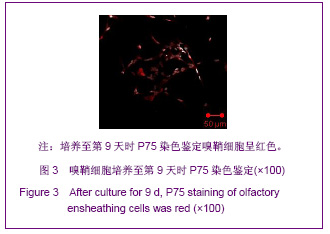
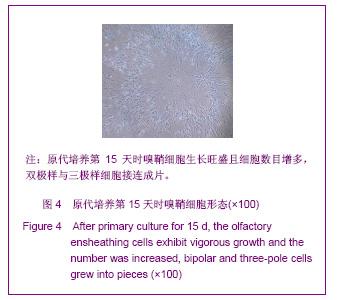
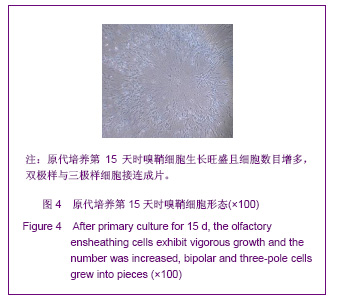
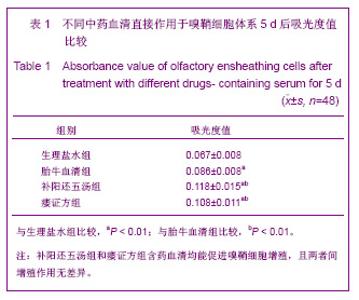
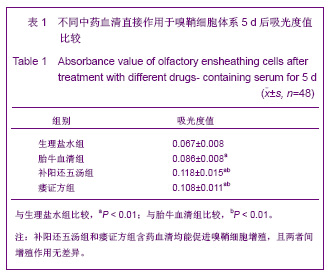
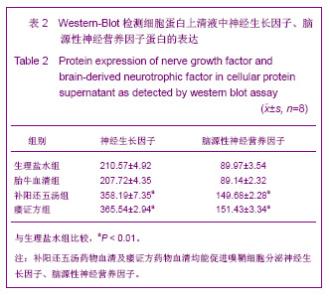
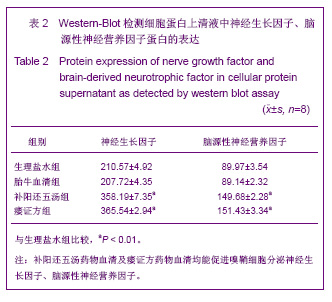
| [1] Xu M. Suzhou Univesity,2004:1-5. 徐明.大鼠嗅鞘细胞移植治疗脊髓损伤的实验研究[D].苏州:苏州大学,2004:1-5.[2] Barnett SC, Riddell JS. Olfactory ensheathing cell transplantation as a strategy for spinal cord repair--what can it achieve. Nat Clin Pract Neurol. 2007;3(3):152-161.[3] Chuah MI, Choi-Lundberg D, Weston S,et al. Olfactory ensheathing cells promote collateral axonal branching in the injured adult rat spinal cord. Exp Neurol. 2004;185(1):15-25.[4] Deumens R, Koopmans GC, Lemmens M,et al. Neurite outgrowth promoting effects of enriched and mixed OEC/ONF cultures. Neurosci Lett. 2006;397(1-2):20-24.[5] Au E, Richter MW, Vincent AJ,et al. SPARC from olfactory ensheathing cells stimulates Schwann cells to promote neurite outgrowth and enhances spinal cord repair.J Neurosci. 2007;27(27):7208-7221. [6] Li Y, Field PM, Raisman G. Regeneration of adult rat corticospinal axons induced by transplanted olfactory ensheathing cells. J Neurosci. 1998;18(24):10514-10524.[7] Santos-Silva A, Fairless R, Frame MC,et al. FGF/heparin differentially regulates Schwann cell and olfactory ensheathing cell interactions with astrocytes: a role in astrocytosis. J Neurosci. 2007;27(27):7154-7167.[8] van den Pol AN, Santarelli JG. Olfactory ensheathing cells: time lapse imaging of cellular interactions, axonal support, rapid morphologic shifts, and mitosis. J Comp Neurol. 2003; 458(2):175-194.[9] Zhi CS,Xie L. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2009;17(18): 1404-1406. 智春升,谢林.骨髓基质干细胞移植对大鼠脊髓损伤后BDNF与GAP-43基因表达的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009, 17(18): 1404-1406.[10] Zhang NS. Nanjing:Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine. 2010:15-16. 张农山.黄芪注射液对嗅鞘细胞增殖及分泌神经营养因子的影响[D].南京:南京中医药大学,2010:15-16.[11] Li YK. Shanghai:Shanghai Science & Technology Press. 2006:38-39. 李仪奎.中药药理实验方法学[M].2版.上海:上海科学技术出版社,2006:38-39.[12] He SL,Wang J,Wang JJ. Changsha:Hunan Science & Technology Press,2008:48-49. 贺石林,王健,王净净.中医科研设计与统计学[M].长沙:湖南科学技术出版社,2008:48-49.[13] Ma YH,Hu ZJ,Wang YJ,et al. Zhongyi Zhenggu. 2008;20(8): 1-3. 马迎辉,胡志俊,王拥军,等.痿症方对嗅鞘细胞增殖影响的药效学研究[J].中医正骨,2008,20(8):1-3.[14] Hu ZJ,Wang YJ,Li CG,et al. Zhongguo Zhongyi Gushangke Zazhi. 2005;13(3):10-13. 胡志俊,王拥军,李晨光,等.痉、痿证方对大鼠脊髓持续性压迫损伤局部NGF、BDNF的调节作用[J].中国中医骨伤科杂志,2005, 13(3):10-13.[15] Ma YH,Hu ZJ,Zhou CJ,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(47):9210-9213. 马迎辉,胡志俊,周重建,等.痿症方联合嗅鞘细胞移植对脊髓慢性压迫损伤后神经营养素3表达的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008,12(47):9210-9213.[16] Situ ZQ,Wu JZ. Xi’an:Xi’an World Publishing Corporation, 2007: 121-122. 司徒镇强,吴军正.细胞培养[M]. 西安:世界图书出版社西安公司, 2007:121-122.[17] Barnett SC, Roskams AJ. Olfactory ensheathing cells: isolation and culture from the neonatal olfactory bulb. Methods Mol Biol. 2008;438:85-94.[18] Chen CJ,He YS. Bengbu Yixueyuan Xuebao. 2000;25(3): 231-233. 陈昌杰,何蕴韶.神经生长因子家族[J].蚌埠医学院学报,2000, 25(3): 231-233.[19] Jin YL, Dong LY, Wu CQ,et al. Buyang Huanwu Decoction fraction protects against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury by attenuating the inflammatory response and cellular apoptosis. Neural Regen Res. 2013; 8(3): 197-207.[20] Chen A,Wang H,Wu XQ,et al. Shenjing Jiepouxue Zazhi. 2007; 23(6):587-590. 陈安,王慧,武校琼,等.补阳还五汤对大鼠脊髓损伤后红核脊髓束再生及功能修复的影响[J].神经解剖学杂志,2007,23(6):587- 590.[21] Chen An,Liao J,Xiong AJ,et al. Shijie Zhongxiyi Jiehe Zazhi. 2007;2(10):570-572. 陈安,廖君,熊艾君,等.补阳还五汤对脊髓损伤后胶质瘢痕及GFAP表达的影响[J].世界中西医结合杂志, 2007,2(10):570- 572.[22] Zhang JP,Lin AH,Li SG,et al. Guangzhou Zhongyiyao Daxue Xuebao, 2009;26(3):256-259. 张继平,林爱华,李蜀光,等.补阳还五汤对脊髓损伤大鼠血浆血小板活化因子含量的影响[J].广州中医药大学学报, 2009,26(3): 256-259.[23] Wang W,Xie J,Fang J,et al. Zhongguo Kangfu. 2005; 20(1):3-5. 王伟,谢杰,方坚,等.补阳还五汤对实验性脊髓损伤大鼠水通道蛋白-4表达的影响[J].中国康复, 2005, 20(1):3-5.[24] Levi-Montalcini R. The nerve growth factor 35 years later. Science. 1987;237(4819):1154-1162.[25] Oppenheim RW. Cell death during development of the nervous system. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1991;14:453-501.[26] Lessmann V, Gottmann K, Malcangio M. Neurotrophin secretion: current facts and future prospects. Prog Neurobiol. 2003;69(5):341-374.[27] Zhi CS,Xie L. Zhongguo Jiaoxing Waike Zazhi. 2009; 17(18): 1404-1406. 智春升,谢林.骨髓基质干细胞移植对大鼠脊髓损伤后BDNF与GAP-43基因表达的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2009, 17(18): 1404-1406.[28] Brunello N, Reynolds M, Wrathall JR,et al. Increased nerve growth factor receptor mRNA in contused rat spinal cord. Neurosci Lett. 1990;118(2):238-240.[29] Grill RJ, Blesch A, Tuszynski MH. Robust growth of chronically injured spinal cord axons induced by grafts of genetically modified NGF-secreting cells. Exp Neurol. 1997;148(2):444-452.[30] Ikeda O, Murakami M, Ino H,et al. Acute up-regulation of brain-derived neurotrophic factor expression resulting from experimentally induced injury in the rat spinal cord. Acta Neuropathol. 2001;102(3):239-245. |