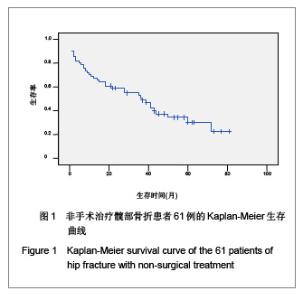
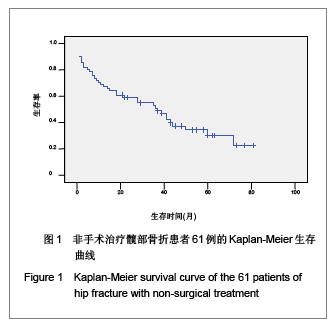
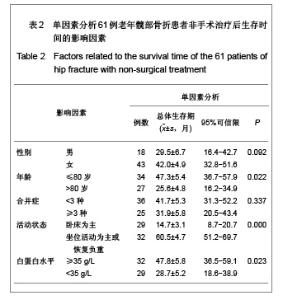
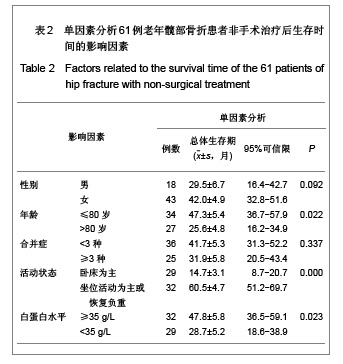
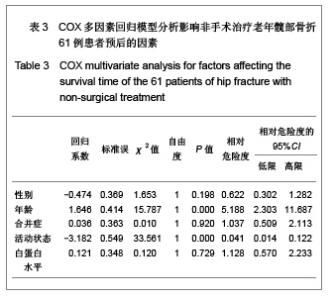
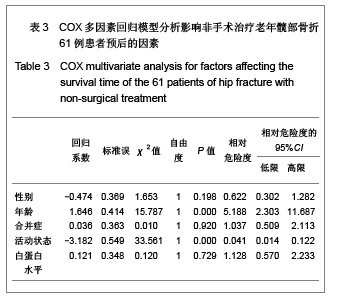
| [1] O'Malley NT, Blauth M, Suhm N,et al. Hip fracture management, before and beyond surgery and medication: a synthesis of the evidence. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011; 131(11):1519-1527.[2] Haleem S, Lutchman L, Mayahi R,et al. Mortality following hip fracture: trends and geographical variations over the last 40 years. Injury. 2008;39(10):1157-1163.[3] Parker M, Johansen A. Hip fracture. BMJ. 2006;333(7557): 27-30.[4] Rosell PA, Parker MJ. Functional outcome after hip fracture. A 1-year prospective outcome study of 275 patients. Injury. 2003; 34(7):529-532.[5] Frihagen F, Nordsletten L, Madsen JE. Hemiarthroplasty or internal fixation for intracapsular displaced femoral neck fractures: randomised controlled trial. BMJ. 2007; 1251-1254.[6] Giversen IM.Time trends of mortality after first hip fractures.Osteoporos Int. 2007;18(6):721-732.[7] Juliebø V, Krogseth M, Skovlund E,et al. Medical treatment predicts mortality after hip fracture. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2010;65(4):442-449.[8] Lofthus CM, Osnes EK, Falch JA,et al. Epidemiology of hip fractures in Oslo, Norway. Bone. 2001;29(5):413-418.[9] Shoda N, Yasunaga H, Horiguchi H,et al. Risk factors affecting inhospital mortality after hip fracture: retrospective analysis using the Japanese Diagnosis Procedure Combination Database. BMJ Open. 2012;2(3). pii: e000416.[10] Rubin CD. Evaluation and management of hip fracture risk in the aged. Am J Med Sci. 2012;343(3):233-242.[11] Vidán MT, Sánchez E, Gracia Y,et al. Causes and effects of surgical delay in patients with hip fracture: a cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(4):226-233.[12] Moroni A, Hoque M, Waddell JP,et al. Surgical treatment and management of hip fracture patients. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg. 2011. [Epub ahead of print][13] Al-Ani AN, Samuelsson B, Tidermark J,et al. Early operation on patients with a hip fracture improved the ability to return to independent living. A prospective study of 850 patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2008;90(7):1436-1442.[14] Zuckerman JD. Hip fracture. N Engl J Med. 1996;334(23): 1519-1525.[15] Raaymakers EL.The non-operative treatment of impacted femoral neck fractures. Injury. 2002;33 Suppl 3:C8-14.[16] Hossain M, Neelapala V, Andrew JG. Results of non-operative treatment following hip fracture compared to surgical intervention. Injury. 2009;40(4):418-421.[17] Pulkkinen P, Glüer CC, Jämsä T. Investigation of differences between hip fracture types: a worthy strategy for improved risk assessment and fracture prevention. Bone. 2011;49(4):600-604.[18] Carriero FP, Christmas C. In the clinic. Hip fracture. Ann Intern Med. 2011;155(11):ITC6-1-ITC6-15.[19] Harris WH.Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 1969;51(4):737-755.[20] Wang MY,Wei J. Zhonghua Chuangshang Guke Zazhi. 2003; 5(1):5-9. 王满宜,危杰.股骨颈骨折临床研究的若干问题与新概念[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2003,5(1):5-9.[21] Rosencher N, Vielpeau C, Emmerich J,et al. Venous thromboembolism and mortality after hip fracture surgery: the ESCORTE study. J Thromb Haemost. 2005;3(9):2006- 2014.[22] Jacobsen SJ, Goldberg J, Miles TP,et al. Race and sex differences in mortality following fracture of the hip. Am J Public Health. 1992;82(8):1147-1150.[23] Cooper C, Atkinson EJ, Jacobsen SJ,et al. Population-based study of survival after osteoporotic fractures. Am J Epidemiol. 1993;137(9):1001-1005.[24] Zhang JW,Jiang C,Zhang XL,et al. Zhonghua Guke Zazhi. 2005;25(1):19-21. 张经纬,蒋矗,张先龙,等.股骨转子间骨折不同手术方法比较[J].中华骨科杂志,2005,25(1):19-21.[25] Hasegawa Y, Suzuki S, Wingstrand H. Risk of mortality following hip fracture in Japan. J Orthop Sci. 2007;12(2): 113-117.[26] Berend ME, Smith A, Meding JB,et al. Long-term outcome and risk factors of proximal femoral fracture in uncemented and cemented total hip arthroplasty in 2551 hips. J Arthroplasty. 2006;21(6 Suppl 2):53-59.[27] Xia J,Huang GY,Huang HY. Zhonghua Laonian Yixue Zazhi. 2005;24(5):355-357. 夏军,黄钢勇,黄煌渊.80岁及以上髋部骨折患者围手术期治疗的探讨[J].中华老年医学杂志, 2005,24(5):355-357.[28] Zeng GJ. Zhongshan Daxue Xuebao:Yixue Kexueban. 2006; 27(3S):167-168. 曾国鉴.全髋关节置换术及内固定术治疗老年股骨颈骨折临床疗效的比较[J].中山大学学报:医学科学版,2006,27(3S):167- 168.[29] Rong GW. Zhonghua Yixue Zazhi. 2005;85(46):3241-3242. 荣国威.应注意老年人新鲜股骨颈骨折治疗的选择[J]. 中华医学杂志,2005,85(46):3241-3242.[30] Luo Q,Cao WX. Zhongguo Linchuang Yingyang Zazhi. 2007;15(5):315-318. 罗茜,曹伟新.白蛋白的临床应用及在营养治疗中的意义[J]. 中国临床营养杂志,2007,15(5):315-318. |