Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (10): 1615-1621.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1884
Previous Articles Next Articles
Research hotspots and progress of bone repair materials in tissue engineering
Wei Chenxu1, He Yiwen1, Wang Dan1, Hou Jingxia1, 2, Xie Hui1, 2, Yin Fangzhou1, 2, Chen Zhipeng1, 2, Li Weidong1, 2
- 1School of Pharmacy, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China; 2Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Processing in Jiangsu Province, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China
-
Received:2019-05-08Revised:2019-05-22Accepted:2019-07-05Online:2020-04-08Published:2020-02-18 -
Contact:Li Weidong, Researcher, School of Pharmacy, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China; Key Laboratory of Chinese Medicine Processing in Jiangsu Province, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China -
About author:Wei Chenxu, School of Pharmacy, Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine, Nanjing 210023, Jiangsu Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81373970; Key Provincial Projects of Innovation and Entrepreneurship Training Program for College Students of Nanjing University of Chinese Medicine in 2018, No. 201810315021Z
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wei Chenxu, He Yiwen, Wang Dan, Hou Jingxia, Xie Hui, Yin Fangzhou, Chen Zhipeng, Li Weidong. Research hotspots and progress of bone repair materials in tissue engineering[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(10): 1615-1621.
share this article
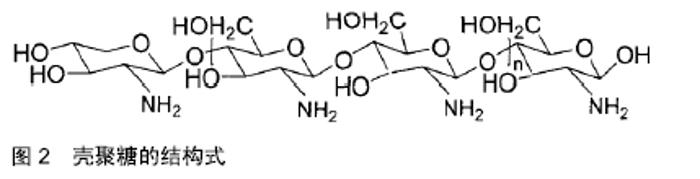
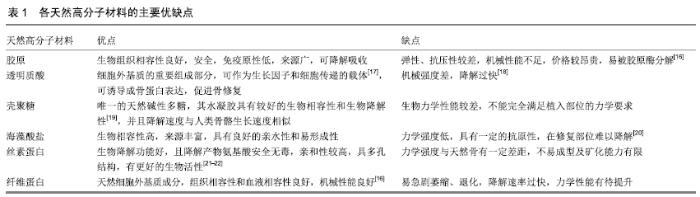
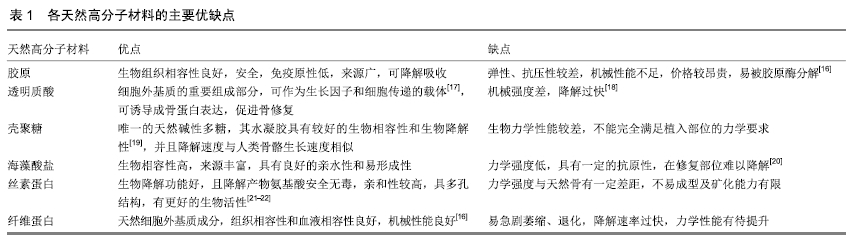
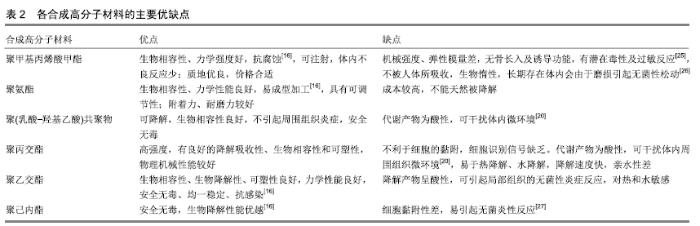
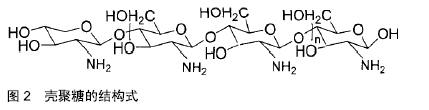
2.1 骨修复材料的特点 目前应用于骨修复的材料有数种,各有其利弊。公认的理想的骨修复材料应具有以下特点:①良好的生物组织相容性[5]:移植到体内后不引起排斥反应、炎症反应和毒性反应;②可塑性:材料可塑为任意的结构,植入后在体内仍可保持特定形状,具有记忆金属的特性;③可降解性:能在生物体内逐渐降解最终由自身骨组织所替代,且降解速率可根据骨组织形成中不同细胞再生速率而进行调整;④良好的力学性能[6]:良好的骨修复材料要能模拟生物体骨组织的结构、成分和性质,与骨组织力学性能相匹配;⑤可作为载体:调节生物活性因子的释放;⑥良好的骨传导性:有利于临近骨组织爬行替代;⑦较高的孔隙率及渗透性能[5]:适当的孔径与孔隙率利于物质交换,能够为细胞生长提供足够空间。 2.2 骨修复材料的种类 2.2.1 天然骨材料 天然骨,顾名思义就是来源于机体,非后天人工合成的骨修复材料。天然骨中成分均为机体的组成成分,所以临床使用安全性较高,天然骨主要有自体骨和(同种)异体骨两类,在骨修复中应用较为广泛,这类材料在骨修复领域中应用起步较早,研究也较为深入。 自体骨:自体骨是较为理想的骨缺损植入材料,是骨移植手术中骨修复材料的首选。自体骨来源于患者本身,临床上易于被患者接受且免疫排斥反应较低,甚至不引起排斥反应,生物相容性较好,骨诱导能力、骨传导能力和骨修复能力均较强,业内称之为“金标准”[7]。同时为避免感染,临床通常使用带血运的自体骨。张云峰等[8]对60例距骨骨软骨损伤患者实施自体软骨骨移植治疗,术后治疗效果显著,疼痛明显降低。高占巍等[9]对9例颧骨颧弓截骨术后骨不连患者实施自体骨移植修复,结果显示临床效果优异,2年内未出现严重并发症,移植骨成活性良好。但另一方面,临床应用中自体骨供骨量有限,术后易发生供区不良反应和神经损伤等问题,以及供体部位发病率高,易出现出血、慢性疼痛、感染、美容效果差等不良反应[10]。 异体骨:主要指同种异体骨,具有良好的骨传导性和骨诱导性,来源比自体骨较广,被广泛应用于填充骨空隙[11]、诱导局部组织的修复。马中瑞等[12]研究发现良性骨肿瘤患者采用异体骨手术12个月后愈合率达97.5%,并且初步愈合时间明显短于人工骨移植。GRACITELLI等[13]研究认为骨软骨同种异体骨移植是治疗膝关节软骨和骨缺损的有效办法,临床症状得到显著改善。膝关节同种异体骨移植有利于膝盖的修复并提升患者生活质量[14]。郜德龙等[15]回顾分析得出,同种异体骨Cage在修复腰椎骨时可提供早期稳定性和较高的融合率。但相对于自体骨,同种异体骨容易出现免疫排斥反应,有疾病传播的危险。同时,异体骨材料较难获得、价格不菲及刚性较低等也是其不足之处。 2.2.2 骨移植替代材料 单一成分的人工骨研究起步较早,目前在临床中已有应用;复合人工骨的研究目前还处于基础研究阶段,虽还有很多未解的难题,但仍有一定的研究成果,目前以复合有骨生长因子或种子细胞的复合材料居多。随着对原位组织再生理解的不断深入以及研究的不断拓展,骨组织工程的研究方向逐渐向基于药物和骨修复材料结合上转变,即将骨修复材料作为一种药物控释载体。下面将分类介绍骨修复材料及其优缺点。 天然高分子材料:目前此类材料常见的主要有胶原、透明质酸、壳聚糖[16](图2)、海藻酸盐、丝素蛋白、纤维蛋白等。总体来说,这类材料的优势在于具有较好的生物相容性,安全无毒,细胞亲和性良好。但同时由于各自天然成分的不同及来源不尽相同,也不可避免的存在着一些如质量重复性不佳等不足之处,见表1。 "
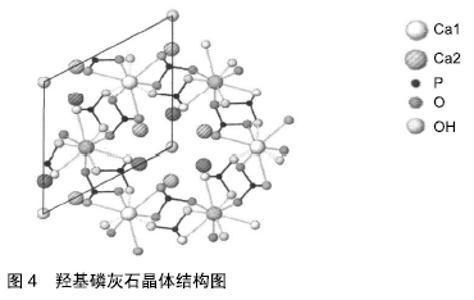
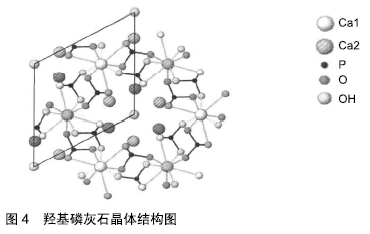
医用生物陶瓷材料:医用生物陶瓷材料有惰性材料与活性材料之分。惰性材料有氧化铝、氧化锆等。肖长江等[28]研究发现加入30 nm氧化铝粉,氧化铝陶瓷的硬度和抗弯强度有所改善。曾峰等[29]研究表明将氧化锆复合到氧化铝粉体中可增强断裂韧性。活性材料:①羟基磷灰石:是自然骨中的无机成分之一。近年来,亦有对纳米羟基磷灰石的临床研究报道[30],临床显示生物相容性良好,无不良反应;②磷酸三钙:WANG等[31]研究发现,磷酸钙陶瓷的相组成可能会调节植入物局部微环境中骨诱导因子的数量;③生物活性玻璃:是一种硅酸盐玻璃。COATHUP等[32]研究发现与具有相同形态的非硅酸盐相比,硅酸盐取代的磷酸钙骨替代材料的骨诱导能力增加。 总体来说,这类材料来源广泛,成本相对较低,生物相容性和骨传导性较好,可与组织表现出良好的亲和性,美中不足的是生物力学性能不足、脆性大。另外,在不同的植入部位上,陶瓷制作的孔径大小及孔隙率尚未有统一标准[33]。羟基磷灰石晶体结构见图4[34]。医用生物陶瓷材料的优缺点见表3。 "
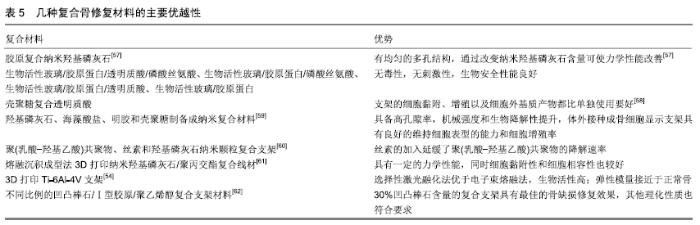
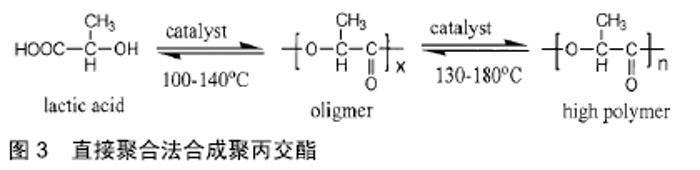
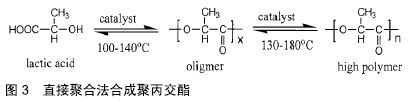
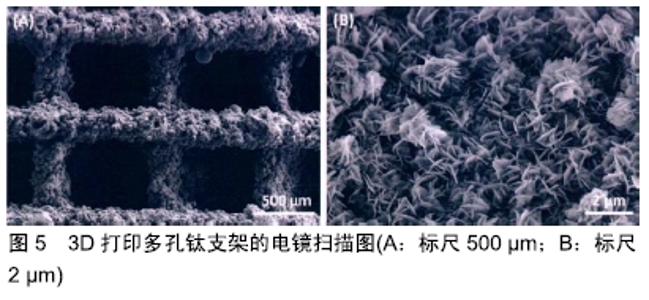
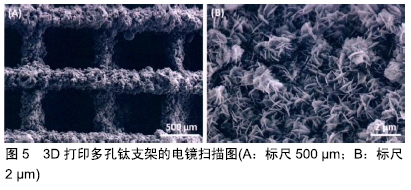
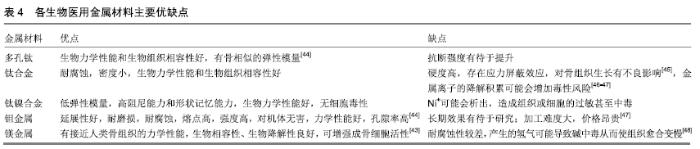
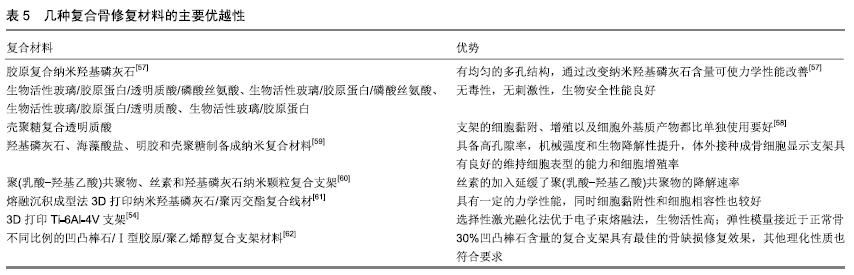
其他新型材料:如以石墨烯材料和碳纳米管为主的碳素材料及脱细胞基质材料等。碳素材料以优良的导电性和热学性能,独特的机械性能,良好的生物相容性,使其在生物医学领域备受关注[49-50]。脱细胞基质是采用一定的方法去除组织或器官中的细胞等成分,获得的接近细胞外基质天然结构与形状、同时保留了活性成分的一种材料[51],具有较好的骨传导性和骨诱导能力[52],生物衍生骨材料在许多方面都具有显著的优势,比如孔隙结构和生物降解等方面,但是其生物力学性能不佳以及免疫原性等问题仍不能令人满意,有待于改善[53]。 随着3D打印技术的发展及个体化治疗的需求不断增长,3D打印的骨修复材料也应运而生,目前常用的3D打印技术有电子束熔融法和选择性激光融化技术[54]。3D打印制备的支架具有良好的生物相容性及物理性能,而且制备的支架更加符合骨修复部位所需的环境条件,但是也有其一定的局限性,比如孔隙率和孔径大小对支架性能的影响仍有一定的争议[55-56]。随着越来越多的生物材料被应用于骨修复,各种复合材料也如雨后春笋般的被研发而出,复合材料可以扬长避短,综合各种材料的优越性能,临床试验效果更佳。几种复合骨修复材料的主要优越性见表5。 "
| [1] 曹谊林.组织工程学:理论与实践[M].上海:上海科学技术出版社, 2004:3-8. [2] LANGER R, VACANTI JP.Tissue engineering.Science. 1993; 260(5110):920-926. [3] 全宸良.两种新型多孔骨组织工程支架的制备及性能研究[D].北京:中国人民解放军医学院,2017. [4] ATALA A.Bioengineered tissues for urogenital repair in children. Pediatr Res.2008;63(5):569-575. [5] HILLSLEY MV, FRANGOS JA.Bone tissue engineering:The role of interstitial fluid flow.Biotechnol Bioeng.1994;43(7): 573-581. [6] THOMSON RC, YASZEMSKI MJ, POWERS JM, et al. Hydroxyapatite fiber reinforced poly(alpha-hydroxy ester) oams for bone regeneration.Biomaterials.1998;19(21): 1935-1943. [7] 李康杰,孙抒.去除移植免疫反应抗原成分脱细胞天然骨基质的制备[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复,2011,15(8):1355-1359. [8] 张云峰,阚世廉.自体骨软骨移植治疗距骨骨软骨损伤对疼痛和关节功能的影响[J].中国医药指南,2018,16(23):8-9. [9] 高占巍,陈波,吉恺.自体骨移植修复颧骨颧弓截骨术后骨不连的临床研究[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2018,29(6):342-345. [10] NOORI A, ASHRAFI SJ, VAEZ-GHAEMI R, et al.A review of fibrin and fibrin composites for bone tissue engineering.Int J Nanomedicine.2017;12:4937-4961. [11] MCCULLOCH PC, SIMON G.Osteochondral Allograft Transplantation:The Rationale and Basic Science.Developing Insights in Cartilage Repair.Springer London, 2014:131-147. [12] 马中瑞,王文己.不同植骨材料在良性骨肿瘤患者植骨重建的疗效[J].中国肿瘤外科杂志,2018,10(5):323-326. [13] GRACITELLI GC, MERIC G, PULIDO PA, et al.Fresh osteochondral allograft transplantation for isolated patellar cartilage injury.Am J Sports Med. 2015;43(4):879-884. [14] VANGSNESS CT JR, GARCIA IA, MILLS CR, et al.Allograft transplantation in the knee:tissue regulation,procurement, processing,and sterilization.Am J Sports Med. 2003;31(3): 474-481. [15] 郜德龙,方忠,孙允龙,等.同种异体骨Cage在经椎间孔腰椎椎间融合手术中的应用[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2018,32(7):927-932. [16] 徐敏.纳米羟基磷灰石的表面改性及其复合材料的制备[D].南昌:南昌大学,2012. [17] MAO QH, XU P.Application of hyaluronic acid in bone tissue engineering.Chin J Tissue Eng Res. 2013;17(20):3738-3745. [18] 张令涛,刘如明,肖建辉.透明质酸在骨组织工程中的应用[J].实用医学杂志,2016,32(8):1364-1366. [19] 陈智捷,陈燕芳,郑军,等.壳聚糖水凝胶的制备及其在药物释放中的应用[J].材料导报,2018,32(S1):169-175. [20] 韩倩倩,薛彬,王涵,等.骨组织工程材料的研究进展[J].组织工程与重建外科杂志,2017,13(6):343-345. [21] LIU B,SONG YW,JIN L,et al.Silk structure and degradation. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces. 2015;131:122-128. [22] 李莹莹,王昉,刘其春,等.丝素蛋白及其复合材料的研究进展[J].材料工程,2018,46(8):14-26. [23] KOHN DH, SARMADI M, HELMAN JI, et al.Effects of pH on human bone marrow stromal cells in vitro:Implications for tissue engineering of bone.J Biomed Mater Res.2002;60(2): 292-299. [24] SANTAVIRTA S, KONTTINEN YT, SAITO T, et al.Immune response to polyglycolic acid implants.J Bone Joint Surg Br. 1990;72(4):597-600. [25] 郭瑛,贾连顺,吴维敏,等.自体富血小板血浆混合磷酸钙骨水泥修复椎体骨缺损的实验研究[J].中国医药导报, 2018,15(25): 13-16,28. [26] 高山,周方,吕扬,等.新型多孔聚甲基丙烯酸甲酯骨水泥的制备及性能分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2019,23(2):204-210. [27] 肖原,张杰,陆燕蓉,等.聚氨酯-脱细胞基质复合支架的制备及体内外生物相容性研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2015,29(8): 1016-1021. [28] 肖长江,朱玲艳,张恒涛,等.纳米氧化铝对氧化铝陶瓷性能的影响[J].佛山陶瓷,2013,23(8):17-18,21. [29] 曾峰,方海亮,王连军,等.氧化锆增韧氧化铝陶瓷的性能研究[J].广东化工,2018,45(4):11-12,21. [30] ZHU WM, WANG DP, XIONG JY, et al.Study on clinical application of nano-hydroxyapatite bone in bone defect repair.Artif cells Nanomed Biotechnol.2015;43(6):361-365. [31] WANG J, CHEN Y, ZHU X, et al.Effect of phase composition on protein adsorption and osteoinduction of porous calcium phosphate ceramics in mice.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2014; 102(12):4234-4243. [32] COATHUP MJ, HING KA, SAMIZADEH S, et al.Effect of increased strut porosity of calcium phosphate bone graft substitute biomaterials on osteoinduction.J Biomed Mater Res A. 2012;100(6):1550-1555. [33] 毛文文,茹江英.羟基磷灰石类陶瓷在骨组织工程中的研究与更广泛应用[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(30):4855-4863. [34] 徐小燕,刘涛涛,郑军,等.壳聚糖/羟基磷灰石骨修复材料的研究进展[J].材料导报,2012,26(15):102-106,129. [35] 朱晓东.抗菌型氧化锆粉体的制备及其抗菌性能研究[D].上海:上 海师范大学,2018. [36] 周游,郭澍.锶及羟基磷灰石在骨组织工程中的研究进展[J].中国美容整形外科杂志,2018,29(11):686-688,706. [37] LEGEROS RZ.Calcium Phosphate-Based Osteoinductive Materials.Chem Rev.2008;108(11):4742-4753. [38] ITO M, YAMAGISHI T, YAGASAKI H, et al.In vitro properties of a chitosan-bonded bone-filling paste:studies on solubility of calcium phosphate compounds.J Biomed Mater Res. 1996; 32(1):95-98. [39] KAUR G, PANDEY OP, SINGH K, et al.A review of bioactive glasses:Their structure,properties,fabrication and apatite formation.J Biomed Mater Res A.2014;102(1):254-274. [40] RAHAMAN MN, DAY DE, BAL BS, et al.Bioactive glass in tissue engineering.Acta Biomater.2011;7(6):2355-2373. [41] NIINOMI M.Mechanical biocompatibilities of titanium alloys for biomedical applications.J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2008; 1(1):30-42. [42] HULBERT SF, YOUNG FA, MATHEWS RS, et al.Potential of ceramic materials as permanently implantable skeletal prostheses.J Biomed Mater Res.1970;4(3):433-456. [43] ZHANG X, ZU H, ZHAO D, et al.Ion channel functional protein kinase TRPM7 regulates Mg ions to promote the osteoinduction of human osteoblast via PI3K pathway:In vitro,simulation of the bone-repairing effect of Mg-based alloy implant.Acta Biomater.2017;63:369-382. [44] 杨伽捷,朱裕昌,杨春喜.多孔金属骨组织支架的研究进展[J].实用骨科杂志,2018,24(2):148-152. [45] NAGELS J, STOKDIJK M, ROZING PM.Stress shielding and bone resorption in shoulder arthroplasty.J Shoulder Elbow Surg. 2003;12(1):35-39. [46] JACOBS JJ, HALLAB NJ, SKIPOR AK, et al.Metal degradation products:a cause for concern in metal-metal bearings? Clin Orthop Relat Res.2003;417(417):139-147. [47] RUBIN JP,YAREMCHUK MJ.Complications and toxicities of implantable biomaterials used in facial reconstructive and aesthetic surgery:a comprehensive review of the literature.Plast Reconstr Surg.1997;100(5):1336-1353. [48] ZOU J, SHI Z, XU H, et al.In Vitro Studies on the Degradability, Bioactivity,and Cell Differentiation of PRP/AZ31B Mg Alloys Composite Scaffold.BioMed Res Int. 2017;2017:5763173. [49] 张莹,温朝辉.碳纳米管及其衍生物在组织工程领域的应用[J].临床与病理杂志,2018,38(4):874-878. [50] 李燕,刘惠亮.碳纳米管在心肌组织工程应用的研究进展[J].中华老年心脑血管病杂志,2016,18(9):993-995. [51] RANA D, ZREIQAT H, BENKIRANE-JESSEL N, et al. Development of decellularized scaffolds for stem cell-driven tissue engineering.J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2015;11(4): 942-965. [52] GRUSKIN E, DOLL BA ,FUTRELL FW, et al.Demineralized bone matrix in bone repair:history and use.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2012;64(12):1063-1077. [53] 蓝旭,杨志明.生物衍生骨材料[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2005 , 19(3):241-244. [54] 郑朋飞.3D打印技术在骨组织工程学和儿童骨科临床的应用研究[D].南京:南京医科大学,2017. [55] ZHANG ZZ, JIANG D, DING JX, et al.Role of scaffold mean pore size in meniscus regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2016;43: 314-326. [56] CAVO M, SCAGLIONE S.Scaffold microstructure effects on functional and mechanical performance:Integration of theoretical and experimental approaches for bone tissue engineering applications.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;68:872-879. [57] CUNNIFFE GM, DICKSON GR, PARTAP S, et al. Development and characterisation of a collagen nano-hydroxyapatite composite scaffold for bone tissue engineering.J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2010;21(8):2293-2298. [58] YAMANE S, IWASAKI N, MAJIMA T, et al.Feasibility of chitosan-based hyaluronic acid hybrid biomaterial for a novel scaffold in cartilage tissue engineering. Biomaterials. 2005; 26(6):611-619. [59] SHARMA C, DINDA AK, POTDAR PD, et al.Fabrication and characterization of novel nano-biocomposite scaffold of chitosan-gelatin-alginate-hydroxyapatite for bone tissue engineering.Mater Sci Eng C Mater Biol Appl. 2016;64: 416-427. [60] SHEIKH FA, JU HW, MOON BM, et al.Hybrid scaffolds based on PLGA and silk for bone tissue engineering.J Tissue Eng Regen Med.2016;10(3):209-221. [61] 肖永昊.用于3D打印人工骨的线材的制备与研究[D].北京:北京印刷学院,2018. [62] 任亚辉.凹凸棒石/Ⅰ型胶原/聚乙烯醇复合支架材料修复骨缺损的实验研究[D].兰州:甘肃农业大学,2018. [63] PARK SA, LEE HJ, KIM KS, et al.In Vivo Evaluation of 3D-Printed Polycaprolactone Scaffold Implantation Combined with β-TCP Powder for Alveolar Bone Augmentation in a Beagle Defect Model.Materials.2018;11(2):238. [64] JIANG Y, ZHANG Y, CHEN W, et al.Achyranthes bidentataextract exerts osteoprotective effects on steroid-induced osteonecrosis of the femoral head in rats by regulating RANKL/RANK/OPG signaling.J Transl Med.2014; 12:334. [65] SHUAI B, SHEN L, ZHU R, et al.Effect of Qing’e formula on the in vitro differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells from proximal femurs of postmenopausal osteoporotic mice.BMC Complement Altern Med. 2015;15:250. [66] 赵根华,翁泽斌,高倩倩,等.自然铜煅制过程物相动态变化规律[J].中国实验方剂学杂志,2015,21(18):1-4. [67] 李伟东,高倩倩,赵根华,等.矿物药炮制研究方法述评[J].南京中医药大学学报,2014,30(6):596-600. [68] 赵根华,翁泽斌,高倩倩,等.自然铜炮制前后促进骨折愈合作用及机制研究[J].中药新药与临床药理,2015,26(4):481-485. |
| [1] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [2] | Yuan Jiawei, Zhang Haitao, Jie Ke, Cao Houran, Zeng Yirong. Underlying targets and mechanism of Taohong Siwu Decoction in prosthetic joint infection on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1428-1433. |
| [3] | Geng Qiudong, Ge Haiya, Wang Heming, Li Nan. Role and mechanism of Guilu Erxianjiao in treatment of osteoarthritis based on network pharmacology [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1229-1236. |
| [4] | Zeng Yanhua, Hao Yanlei. In vitro culture and purification of Schwann cells: a systematic review [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1135-1141. |
| [5] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [6] | Zhang Bin, Sun Lihua, Zhang Junhua, Liu Yusan, Cui Caiyun. A modified flap immediate implant is beneficial to soft tissue reconstruction in maxillary aesthetic area [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 707-712. |
| [7] | Xu Dongzi, Zhang Ting, Ouyang Zhaolian. The global competitive situation of cardiac tissue engineering based on patent analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 807-812. |
| [8] | Fu Shuanhu, Qin Kai, Lu Dahan, Qin Haibiao, Gu Jin, Chen Yongxi, Qin Haoran, Wei Jiading, Wu Liang, Song Quansheng. Lumbar spinal tuberculosis implanted with artificial bone with streptomycin sulfate and percutaneous pedicle screw under transforaminal endoscopy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 493-498. |
| [9] | Li Chenjie, Lü Linwei, Song Yang, Liu Jingna, Zhang Chunqiu. Measurement and statistical analysis of trabecular morphological parameters of titanium alloy peri-prosthesis under preload [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 516-520. |
| [10] | Wu Zijian, Hu Zhaoduan, Xie Youqiong, Wang Feng, Li Jia, Li Bocun, Cai Guowei, Peng Rui. Three-dimensional printing technology and bone tissue engineering research: literature metrology and visual analysis of research hotspots [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [11] | Chang Wenliao, Zhao Jie, Sun Xiaoliang, Wang Kun, Wu Guofeng, Zhou Jian, Li Shuxiang, Sun Han. Material selection, theoretical design and biomimetic function of artificial periosteum [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 600-606. |
| [12] | Liu Fei, Cui Yutao, Liu He. Advantages and problems of local antibiotic delivery system in the treatment of osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 614-620. |
| [13] | Li Xiaozhuang, Duan Hao, Wang Weizhou, Tang Zhihong, Wang Yanghao, He Fei. Application of bone tissue engineering materials in the treatment of bone defect diseases in vivo [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 626-631. |
| [14] | Zhang Zhenkun, Li Zhe, Li Ya, Wang Yingying, Wang Yaping, Zhou Xinkui, Ma Shanshan, Guan Fangxia. Application of alginate based hydrogels/dressings in wound healing: sustained, dynamic and sequential release [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 638-643. |
| [15] | Chen Jiana, Qiu Yanling, Nie Minhai, Liu Xuqian. Tissue engineering scaffolds in repairing oral and maxillofacial soft tissue defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 644-650. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||