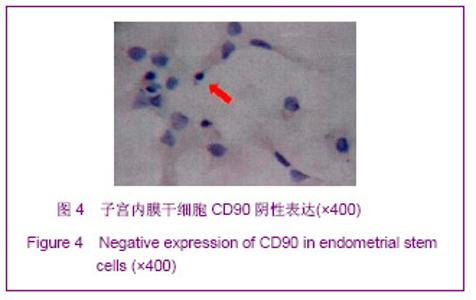
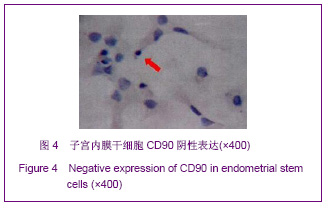
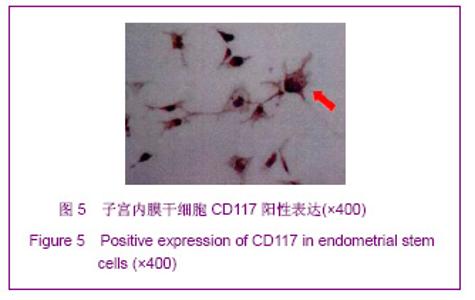
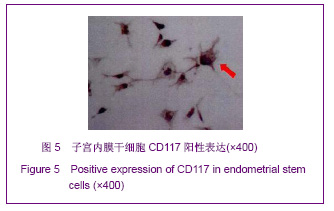
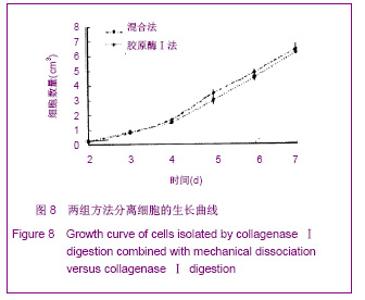
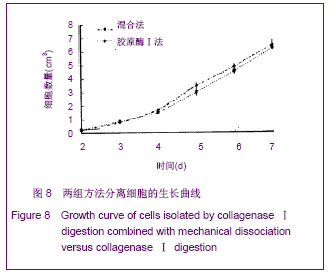
| [1] Prianishnikov VA.On the concept of stem cell and a model of functional-morphological structure of the endometrium. Contraception. 1978;18(3):213-223. [2] Chan RW, Gargett CE. Identification of label-retaining cells in mouse endometrium.Stem Cells. 2006;24(6):1529-1538.[3] Masuda H, Maruyama T, Hiratsu E,et al. Noninvasive and real-time assessment of reconstructed functional human endometrium in NOD/SCID/gamma c(null) immunodeficient mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(6):1925-1930.[4] Hong IS, Kim SH, Koong MK,et al. Roles of p38 and c-jun in the differentiation, proliferation and immortalization of normal human endometrial cells.Hum Reprod. 2004;19(10): 2192-2199.[5] Aghajanova L, Horcajadas JA, Esteban FJ,et al. The bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cell: potential progenitor of the endometrial stromal fibroblast. Biol Reprod. 2010;82(6):1076-1087.[6] Kato K, Takao T, Kuboyama A,et al. Endometrial cancer side-population cells show prominent migration and have a potential to differentiate into the mesenchymal cell lineage. Am J Pathol. 2010;176(1):381-392.[7] Meng X, Ichim TE, Zhong J, et al. Endometrial regenerative cells: a novel stem cell population. J Transl Med. 2007;5:57.[8] Aghajanova L, Horcajadas JA, Esteban FJ,et al. The bone marrow-derived human mesenchymal stem cell: potential progenitor of the endometrial stromal fibroblast. Biol Reprod. 2010;82(6):1076-1087.[9] Cho NH, Park YK, Kim YT,et al. Lifetime expression of stem cell markers in the uterine endometrium.Fertil Steril. 2004; 81(2):403-407.[10] Musina RA, Belyavski AV, Tarusova OV,et al. Endometrial mesenchymal stem cells isolated from the menstrual blood. Bull Exp Biol Med. 2008;145(4):539-543.[11] Chan RW, Schwab KE, Gargett CE. Clonogenicity of human endometrial epithelial and stromal cells. Biol Reprod. 2004; 70(6):1738-1750.[12] Zemel'ko VI, Grinchuk TM, Domnina AP,et al. Multipotent mesenchymal stem cells of desquamated endometrium: isolation, characterization and use as feeder layer for maintenance of human embryonic stem cell lines.Tsitologiia. 2011;53(12):919-929. [13] Cervelló I, Mas A, Gil-Sanchis C,et al. Reconstruction of endometrium from human endometrial side population cell lines. PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e21221.[14] Taylor HS. Endometrial cells derived from donor stem cells in bone marrow transplant recipients. JAMA. 2004;292(1):81-85.[15] Gargett CE, Schwab KE, Zillwood RM,et al. Isolation and culture of epithelial progenitors and mesenchymal stem cells from human endometrium. Biol Reprod. 2009;80(6):1136- 1145. [16] Kyurkchiev S, Shterev A, Dimitrov R. Assessment of presence and characteristics of multipotent stromal cells in human endometrium and decidua. Reprod Biomed Online. 2010;20(3):305-313. |