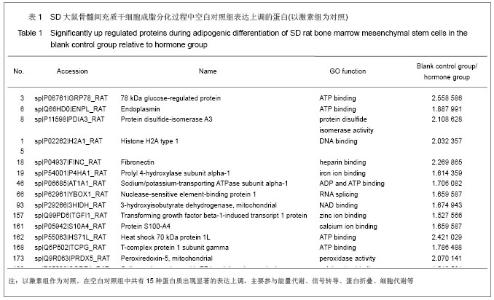
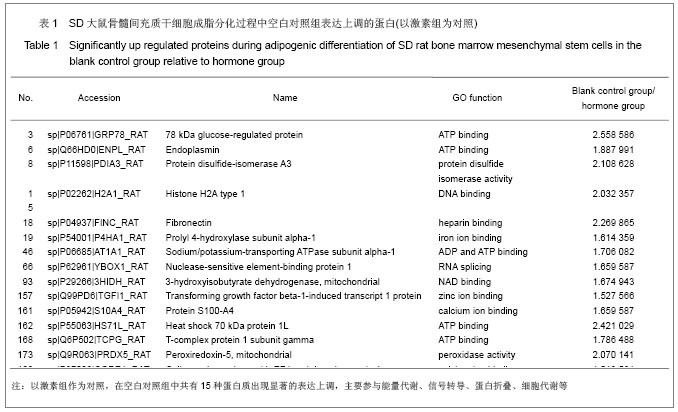
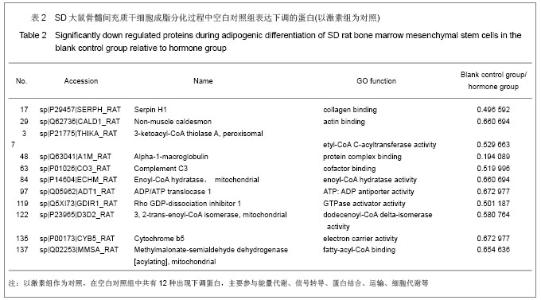
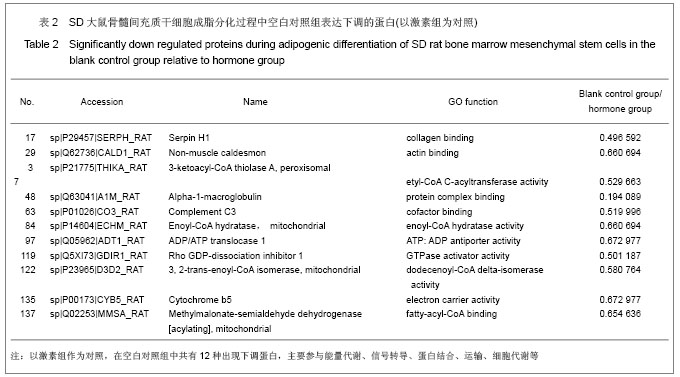
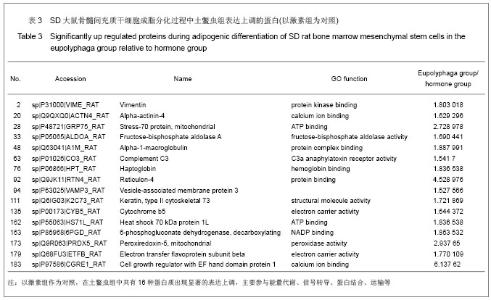
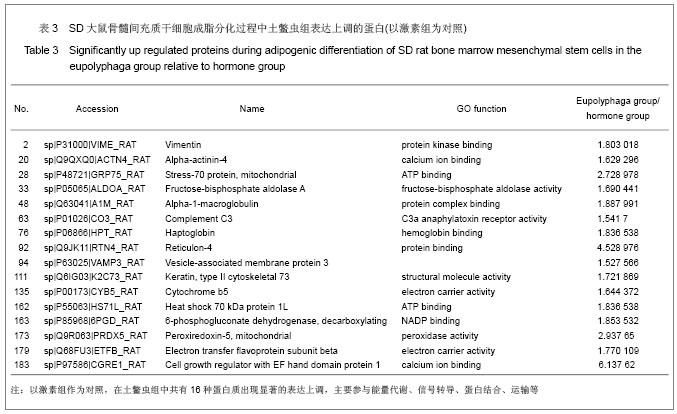
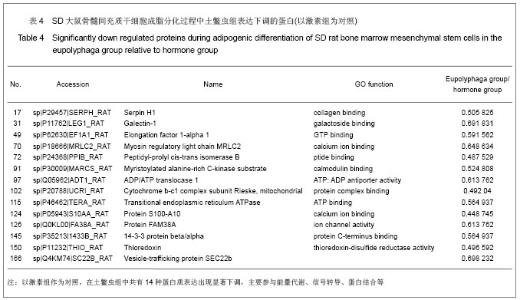
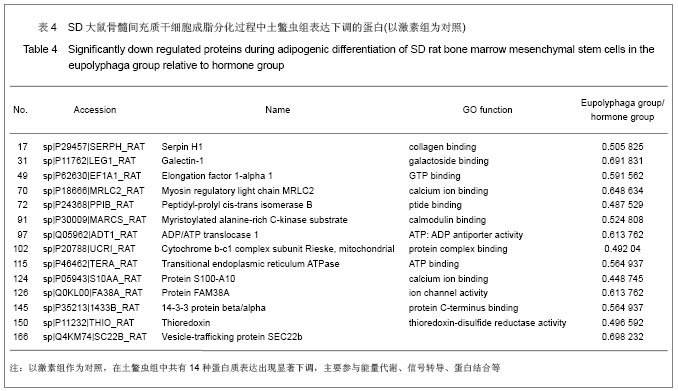
| [1] Qi ZX,Cao Y. Zhongguo Gushang. 2002;15(2):77-78.齐振熙,曹阳.不同治法防治激素性股骨头缺血性坏死的实验研究[J].中国骨伤,2002,15(2):77-78.[2] Kiang JG, Tsokos GC. Heat shock protein 70 kDa: molecular biology, biochemistry, and physiology. Pharmacol Ther. 1998; 80(2):183-201.[3] Sun PM,Wang ZL,Li JM. Zhongguo Shouyi Xuebao. 2007; 27(2): 284-288.孙培明,王志亮,李金明.热休克蛋白70研究新进展[J].中国兽医学报,2007,27(2):284-288.[4] Chen H,Xiao WM,Zhang YD. Zhongguo Xiandai Yixue Zazhi. 2002;12(14):4-7.陈辉,肖卫民,张阳德.肝细胞生长因子对TNF-α诱导肝细胞凋亡的保护作用及其机制的研究[J].中国现代医学杂志,2002,12(14): 4-7.[5] O'Brien CA, Jia D, Plotkin LI,et al. Glucocorticoids act directly on osteoblasts and osteocytes to induce their apoptosis and reduce bone formation and strength. Endocrinology. 2004; 145(4):1835-1841.[6] Yun SI, Yoon HY, Jeong SY,et al. Glucocorticoid induces apoptosis of osteoblast cells through the activation of glycogen synthase kinase 3beta. J Bone Miner Metab. 2009; 27(2):140-148.[7] Asea A, Kraeft SK, Kurt-Jones EA,et al. HSP70 stimulates cytokine production through a CD14-dependant pathway, demonstrating its dual role as a chaperone and cytokine. Nat Med. 2000;6(4):435-442.[8] Zhang B,Xiang YM,Bai Y. Shengli Kexue Jinzhan. 2004;35(4): 352-355.章波,向渝梅,白云.抗氧化蛋白Peroxiredoxin家族研究进展[J].生理科学进展,2004,35(4):352-355.[9] Declercq JP, Evrard C, Clippe A,et al. Crystal structure of human peroxiredoxin 5, a novel type of mammalian peroxiredoxin at 1.5 A resolution. J Mol Biol. 2001;311(4): 751-759.[10] Zeng YP,Liu J,Wang BX. Aizheng Jinzhan. 2010;8(2):164-166.曾跃平,刘洁,王宝玺.过氧化物酶Peroxiredoxin家族与肿瘤关系研究进展[J]. 癌症进展,2010,8(2):164-166.[11] Karihtala P, Mäntyniemi A, Kang SW,et al. Peroxiredoxins in breast carcinoma.Clin Cancer Res. 2003;9(9):3418-3424.[12] Tang V, Dhirapong A, Yabes AP,et al. TNF-alpha-mediated apoptosis in vascular smooth muscle cells requires p73. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 2005;289(1):C199-206.[13] Madden SL, Galella EA, Riley D,et al. Induction of cell growth regulatory genes by p53. Cancer Res. 1996;56(23): 5384-5390.[14] van Gent D, Sharp P, Morgan K,et al. Serpins: structure, function and molecular evolution. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2003;35(11):1536-1547.[15] Dafforn TR, Della M, Miller AD. The molecular interactions of heat shock protein 47 (Hsp47) and their implications for collagen biosynthesis. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(52):49310- 49319.[16] Koide T, Nishikawa Y, Asada S,et al. Specific recognition of the collagen triple helix by chaperone HSP47. II. The HSP47-binding structural motif in collagens and related proteins. J Biol Chem. 2006;281(16):11177-11185.[17] Christiansen HE, Schwarze U, Pyott SM,et al. Homozygosity for a missense mutation in SERPINH1, which encodes the collagen chaperone protein HSP47, results in severe recessive osteogenesis imperfecta. Am J Hum Genet. 2010; 86(3):389-398.[18] Oxlund H, Mosekilde L, Ortoft G. Reduced concentration of collagen reducible cross links in human trabecular bone with respect to age and osteoporosis. Bone. 1996;19(5):479-484.[19] Schmitz-Esser S, Linka N, Collingro A,et al. ATP/ADP translocases: a common feature of obligate intracellular amoebal symbionts related to Chlamydiae and Rickettsiae. J Bacteriol. 2004;186(3):683-691.[20] Schiebel K, Weiss B, Wöhrle D,et al. A human pseudoautosomal gene, ADP/ATP translocase, escapes X-inactivation whereas a homologue on Xq is subject to X-inactivation. Nat Genet. 1993;3(1):82-87.[21] Lehenkari PP, Kellinsalmi M, Näpänkangas JP,et al. Further insight into mechanism of action of clodronate: inhibition of mitochondrial ADP/ATP translocase by a nonhydrolyzable, adenine-containing metabolite. Mol Pharmacol. 2002;61(5): 1255-1262. |