Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (1): 7-13.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1874
Previous Articles Next Articles
Conditioned medium of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with bone morphogenetic protein 2 effectively mitigates ovariectomy induced osteoporosis in rats
Yang Jiujie1, Zhao Wei2, Wang Nan2, Chen Xiaochun2, Li Zhi2, Ma Ji2, Shen Dewei2, Wang Yong2, Niu Qingfei2, Wang Tao2, Zhou Yubo2, Zhang Yang2
- 1Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 1100247, Liaoning Province, China; 2Central Hospital Affiliated to Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China
-
Received:2019-04-29Revised:2019-05-06Accepted:2019-06-22Online:2020-01-08Published:2019-12-11 -
Contact:Zhang Yang, MD, Associate chief physician, Central Hospital Affiliated to Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 110000, Liaoning Province, China -
About author:Yang Jiujie, Master candidate, Physician, Shenyang Medical College, Shenyang 1100247, Liaoning Province, China -
Supported by:the Youth Foundation of Shenyang Medical College, No. 20152033
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yang Jiujie, Zhao Wei, Wang Nan, Chen Xiaochun, Li Zhi, Ma Ji, Shen Dewei, Wang Yong, Niu Qingfei, Wang Tao, Zhou Yubo, Zhang Yang. Conditioned medium of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells combined with bone morphogenetic protein 2 effectively mitigates ovariectomy induced osteoporosis in rats[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(1): 7-13.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
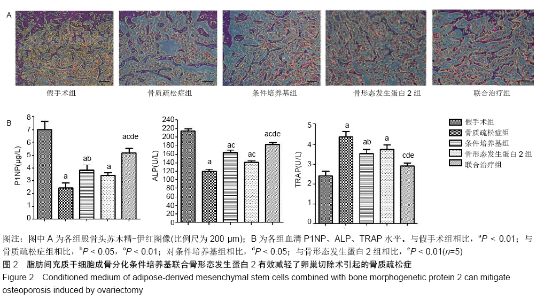
2.2 脂肪间充质干细胞成骨分化条件培养基联合骨形态发生蛋白2有效地减轻了卵巢切除术引起的骨质疏松 骨切片结果显示,与假手术组相比,骨质疏松症组大鼠的骨小梁间距扩大,骨小梁数量明显减少,骨小梁失去正常结构并且不连续。在条件培养基组、骨形态发生蛋白2组以及联合治疗组,骨小梁间距扩大较少,骨小梁显得更连续,见图2A。与其他组相比,联合治疗组与假手术组更相似。 ELISA检测成骨因子的表达,见图2B。造模各组血清P1NP水平显著低于假手术组(P < 0.05);与骨质疏松症组比较,条件培养基组、骨形态发生蛋白2组以及联合治疗组血清P1NP水平显著升高(P < 0.05);同时,联合治疗组血清P1NP水平显著高于条件培养基组、骨形态发生蛋白2组 (P < 0.05)。血清ALP水平与P1NP相似。造模各组血清ALP水平显著低于假手术组(P < 0.01)。与骨质疏松症组相比,条件培养基组、骨形态发生蛋白2组以及联合治疗组血清ALP水平显著升高(P < 0.01);同时,联合治疗组血清ALP水平显著高于条件培养基组、骨形态发生蛋白2组(P < 0.05)。骨质疏松症组、条件培养基组、骨形态发生蛋白2组血清TRAP水平显著高于假手术组(P < 0.01)。值得注意的是,联合治疗组与假手术组之间差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。与骨质疏松症组相比,条件培养基组和联合治疗组血清TRAP水平显著降低(P < 0.05),而骨形态发生蛋白2组差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。与条件培养基组、骨形态发生蛋白2组相比,联合治疗组TRAP水平显著降低(P < 0.05)。这些结果表明脂肪间充质干细胞成骨分化条件培养基联合骨形态发生蛋白2主要影响成骨细胞的活性和骨形成,也与骨吸收有关。"

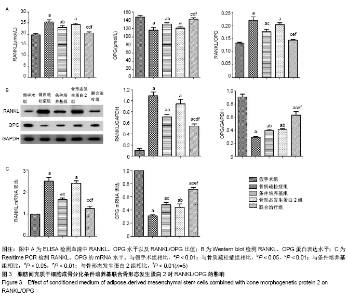
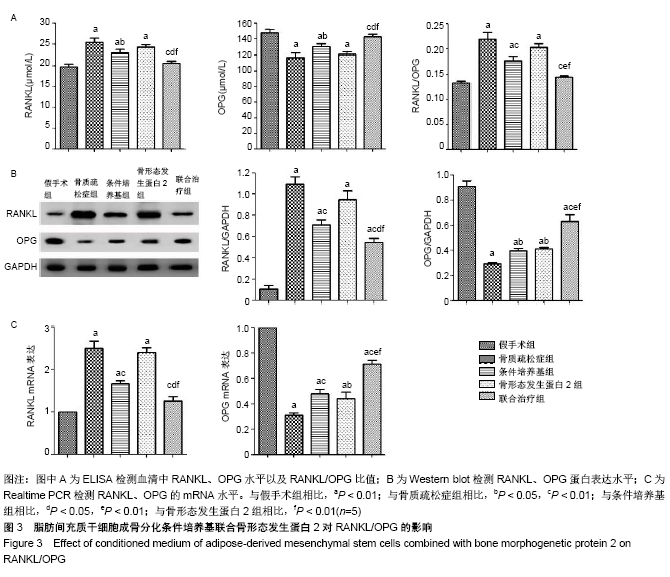
2.3 脂肪间充质干细胞成骨分化条件培养基联合骨形态发生蛋白2对RANKL、OPG表达的影响 通过ELISA,Western blot、Real time PCR测定血清和股骨组织OPG和RANKL水平。与假手术组比较,血清RANKL、OPG水平和RANKL/OPG比值在骨质疏松症组、条件培养基组和骨形态发生蛋白2组显著增加(P < 0.01),而联合治疗组与假手术组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。与骨质疏松症组相比,条件培养基组和联合治疗组血清RANKL、OPG水平和RANKL/OPG比值显著降低(P < 0.01),骨质疏松症组与骨形态发生蛋白2组比较差异无显著性意义(P > 0.05)。与条件培养基组和骨形态发生蛋白2组相比,联合治疗组血清RANKL、OPG水平和RANKL/OPG比值显著降低(P < 0.01)。RANKL、OPG、RANKL/OPG的变化趋势见图3A。RANKL、OPG的蛋白和mRNA表达水平与ELISA结果具有相似的趋势,见图3B,C。因此,结果说明脂肪间充质干细胞成骨分化条件培养基联合骨形态发生蛋白2能够促进更多的骨形成。"
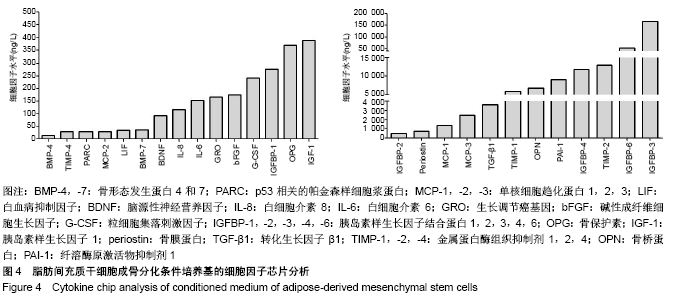
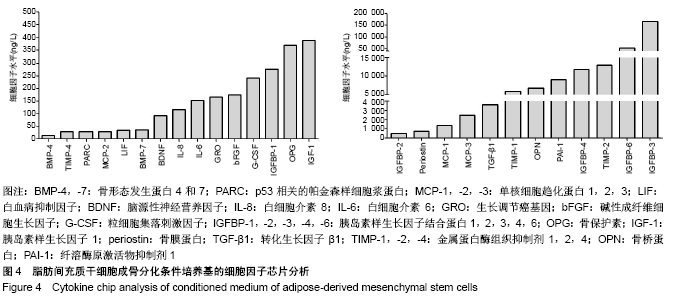
2.4 脂肪间充质干细胞成骨分化条件培养基的细胞因子分析 细胞因子芯片分析,见图4。脂肪间充质干细胞成骨分化条件培养基含有多种细胞因子,包括骨形态发生蛋白4和7(BMP4,7)、p53相关的帕金森样细胞浆蛋白(PARC)、单核细胞趋化蛋白1,2,3(MCP-1,-2,-3)、白血病抑制因子(LIF)、脑源性神经营养因子(BDNF)、白细胞介素8 (IL-8)、白细胞介素6(IL-6)、生长调节癌基因(GRO)、碱性成纤维细胞生长因子(bFGF)、粒细胞集落刺激因子(G-CSF)、胰岛素样生长因子结合蛋白1,2,3,4,6 (IGFBP-1,-2,-3,-4,-6)、骨保护素(OPG)、胰岛素样生长因子1(IGF-1)、骨膜蛋白(periostin)、转化生长因子β1 (TGF-β1)、金属蛋白酶组织抑制剂1,2,4(TIMP-1,-2,-4)、骨桥蛋白(OPN)、纤溶酶原激活物抑制剂1(PAI-1),这些因子对于骨形成和重塑是必不可少的。"
| [1] HIDAKA S, OKAMOTO Y, UCHIYAMA S, et al. Royal jelly prevents osteoporosis in rats: beneficial effects in ovariectomy model and in bone tissue culture model. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2006;3(3):339-348. [2] MCNAMARA LM. Perspective on post-menopausal osteoporosis: establishing an interdisciplinary understanding of the sequence of events from the molecular level to whole bone fractures. J R Soc Interface. 2010;7(44):353-372. [3] LAW YY, CHIU HF, LEE HH, et al. Consumption of onion juice modulates oxidative stress and attenuates the risk of bone disorders in middle-aged and post-menopausal healthy subjects. Food Funct. 2016;7(2):902-912. [4] TOGHRAIE FS, CHENARI N, GHOLIPOUR MA, et al. Treatment of osteoarthritis with infrapatellar fat pad derived mesenchymal stem cells in Rabbit. Knee. 2011;18(2):71-75. [5] TER HUURNE M, SCHELBERGEN R, BLATTES R, et al. Antiinflammatory and chondroprotective effects of intraarticular injection of adipose-derived stem cells in experimental osteoarthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 2012;64(11):3604-3613. [6] STRONG AL, OHLSTEIN JF, JIANG Q, et al. Novel daidzein analogs enhance osteogenic activity of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells and adipose-derived stromal/stem cells through estrogen receptor dependent and independent mechanisms. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014;5(4):105. [7] ZUK PA, ZHU M, ASHJIAN P, et al. Human adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol Cell. 2002;13(12): 4279-4295. [8] GIMBLE JM, KATZ AJ, BUNNELL BA. Adipose-derived stem cells for regenerative medicine. Circ Res. 2007;100(9):1249-1260. [9] PARK BS, KIM WS, CHOI JS, et al. Hair growth stimulated by conditioned medium of adipose-derived stem cells is enhanced by hypoxia: evidence of increased growth factor secretion. Biomed Res. 2010;31(1):27-34. [10] LEVI B, JAMES AW, NELSON ER, et al. Human adipose derived stromal cells heal critical size mouse calvarial defects. PLoS One. 2010;5(6):e11177. [11] MOHAMMADZADEH A, POURFATHOLLAH AA, SHAHROKHI S, et al. Immunomodulatory effects of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells on the gene expression of major transcription factors of T cell subsets. Int Immunopharmacol. 2014;20(2):316-321. [12] WANG X, LIU C, LI S, et al. Effects of continuous passage on immunomodulatory properties of human adipose-derived stem cells. Cell Tissue Bank. 2015;16(1):143-150. [13] TOMA C, WAGNER WR, BOWRY S, et al. Fate of culture- expanded mesenchymal stem cells in the microvasculature: in vivo observations of cell kinetics. Circ Res. 2009;104(3):398-402. [14] LEE SC, KIM JO, KIM SJ. Secretome from human adipose- derived stem cells protects mouse liver from hepatic ischemia-reperfusion injury. Surgery. 2015;157(5):934-943. [15] MARIE PJ, KASSEM M. Osteoblasts in osteoporosis: past, emerging, and future anabolic targets. Eur J Endocrinol. 2011; 165(1):1-10. [16] CAO JJ. Effects of obesity on bone metabolism. J Orthop Surg Res. 2011;6:30. [17] LU S, WANG J, Ye J, et al. Bone morphogenetic protein 9 (BMP9) induces effective bone formation from reversibly immortalized multipotent adipose-derived (iMAD) mesenchymal stem cells. Am J Transl Res. 2016;8(9):3710-3730. [18] 卫亚琳,牟代勇,廉静,等. BMP2诱导MEFs成骨分化中Notch信号的作用及机制研究[J].中国细胞生物学学报, 2018, 40(4): 478-489. [19] WANG YG, JIANG LB, GOU B. Protective effect of vanillic acid on ovariectomy-induced osteoporosis in rats. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2017;14(4):31-38. [20] WANG T, GUO S, LIU X, et al. Protective effects of adipose- derived stem cells secretome on human dermal fibroblasts from ageing damages. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2015; 8(12):15739-15748. [21] BURGE R, DAWSON-HUGHES B, SOLOMON DH, et al. Incidence and economic burden of osteoporosis-related fractures in the United States, 2005-2025. J Bone Miner Res. 2007;22(3): 465-475. [22] KURODA K, KABATA T, HAYASHI K, et al. The paracrine effect of adipose-derived stem cells inhibits osteoarthritis progression. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2015;16:236. [23] CHO SW, SUN HJ, YANG JY, et al. Human adipose tissue- derived stromal cell therapy prevents bone loss in ovariectomized nude mouse. Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(9-10):1067-1078. [24] LEE SM, LEE SC, KIM SJ. Contribution of human adipose tissue-derived stem cells and the secretome to the skin allograft survival in mice. J Surg Res. 2014;188(1):280-289. [25] WRIGHT KT, UCHIDA K, BARA JJ, et al. Spinal motor neurite outgrowth over glial scar inhibitors is enhanced by coculture with bone marrow stromal cells. Spine J. 2014;14(8):1722-1733. [26] LEE K, KIM H, KIM JM, et al. Systemic transplantation of human adipose-derived stem cells stimulates bone repair by promoting osteoblast and osteoclast function. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(10): 2082-2094. [27] THEOLEYRE S, WITTRANT Y, TAT SK, et al. The molecular triad OPG/RANK/RANKL: involvement in the orchestration of pathophysiological bone remodeling. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2004;15(6):457-475. [28] 韩小婉,宫世强,李雪虹,等. BMP2 表达上调剂E40071 体外抗骨质疏松活性研究[J].药学学报,2016, 51(3):396-402. [29] YE X, ZHANG P, XUE S, et al. Adipose-derived stem cells alleviate osteoporosis by enhancing osteogenesis and inhibiting adipogenesis in a rabbit model. Cytotherapy. 2014;16(12): 1643-1655. [30] SATO AY, CREGOR M, DELGADO-CALLE J, et al. Protection From Glucocorticoid-Induced Osteoporosis by Anti-Catabolic Signaling in the Absence of Sost/Sclerostin. J Bone Miner Res. 2016;31(10):1791-1802. [31] JIANG L, SONG J, HU X, et al. The Proteasome Inhibitor Bortezomib Inhibits Inflammatory Response of Periodontal Ligament Cells and Ameliorates Experimental Periodontitis in Rats. J Periodontol. 2017;88(5):473-483. [32] KURINAMI H, SHIMAMURA M, NAKAGAMI H, et al. A Novel Therapeutic Peptide as a Partial Agonist of RANKL in Ischemic Stroke. Sci Rep. 2016;6:38062. [33] YUAN Y, ZHANG L, TONG X, et al. Mechanical Stress Regulates Bone Metabolism Through MicroRNAs. J Cell Physiol. 2017; 232(6):1239-1245. [34] 颜春鲁,李盛华,安方玉,等.藤黄健骨胶囊对骨质疏松大鼠OPG/RANK/ RANKL调节轴的影响[J].解放军药学学报, 2018,34(3):217-220. [35] LEE K, KIM H, KIM JM, et al. Systemic transplantation of human adipose-derived stem cells stimulates bone repair by promoting osteoblast and osteoclast function. J Cell Mol Med. 2011;15(10): 2082-2094. [36] PEINADO JR, PARDO M, DE LA ROSA O, et al. Proteomic characterization of adipose tissue constituents, a necessary step for understanding adipose tissue complexity. Proteomics. 2012; 12(4-5): 607-620. [37] 史晶晶,周琼.老年2型糖尿病患者OPG和TNF-α水平与骨质疏松关系的探讨[J].医学理论与实践, 2019,32(4):585-586. [38] 张莉莉,王丽慧,胡淑国,等.2型糖尿病性骨质疏松大鼠骨组织IGF-1表达变化[J]. 河北医科大学学报,2019,40(5):512-515. [39] 杨璇璇,曹猛,杨振华,等.雌激素增强去势大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中Periostin的表达[J].牙体牙髓牙周病学杂志, 2016, 26(12):703-707. |
| [1] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [2] | Fan Quanbao, Luo Huina, Wang Bingyun, Chen Shengfeng, Cui Lianxu, Jiang Wenkang, Zhao Mingming, Wang Jingjing, Luo Dongzhang, Chen Zhisheng, Bai Yinshan, Liu Canying, Zhang Hui. Biological characteristics of canine adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells cultured in hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1002-1007. |
| [3] | Geng Yao, Yin Zhiliang, Li Xingping, Xiao Dongqin, Hou Weiguang. Role of hsa-miRNA-223-3p in regulating osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1008-1013. |
| [4] | Liu Bo, Chen Xianghe, Yang Kang, Yu Huilin, Lu Pengcheng. Mechanism of DNA methylation in exercise intervention for osteoporosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(5): 791-797. |
| [5] | Wang Yujiao, Liu Dan, Sun Song, Sun Yong. Biphasic calcium phosphate loaded with advanced platelet rich fibrin can promote the activity of rabbit bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 504-509. |
| [6] | Liu Jiangfeng. Nano-hydroxyapatite/polyamide 66 composite filling combined with locking plate in the treatment of fibrous dysplasia of femoral bone [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 542-547. |
| [7] | Ye Haimin, Ding Linghua, Kong Weihao, Huang Zutai, Xiong Long. Role and mechanism of hierarchical microchanneled bone scaffolds in promoting osteogenesis and angiogenesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(4): 621-625. |
| [8] | Chen Yang, Huang Denggao, Gao Yuanhui, Wang Shunlan, Cao Hui, Zheng Linlin, He Haowei, Luo Siqin, Xiao Jingchuan, Zhang Yingai, Zhang Shufang. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound promotes the proliferation and adhesion of human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(25): 3949-3955. |
| [9] | He Fan, Xiong Xiuli, Shan Xianfeng, Zhang Shutong, Hu Jian, Wang Xuejin. Guided bone regeneration in a small animal model of critical size craniofacial bone defects [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(20): 3226-3231. |
| [10] | Li Zhen, Huang Yonghui, Sun Jifu, Sun Haitao. Role and mechanism of focal adhesion kinase in inducing osteogenic differentiation of mouse embryonic fibroblasts cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(2): 165-171. |
| [11] | Guo Zhibin, Wu Chunfang, Liu Zihong, Zhang Yuying, Chi Bojing, Wang Bao, Ma Chao, Zhang Guobin, Tian Faming. Simvastatin stimulates osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2963-2968. |
| [12] | Zhang Jianhui, Ma Heran, Tan Yi, Wang Zhihui. Knee injury repair using human adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells-based scaffold-free three-dimensional gel-like construct in pigs [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2969-2975. |
| [13] | Zhang Shengmin, Cao Changhong, Liu Chao. Adipose-derived stem cells integrated with concentrated growth factors prevent bisphosphonate-related osteonecrosis of the jaws in SD rats [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 2982-2987. |
| [14] | Wang Liu, Song Dongzhe, Huang Dingming. Bone morphogenetic protein 9 regulates stem cell differentiation and bone regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3064-3070. |
| [15] | Chen Liang, Meng Shu, Cheng Guoping, Ding Yi . Effects of fish scale collagen membrane on adhesion, proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2494-2499. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||