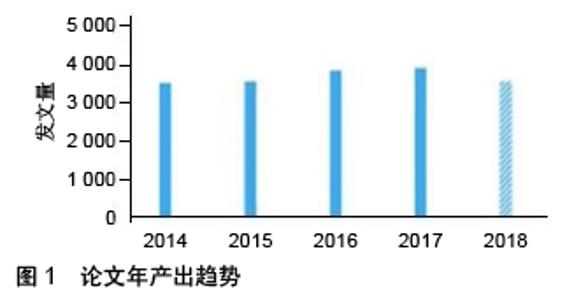
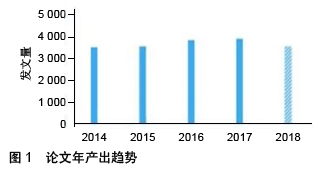
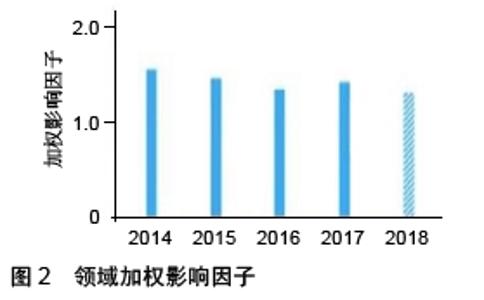
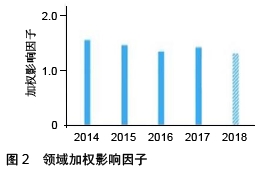
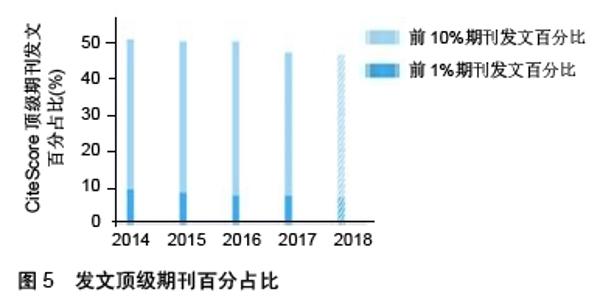
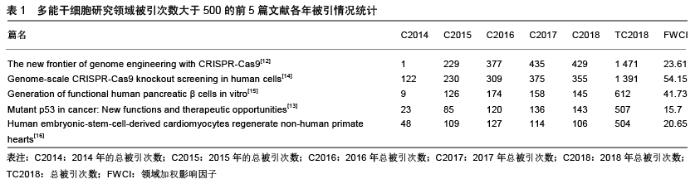
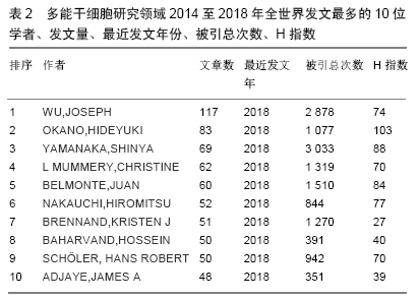
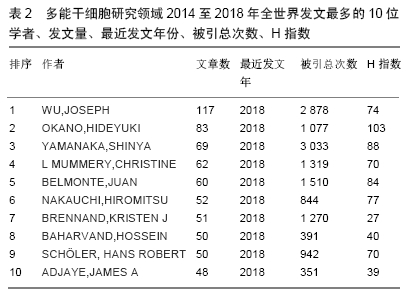
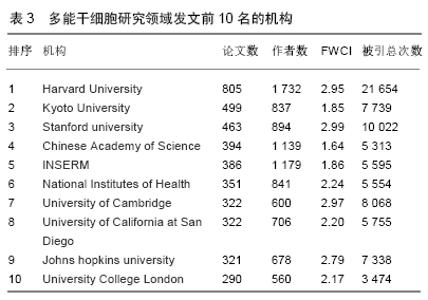
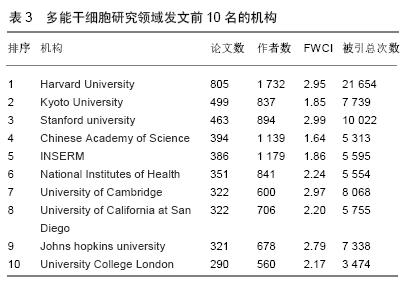
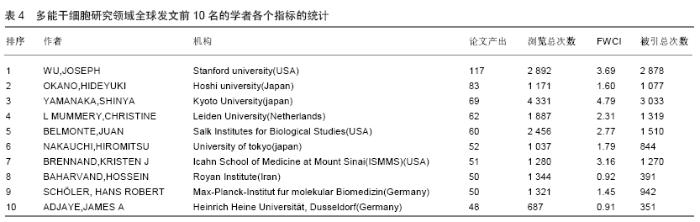
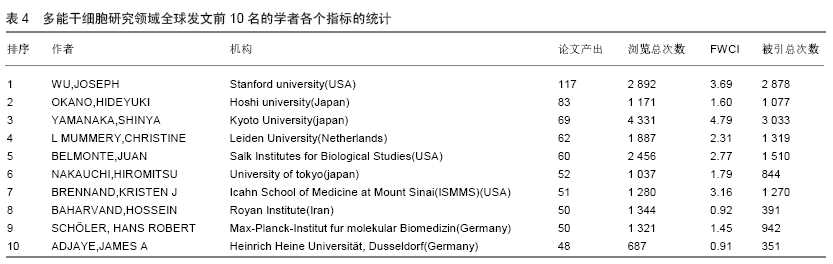
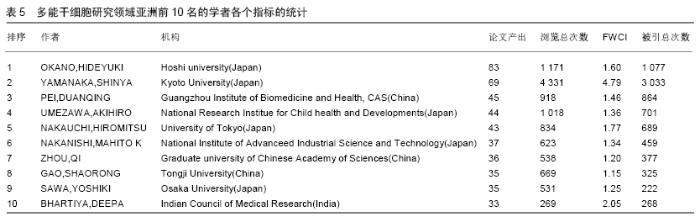
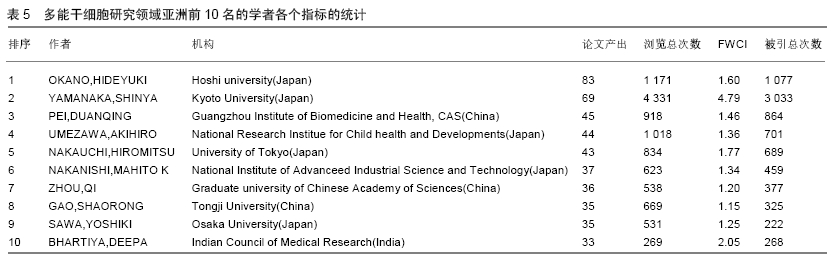
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (7): 1144-1148.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2013
A bibliometric analysis on articles, authors and high-impact
institutions in the field of pluripotent stem cells based on data from Scopus
He Lin, Bai Jinwei, Su Wei
- Department of Science & Technology of West China Hospital, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610041, Sichuan Province, China