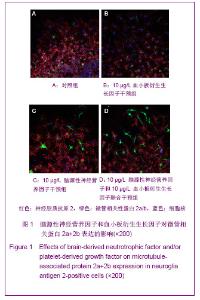
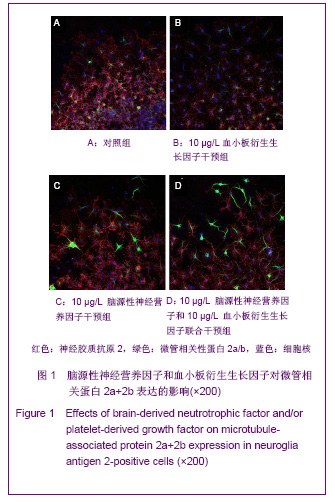
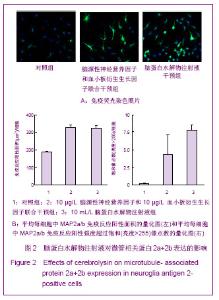
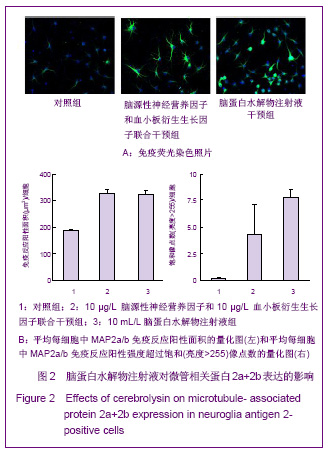
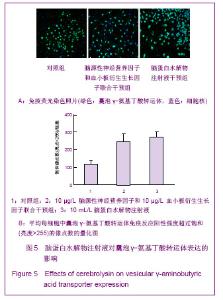
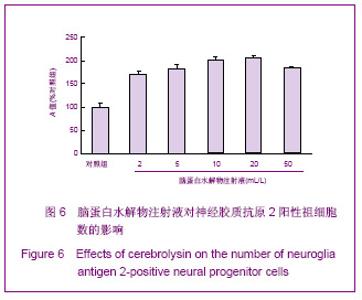
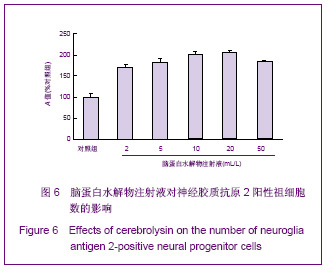
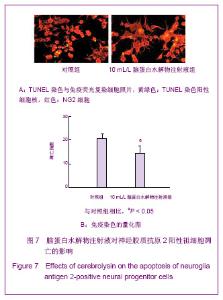
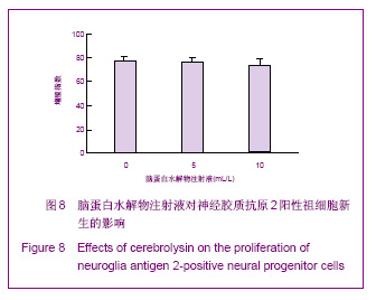
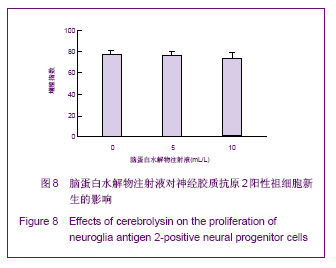
| [1] Belachew S, Chittajallu R, Aguirre AA,et al. Postnatal NG2 proteoglycan-expressing progenitor cells are intrinsically multipotent and generate functional neurons.J Cell Biol. 2003;161(1):169-186.[2] Nunes MC, Roy NS, Keyoung HM,et al.Identification and isolation of multipotential neural progenitor cells from the subcortical white matter of the adult human brain.Nat Med. 2003;9(4):439-447.[3] Lin SC, Huck JH, Roberts JD,et al. Climbing fiber innervation of NG2-expressing glia in the mammalian cerebellum.Neuron. 2005;46(5):773-785.[4] Levine JM, Reynolds R, Fawcett JW.The oligodendrocyte precursor cell in health and disease.Trends Neurosci. 2001; 24(1):39-47.[5] Wennström M, Hellsten J, Ekdahl CT,et al. Electroconvulsive seizures induce proliferation of NG2-expressing glial cells in adult rat hippocampus.Biol Psychiatry. 2003;54(10): 1015-1024.[6] Wennström M, Hellsten J, Tingström A. Electroconvulsive seizures induce proliferation of NG2-expressing glial cells in adult rat amygdala. Biol Psychiatry. 2004;55(5):464-471.[7] Gschanes A, Valousková V, Windisch M. Ameliorative influence of a nootropic drug on motor activity of rats after bilateral carotid artery occlusion. J Neural Transm. 1997; 104(11-12):1319-1327.[8] Tatebayashi Y, Lee MH, Li L,et al. The dentate gyrus neurogenesis: a therapeutic target for Alzheimer's disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2003;105(3):225-232.[9] Yu XJ,Li ZZ,Guo L,et al. Nao yu Shenjing Jibing Zazhi. 2009; 17(2):93-96. 于秀军,李震中,郭力,等.从成年大鼠中枢神经系统不同区域分离NG2蛋白聚糖阳性神经祖细胞[J].脑与神经疾病杂志,2009, 17(2): 93-96.[10] Buffo A, Vosko MR, Ertürk D,et al. Expression pattern of the transcription factor Olig2 in response to brain injuries: implications for neuronal repair.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(50):18183-18188.[11] Greenwood K, Butt AM.Evidence that perinatal and adult NG2-glia are not conventional oligodendrocyte progenitors and do not depend on axons for their survival.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2003;23(4):544-558.[12] Mohapel P, Frielingsdorf H, Häggblad J,et al. Platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF-BB) and brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) induce striatal neurogenesis in adult rats with 6-hydroxydopamine lesions. Neuroscience. 2005;132(3): 767-776.[13] Jacobs BL, van Praag H, Gage FH.Adult brain neurogenesis and psychiatry: a novel theory of depression.Mol Psychiatry. 2000;5(3):262-269.[14] Bogen IL, Boulland JL, Mariussen E,et al. Absence of synapsin I and II is accompanied by decreases in vesicular transport of specific neurotransmitters.J Neurochem. 2006; 96(5):1458-1466.[15] Lovell MA, Geiger H, Van Zant GE,et al. Isolation of neural precursor cells from Alzheimer's disease and aged control postmortem brain.Neurobiol Aging. 2006;27(7):909-917.[16] Sugaya K, Alvarez A, Marutle A,et al. Stem cell strategies for Alzheimer's disease therapy.Panminerva Med. 2006;48(2): 87-96.[17] Torrey EF, Barci BM, Webster MJ,et al. Neurochemical markers for schizophrenia, bipolar disorder, and major depression in postmortem brains.Biol Psychiatry. 2005; 57(3):252-260. [18] Stanley DP, Shetty AK.Aging in the rat hippocampus is associated with widespread reductions in the number of glutamate decarboxylase-67 positive interneurons but not interneuron degeneration.J Neurochem. 2004;89(1):204-216. |