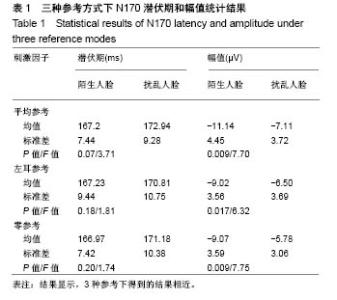
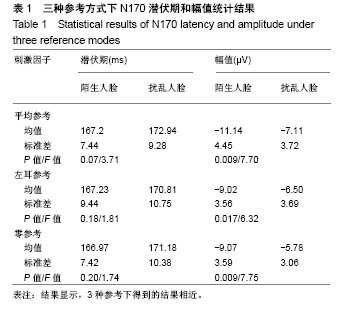
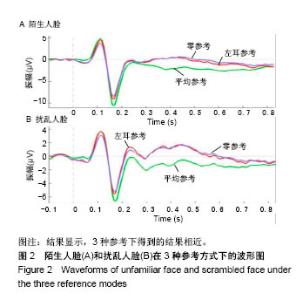
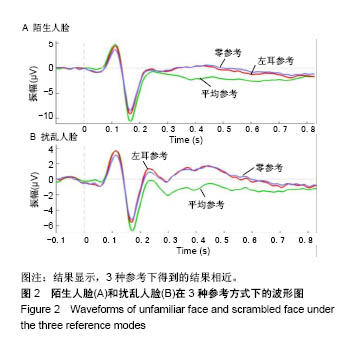
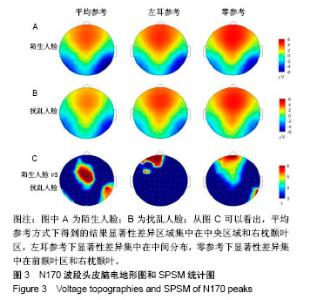
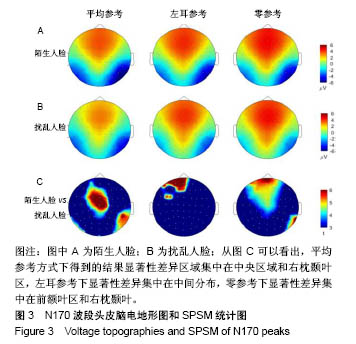
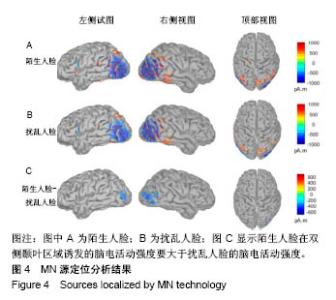
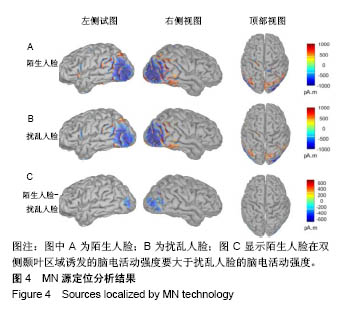
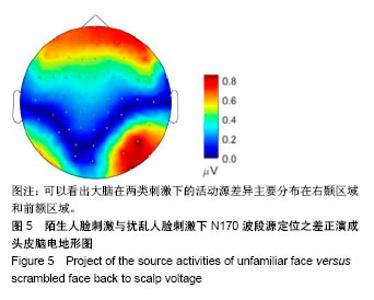
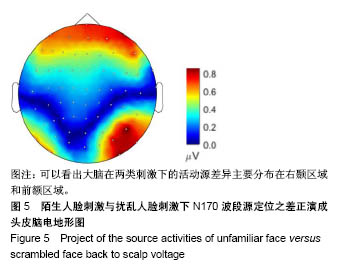
| [1]蒋辰伟.脑电和脑磁信号的处理与分析[D].上海:复旦大学, 2009.[2]Yao D. A method to standardize a reference of scalp EEG recordings to a point at infinity. Physiol Meas. 2001;22(4): 693-711.[3]Geselowitz DB.The zero of potential. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag. 1998;17(1):128-132.[4]Qin Y, Xu P, Yao D.A comparative study of different references for EEG default mode network: the use of the infinity reference. Clin Neurophysiol. 2010;121(12):1981-1991. [5]Chella F, Pizzella V, Zappasodi F, et al.Impact of the reference choice on scalp EEG connectivity estimation. J Neural Eng. 2016;13(3):036016.[6]Thatcher RW. Coherence, phase differences, phase shift, and phase lock in EEG/ERP analyses. Dev Neuropsychol. 2012; 37(6):476-496.[7]Nunez PL.REST: a good idea but not the gold standard. Clin Neurophysiol. 2010;121(12):2177-2180.[8]Yao D, Wang L, Arendt-Nielsen L, et al.The effect of reference choices on the spatio-temporal analysis of brain evoked potentials: the use of infinite reference. Comput Biol Med. 2007;37(11):1529-1538.[9]Nunez PL, Srinivasan R, Westdorp AF,et al.Cadusch, EEG coherency. I: Statistics, reference electrode, volume conduction, Laplacians, cortical imaging, and interpretation at multiple scales. Electroencephalogr Clin Neurophysiol. 1997; 103(5):499-515. [10]Cao X, Ma X, Qi C. N170 adaptation effect for repeated faces and words. Neuroscience. 2015;294:21-28.[11]Németh K, Zimmer M, Schweinberger SR,et al.The background of reduced face specificity of N170 in congenital prosopagnosia. PLoS One. PLoS One. 2014;9(7):e101393.[12]Zion-Golumbic E, Bentin S.Dissociated neural mechanisms for face detection and configural encoding: evidence from N170 and induced gamma-band oscillation effects. Cereb Cortex. 2007;17(8):1741-1749. [13]Wakeman DG, Henson RN.A multi-subject, multi-modal human neuroimaging dataset. Sci Data. 2015;2:150001.[14]Liu T, Mu S, He H, et al.The N170 component is sensitive to face-like stimuli: a study of Chinese Peking opera makeup. Cogn Neurodyn. 2016;10(6):535-541.[15]Balas B, Stevenson K.Children's neural response to contrast-negated faces is species specific. J Exp Child Psychol. 2014;119:73-86.[16]Lueschow A, Weber JE, Carbon CC, et al. The 170ms Response to Faces as Measured by MEG (M170) Is Consistently Altered in Congenital Prosopagnosia. PLoS One. 2015;10(9):e0137624. [17]Sagiv N,Bentin S.Structural Encoding of Human and Schematic Faces: Holistic and Part-Based Processes. J Cogn Neurosci. 2001;13(7):937-951. [18]Eimer M, Gosling A, Nicholas S,et al.The N170 component and its links to configural face processing: a rapid neural adaptation study. Brain Res. 2011;1376:76-87.[19]Eimer M. The face-specific N170 component reflects late stages in the structural encoding of faces. Neuroreport. 2000; 11(10):2319-2324. [20]Tian Y, Xu W, Zhang H, et al.The Scalp Time-Varying Networks of N170: Reference, Latency, and Information Flow. Front Neurosci. 2018;12:250.[21]Michel CM, Murray MM, Lantz G, et al.EEG source imaging. Clin Neurophysiol. 2004;115(10):2195-222.[22]Dundas EM, Plaut DC, Behrmann M.Behrmann, Variable left-hemisphere language and orthographic lateralization reduces right-hemisphere face lateralization. J Cogn Neurosci. 2015;27(5):913-25.[23]李明芳,张烨,张庆林, 面孔识别中脑电成分N170的研究概述[J].心理科学进展,2010,18(120:1942-1948.[24]Tian Y, Yao D.Why do we need to use a zero reference? Reference influences on the ERPs of audiovisual effects. Psychophysiology. 2013;50(12):1282-1290. [25]Yang P, Fan C, Wang M, et al.A Comparative Study of Average, Linked Mastoid, and REST References for ERP Components Acquired during Fmri. Front Neurosci. 2017;11: 247. |