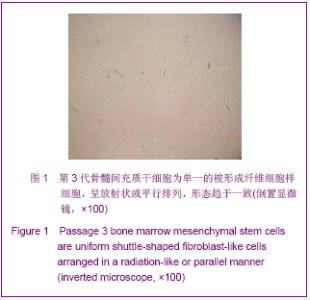
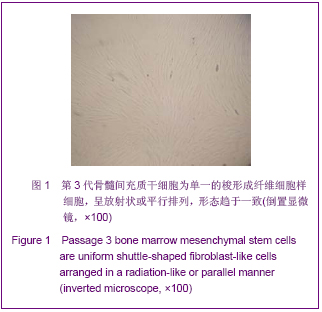
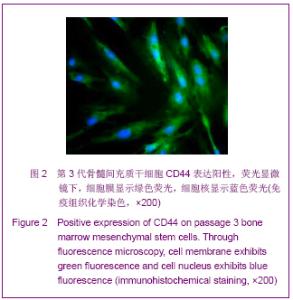
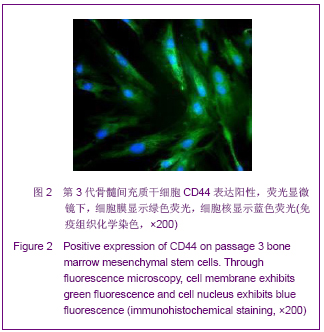
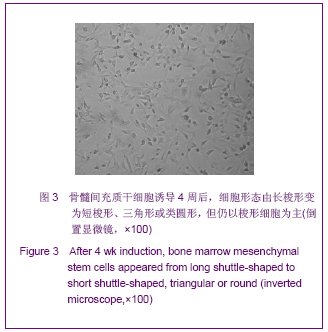
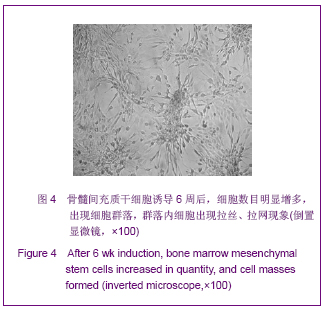
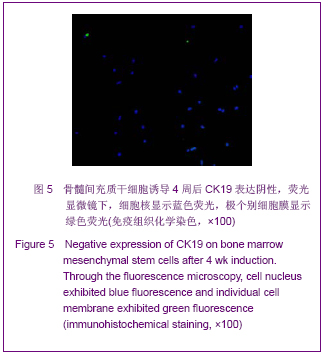
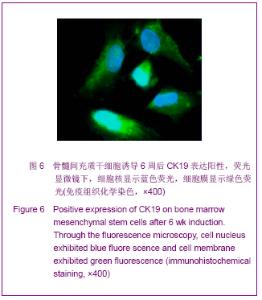
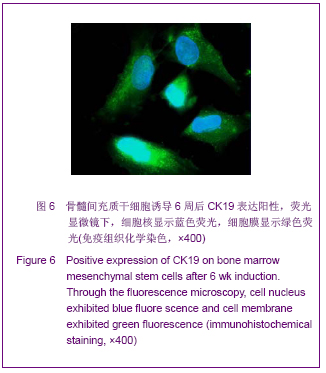
| [1] Roberts SK, Ludwig J, Larusso NF. The pathobiology of biliary epithelia. Gastroenterology. 1997;112(1):269-279.[2] Minguell JJ, Erices A, Conget P. Mesenchymal stem cells. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2001;226(6):507-520.[3] Li Y, Yu J, Li M,et al. Mouse mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow differentiate into smooth muscle cells by induction of plaque-derived smooth muscle cells. Life Sci. 2011;88(3-4):130-140.[4] Peura M, Bizik J, Salmenperä P,et al. Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells undergo nemosis and induce keratinocyte wound healing utilizing the HGF/c-Met/PI3K pathway.Wound Repair Regen. 2009;17(4):569-577.[5] Huang NF, Li S. Mesenchymal stem cells for vascular regeneration. Regen Med. 2008;3(6):877-892.[6] Zhang T,Zhao ZG,Gao H. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(36):6669-6672.张涛,赵振国,高辉.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外诱导为肝细胞样细胞[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(36):6669- 6672.[7] Feng Z, Li C, Jiao S,et al. In vitro differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells into hepatocytes. Hepatogastroenterology. 2011;58(112):2081-2086.[8] He JQ,Yang LL,Lei YC,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2011;15(10):1799-1802.何金秋,杨玲玲,雷延昌,等.同种异体骨髓间充质干细胞移植治疗急性肝功能衰竭[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2011,15(10): 1799-1802.[9] Ma JX,Yang LP,He ZJ,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2008;12(21):4026-4030.马俊勋,杨丽萍,何忠杰,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞诱导为类肝细胞移植修复急性肝损伤[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2008, 12(21):4026-4030.[10] Lange C, Bassler P, Lioznov MV, et al. Liver-specific gene expression in mesenchymal stem cells is induced by liver cells. World J Gastroenterol. 2005;11(29):4497-4504.[11] Malekzadeh R, Hollinger JO, Buck D,et al. Isolation of human osteoblast-like cells and in vitro amplification for tissue engineering. J Periodontol. 1998;69(11):1256-1262.[12] Majumdar MK, Thiede MA, Mosca JD,et al. Phenotypic and functional comparison of cultures of marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) and stromal cells. J Cell Physiol. 1998;176(1):57-66.[13] Zhang MM,Jia GQ,Luo T,et al. Huaxi Yixue. 2009;24(2):371- 374.张明鸣,贾贵清,罗婷,等.大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞体外两种分离方法和培养条件下生物学特点的比较[J].华西医学, 2009,24(2): 371-374.[14] Vaquero J, Zurita M, Oya S,et al. Cell therapy using bone marrow stromal cells in chronic paraplegic rats: systemic or local administration. Neurosci Lett. 2006;398(1-2):129-134.[15] Foster LJ, Zeemann PA, Li C,et al. Differential expression profiling of membrane proteins by quantitative proteomics in a human mesenchymal stem cell line undergoing osteoblast differentiation. Stem Cells. 2005;23(9):1367-1377.[16] Jiang Y, Jahagirdar BN, Reinhardt RL,et al. Pluripotency of mesenchymal stem cells derived from adult marrow. Nature. 2002;418(6893):41-49.[17] De Ugarte DA, Alfonso Z, Zuk PA,et al. Differential expression of stem cell mobilization-associated molecules on multi-lineage cells from adipose tissue and bone marrow. Immunol Lett. 2003;89(2-3):267-270.[18] Ranera B, Lyahyai J, Romero A,et al. Immunophenotype and gene expression profiles of cell surface markers of mesenchymal stem cells derived from equine bone marrow and adipose tissue. Vet Immunol Immunopathol. 2011; 144 (1-2): 147-154.[19] Harkness L, Mahmood A, Ditzel N,et al. Selective isolation and differentiation of a stromal population of human embryonic stem cells with osteogenic potential. Bone. 2011; 48(2):231-241.[20] Dominici M, Le Blanc K, Mueller I,et al. Minimal criteria for defining multipotent mesenchymal stromal cells. The International Society for Cellular Therapy position statement. Cytotherapy. 2006;8(4):315-317.[21] Wang PP, Wang JH, Yan ZP,et al. Expression of hepatocyte-like phenotypes in bone marrow stromal cells after HGF induction. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2004; 320(3):712-716.[22] Pulavendran S, Rajam M, Rose C,et al. Hepatocyte growth factor incorporated chitosan nanoparticles differentiate murine bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell into hepatocytes in vitro. IET Nanobiotechnol. 2010;4(3):51-60.[23] Efimova EA, Glanemann M, Liu L,et al. Effects of human hepatocyte growth factor on the proliferation of human hepatocytes and hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines. Eur Surg Res. 2004;36(5):300-307.[24] Joplin R, Hishida T, Tsubouchi H,et al. Human intrahepatic biliary epithelial cells proliferate in vitro in response to human hepatocyte growth factor. J Clin Invest. 1992;90(4):1284-1289.[25] Chai C, Zheng S, Feng J,et al. A novel method for establishment and characterization of extrahepatic bile duct epithelial cells from mice. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2010; 46(10):820-823.[26] Cai CW,Zheng SY,Wei MF,et al. Zhongguo Xiandai Yixue Zazhi. 2010;20(20):3057-3060.柴成伟,郑帅玉,魏明发,等.表皮生长因子对小鼠肝外胆管上皮细胞原代培养的影响[J].中国现代医学杂志, 2010,20(20): 3057-3060.[27] Uenishi T, Kubo S, Yamamoto T,et al. Cytokeratin 19 expression in hepatocellular carcinoma predicts early postoperative recurrence .Cancer Sci. 2003;94(10):851-857. [28] Qi AD,Zhang J,Yu SN,et al. Zhongguo Zuzhi Gongcheng Yanjiu yu Linchuang Kangfu. 2009;13(27):5243-5246.齐安东,张杰,于树娜,等.第3-12周人胚肝甲胎蛋白及细胞角蛋白19和c-Met的时空表达[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2009, 13(27):5243-5246. |