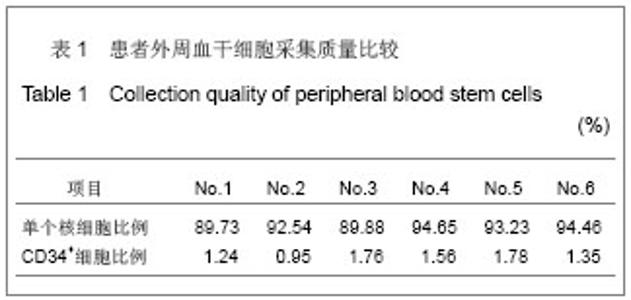
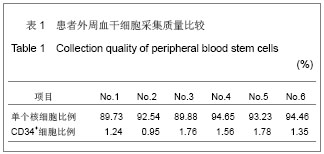
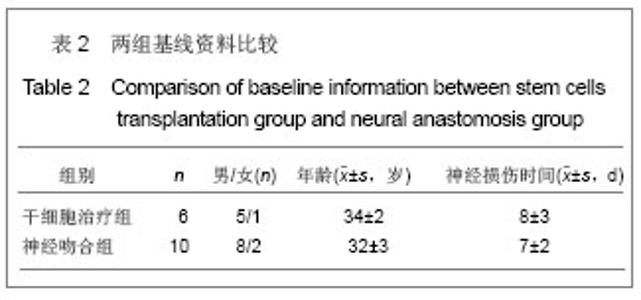
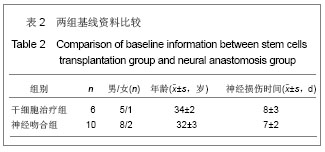
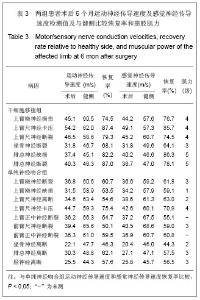
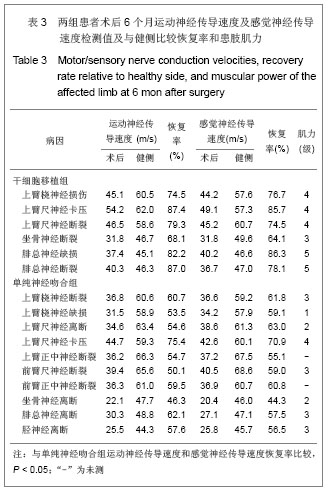
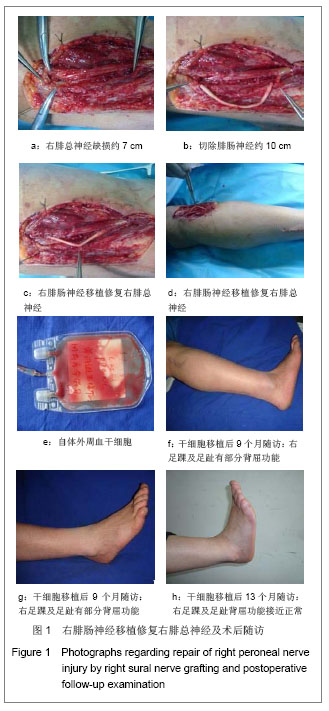
| [1] He CS,Liu RL.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(27):5099-5012.何传胜,刘瑞莲.干细胞及神经相关因子对运动性周围神经损伤再生的影响[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(27): 5099-5012.[2] Dong MM, Yi TH.Stem Cell and Peripheral Nerve Injury and Repair.Facial Plast Surg.2010;26(5):421-427.[3] Zhang SC,Ma YH,Sun LQ,et al.Zhonghua Chuangshang Guke Zazhi. 2005;7(4):335-340.张少成,马玉海,孙来卿,等.神经束间侧侧缝接预防高位神经损伤后不可逆肌萎缩[J].中华创伤骨科杂志,2005,7(4):335-340.[4] Wang SK,Hong GX.Zhonghua Shouwaike Zazhi. 2002;18(1): 43-45.王栓科,洪光祥.细胞外ATP防治失神经肌肉萎缩的实验研究[J].中华手外科杂志,2002,18(1):43-45.[5] Pittock SJ,Lucchinetti CF.The pathology of MS:new insights and potential clinical applications.Neurologist.2007;13(2): 45-56.[6] Guardiola P, Runde V, Bacigalupo A, et al.Retrospective comparison of bone marrow and granulocyte colony-stimulating factor-mobilized peripheral blood progenitor cells for allogeneic stem cell transplantation using HLA identical sibling donors in myelodysplastic syndromes. Blood.2002;99(12):4370-4378.[7] Pettengell R,Luft T,Henschler R,et al.Direct comparison by limiting dilution anylysis of long-term culture-initiating cells in human bone marrow,umbilical cord blood,and blood stem cells.Blood.1994;84(11):3653-3659.[8] Jansen J,Thompson JM, Dugan MJ,et al.Peripheral blood progenitor cell transplantation.Ther Apher.2002;6(1):5-14.[9] Boudoulas KD, Hatzopoulos AK. Cardiac repair and regeneration:the Rubik’s cube of cell therapy for heart disease.DMM.2011;4(3):344-358.[10] Yang SX, Xu J, Xu GY, et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(34):6657-6660.杨水祥,徐静,徐桂玉,等.自体骨髓干细胞移植治疗心肌梗死6例4年随访[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2008,12(34): 6657-6660.[11] Metz I, Lucchinetti CF, Openshaw H, et al.Autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation fails to stop demyelination and neurodegeneration in multiple sclerosis. Brain.2007;130(5):1254-1262.[12] Zhou SY,Zhang CW,Tang BJ,et al.Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(1):142-146.周少余,张成文,汤璧嘉,等.外周血干细胞移植治疗神经系统疾病:可能,可行与可信[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010, 14(1):142-146.[13] Moriya J, Minamino T, Tateno K,et al.Long-Term Outcome of Therapeutic Neovascularization Using Peripheral Blood Mononuclear Cells for Limb Ischemia.Circ Cardiovasc Interv. 2009;2:245-254.[14] Yu JS, Wang YG. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(20):7560-7564.于江苏,王颜刚.糖尿病足的发病机制及干细胞移植治疗[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(20):7560-7564.[15] Zhang L,Chu TB,Wang XJ,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2010;14(19);3589-3592.张雷,楚同彬,王新建,等,自体外周血干细胞移植治疗糖尿病足[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2010,14(19);3589-3592.[16] Wang DH,Xu JG,Jiang H,et al.Zhonghua Shouwaike Zazhi. 2004;6(20):96-99.王德华,徐建光,姜浩,等.神经干细胞移植再支配失神经骨骼肌的实验研究[J].中华手外科杂志,2004,6(20):96-99.[17] Liao W,Liu SH,Zhang YF,et al.Huazhong Keji Daxue Xuebao: Yixueban. 2004;33(4):459-462.廖文,刘淑红,张玉富,等,自体骨髓间充质干细胞促进大鼠坐骨神经缺损修复的试验研究[J].华中科技大学学报:医学版,2004, 3(4): 459-462.[18] di Summa PG, Kingham PJ, Raffoul W, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells enhance peripheral nerve regeneration. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg.2010;63(9):1544-1552. |