Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (32): 5085-5091.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1480
Relationship between femoral head diameter and edge load under dynamic micro-separation of ceramic hip joints
Lian Chao, Zhang Maorong, Wang Junyuan, Cheng Bo, Liu Feng
- School of Mechanical Engineering, North University of China, Taiyuan 030051, Shanxi Province, China
-
Online:2019-11-18Published:2019-11-18 -
Contact:Liu Feng, Professor, School of Mechanical Engineering, North University of China, Taiyuan 030051, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Lian Chao, Master candidate, School of Mechanical Engineering, North University of China, Taiyuan 030051, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 21604074 (to CB)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lian Chao, Zhang Maorong, Wang Junyuan, Cheng Bo, Liu Feng. Relationship between femoral head diameter and edge load under dynamic micro-separation of ceramic hip joints[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5085-5091.
share this article
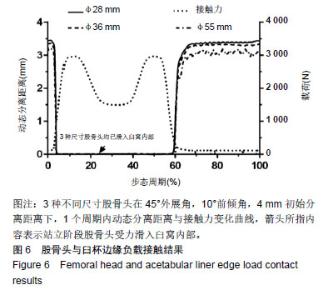
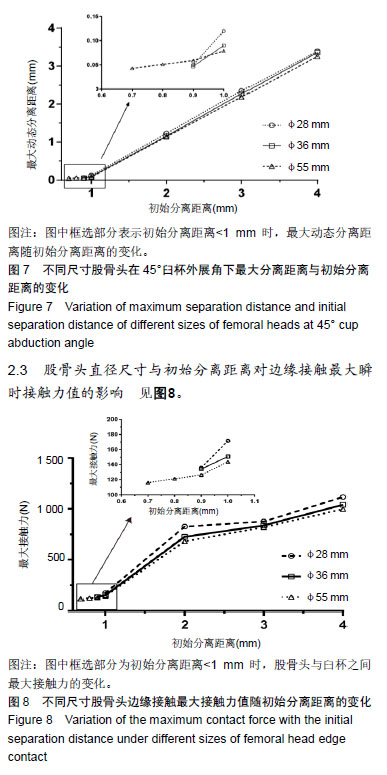
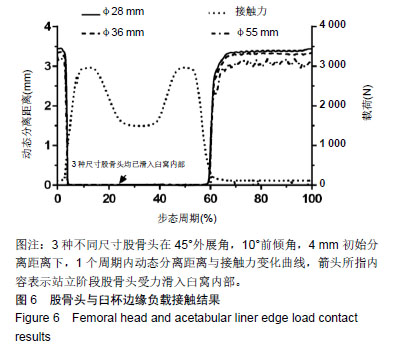
2.1 股骨头与臼杯边缘负载接触结果 3种尺寸股骨头与臼杯在一个稳定周期内的动态分离过程见图6。当动态分离距离为0 mm时,即人体处于站立状态,3种尺寸股骨头在地面给予的反作用力下均滑进臼窝内部,载荷2次峰值为 3 000 N,数值上基本与外载相同。当动态分离距离大于 0 mm时,受力开始减小,股骨头与臼杯发生分离,产生边缘接触现象。大概在步态周期的3%-5%处,是股骨头与臼杯发生边缘接触的临界位置,在这一时刻,股骨头受到地面给予的反作用力快速滑进臼窝,接触力瞬间增大,在臼杯边缘造成应力集中现象。股骨头与臼杯之间发生的边缘接触问题,是磨损量增大的主要原因,要想有效保护假体,延长人工关节寿命,就要尽可能的避免边缘接触现象。从图中还可以看出当初始分离距离为4 mm时,φ28 mm股骨头髋关节假体产生最大分离距离为3.38 mm,φ36 mm股骨头髋关节假体最大分离距离为3.36 mm,φ55 mm股骨头髋关节假体最大分离距离为3.26 mm。随着直径的增大,股骨头产生的最大分离距离有小幅减小。"
| [1]Mak M, Jin Z, Fisher J, et al. Influence of acetabular cup rim design on the contact stress during edge loading in ceramic-on-ceramic hip prostheses. J Arthroplasty. 2011; 26(1):131-136.[2]Hua X, Wang L, Al-Hajjar M, Jin Z, et al. Experimental validation of finite element modelling of a modular metal-on-polyethylene total hip replacement. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2014;228:682-692.[3]Brodner W, Grubl A, Jankovsky R, et al. Cup inclination and serum concentration of cobalt and chromium after metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2004; 19 :66-70.[4]冯莉,王俊元,刘峰,等. 陶瓷髋关节球头与臼杯分离引起边缘负载的动力学仿真模拟[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018,22(7): 985-990. [5]Hjorth MH, Mechlenburg I, Soballe K, et al. Higher prevalence of mixed or solid pseudotumors in metal-on-polyethylene total hip arthroplasty compared with metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty and resurfacing hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty. 2018;33(7):2279-2286.[6]Williams S, Butterfield M, Stewart T, et al. Wear and deformation of ceramic-on-polyethylene total hip replacements with joint laxity and swing phase microseparation. Proc Inst Mech Eng [H]. 2003;217:147-153.[7]Williams S, Butter S, Stewart T, et al. Wear and deformation of ceramic-on-polyethylene total hip replacements with joint laxity and swing phase microseparation. Proc Inst Mech Eng. 2003;217(2):147-153. [8]Komistek RD, Dennis DA, Ochoa JA, et al. In vivo comparison of hip separation after metal-on-metal or metal-onpolyethylene total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2002; 84:1836-1841.[9]Dennis DA , Komistek RD , Northcut EJ , et al. “In vivo” determination of hip joint separation and the forces generated due to impact loading conditions. J Biomech. 2001;34(5): 623-629.[10]Glaser D, Komistek RD, Cates HE, et al. Clicking and squeaking: in vivo correlation of sound and separation for different bearing surfaces. J Bone Joint Surgam. 2008; 90 Suppl 4 :112-120.[11]Nevelos J, Ingham C, Doyle R, et al. Micro-separation of the centers of alumina–alumina artificial hip joints during simulator testing produces clinically relevant wear rates and patterns. J Arthroplasty. 2000;15(6): 793-795.[12]Lusty PJ, Watson A, Tuke MA, et al. Wear and acetabular component orientation in third generation alumina-on-alumina ceramic bearings: an analysis of 33 retrievals. J Bone Jt Surg (Br). 2007;89B(9):1158-1164.[13]Al-Hajjar M, Fisher J, Tipper JL, et al. Wear of 36-mm BIOLOX (R) delta ceramic-on-ceramic bearing in total hip replacements under edge loading conditions. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2013;227(5):535-542. [14]Parkes M , Sayer K , Goldhofer M , et al. Zirconia phase transformation in retrieved, wear simulated, and artificially aged ceramic femoral heads. J Orthop Res. 2017;35(12): 2781-2789.[15]Saverio A , Francesco T , Aldo T . Microseparation and stripe wear in alumina-on-alumina hip implants. Int J Artif Organs. 2011; 34(6):506-512.[16]Wang L , Williams S , Udofia I , et al. The effect of cup orientation and coverage on contact mechanics and range of motion of metal-on-metal hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2012;226(11):877-886.[17]Fisher J. Bioengineering reasons for the failure of metal-on-metal hip prostheses: an engineer’s perspective. J Bone Joint Surg Br. 2011; 93: 1001-1004.[18]Bouziane MM , Benbarek S , Tabeti SMH , et al. Finite element analysis of the mechanical behaviour of the different cemented hip femoral prostheses. K Eng Mater. 2013; 577-578:349-352.[19]Affatato S, Zavalloni M, Spinelli M, et al. Long-term in-vitro wear performance of an innovative thermo-compressed cross-linked polyethylene. Tribol Int. 2010;43(102):22-28. [20]Ashkanfar A , Langton DJ , Joyce TJ. Does a micro-grooved trunnion stem surface finish improve fixation and reduce fretting wear at the taper junction of total hip replacements? A finite element evaluation. J Biomech. 2017;63:47-54.[21]Arirajan KA, Chockalingam K, Vignesh C. Selection of contact bearing couple materials for hip prosthesis using finite element analysis under static conditions//American Institute of Physics Conference Series. American Institute of Physics Conference Series, 2018.[22]Tan R, Fan H, Wu F, et al. Three-dimensional finite element analysis of bone stress distribution around the hip joint prosthesis with stepped stem. J Biomed Eng. 2011;28(4):732.[23]Polyakov A. Improving the finite element simulation of wear of total hip prosthesis’ spherical joint with the polymeric component. Procedia Engin. 2015;100:539-548.[24]Fouad H. In vitro evaluation of stiffness graded artificial hip joint femur head in terms of joint stresses distributions and dimensions: finite element study. J Mater Sci Mater Med. 2011;22(6):1589-1598. [25]Darwish SM , Al-Samhan AM. Optimization of artificial hip joint parameters. Materialwissenschaft Werkstofftechnik. 2009; 40(3):218-223.[26]Sariali E , Stewart T , Jin Z , et al. Three-dimensional modeling of in vitro hip kinematics under micro-separation regime for ceramic on ceramic total hip prosthesis: An analysis of vibration and noise. J Biomech. 2010;43(2): 326-333.[27]Leng J, Al-Hajjar M, Wilcox R, et al. Dynamic virtual simulation of the occurrence and severity of edge loading in hip replacements associated with variation in the rotational and translational surgical position. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2017;231(4):299-306.[28]Liu F, Feng L, Wang J. A computational parametric study on edge loading in ceramic-on-ceramic total hip joint replacements. J Mech Behav Biomed. 2018: S1751616118301292.[29]谢龙汉,蔡明京,苏延全,等.SolidWorks 2013三维设计全解视频讲解[M].北京:电子工业出版社,2013:1-167.[30]ISO14242-1Implants for surgery-wear of total hip-joint prostheses-Part1:Loading and displacement parameters for wear-testing machines and corresponding environmental conditions for test. ISO 14242-1:2012.[31]裴未迟,李耀刚,机技术-ADAMS的冲击力模型[J].河北理工大学学报,2008,30(4):59-63.[32]李增刚.ADAMS入门详解与实例[M].北京:国防工业出版社, 2014: 126-130.[33]Boer A, Ellenbroek MHM, Hemmes HK, et al. Contact mechanics in MSC Adams - A technical evaluation of the contact models in multibody dynamics software MSC Adams. Twente, 2011.[34]Antoine JF, Visa C, Abba G. Approximate analytical model for hertzian elliptical contact problem. Ttibol Int. 2006;128(3): 660-664.[35]Sanders AP , Brannon RM . Assessment of the applicability of the Hertzian contact theory to edge-loaded prosthetic hip bearings. J Biomech. 2011;44(16):2802-2808.[36]Tichy J. Contact mechanics and lubrication hydrodynamics of chemical-mechanical planarization. Ttribol Int. 2001;39(10): 63-68.[37]Mak MM, Besong AA, Jin ZM, et al. Effect of microseparation on contact mechanics in ceramic-on-ceramic hip joint replacements. Proc Inst Mech Eng H. 2002;216(6):403-408.[38]Liu F, Fisher J . Effect of an edge at cup rim on contact stress during micro-separation in ceramic-on-ceramic hip joints. Tribol Int. 2017:S0301679X17300129.[39]O'Dwyer Lancaster-Jones O, Williams S, Jennings LM, et al. An in vitro simulation model to assess the severity of edge loading and wear, due to variations in component positioning in hip joint replacements. J Biomed Mater Res B Appl Biomater. 2018;106(5):1897-1906.[40]Cooper HJ , Della Valle CJ . Large diameter femoral heads: is bigger always better? Bone Joint J. 2014; 96-B(11 Supple A):23-26. |
| [1] |
Zhang Cong, Zhao Yan, Du Xiaoyu, Du Xinrui, Pang Tingjuan, Fu Yining, Zhang Hao, Zhang Buzhou, Li Xiaohe, Wang Lidong.
Biomechanical analysis of the lumbar spine and pelvis in adolescent
idiopathic scoliosis with lumbar major curve |
| [2] | He Yujie, Wang Haiyan, Li Zhijun, Li Xiaohe, Cai Yongqiang, Dai Lina, Xu Yangyang, Wang Yidan, Xu Xuebin. Digital measurements of the anatomical parameters of pedicle-rib unit screw fixation in thoracic vertebrae of preschoolers [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(6): 869-876. |
| [3] | Sun Jian, Fang Chao, Gao Fei, Wei Laifu, Qian Jun. Clinical efficacy and complications of short versus long segments of internal fixation for the treatment of degenerative scoliosis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 438-445. |
| [4] | Xu Yangyang, Zhang Kai, Li Zhijun, Zhang Yunfeng, Su Baoke, Wang Xing, Wang Lidong, Wang Yidan, He Yujie, Li Kun, Wang Haiyan, Li Xiaohe. Morphological analysis of optimal selection of lumbar pedicle screws in adolescents aged 12-15 years [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(21): 3321-3328. |
| [5] | Qin Haikuo, Luo Shixing. Correlation of cortical bone thickness and X-ray gray value in different planes of proximal femur with brittle fracture of female hip [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(18): 2867-2872. |
| [6] | Huang Tianji, Yang Shengdong, Lin Hao, Zhang Chunyang, Deng Zhongqi, Zhong Weiyang, Luo Xiaoji. Mapping knowledge domains of bibliometrics regarding percutaneous vertebroplasty and percutaneous kyphoplasty based on VOSviewer [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(15): 2410-2417. |
| [7] | Qu Renfei, Mai Yuying, Chen Xiaowei, Hu Huanying, Chen Guozhi, Li Dongdong, Liao Hongbing. Relationship between lactic acid concentration and osteoclast differentiation of mouse monocytes [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(14): 2177-2183. |
| [8] | Liu Yapu, Lin Junyu, Yang Zhou, Wu Xiuhua, Wu Xiaoliang, Zhu Qing’an. Three-dimensional visualization and quantitative analysis of microvessels in rat cervical spinal cord using barium sulfate perfusion combined with micro-CT scanning [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(36): 5836-5840. |
| [9] | Gao Yangyang, Che Xianda, Han Pengfei, Liang Bin, Li Pengcui. Clinical efficacy of unicompartmental knee arthroplasty between robotic-assisted and conventional manual methods: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(36): 5889-5895. |
| [10] | Shao Yijie1, Jiang Huaye1, Gao Chao1, Luo Zongping2, Yang Huilin1. Effect of reduction of mechanical loading on subchondral bone and articular cartilage of early osteoarthritis in mice [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(35): 5611-5618. |
| [11] | Liu Hongwei, Jiang Junfeng, Zhang Yunkun, Xu Nanwei, Wang Caimei, Zhang Wen. Biomechanical comparison of personalized titanium femoral prosthesis fabricated by three-dimensional printing to four types of cementless prosthesis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(32): 5151-5157. |
| [12] | Shi Songyuan1, Peng Zhihui2. Current problems and potential treatment options for sports cartilage injury [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(31): 5059-5064. |
| [13] | Yi Guoliang, Wang Shankun, Song Xizheng. Biomechanical testing of the locking axial lumbosacral interbody fusion [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4546-4551. |
| [14] | Shen Yingshan, Gong Shuidi, He Xiaoming, Pang Fengxiang, Chen Xiaojun, Li Weifeng, Chen Lixin, Yang Fan, Yang Peng, Chen Zhenqiu, He Wei, Wei Qiushi. Research status and development trend of bibliometrics and visualization analysis in the assessment of Perthes disease [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(28): 4503-4509. |
| [15] | Liang Lichang1, 2, Fan Yawen1, 2, Mu Lei1, 2, Xie Tian1, 2, Jiang Xiaobing3, Ren Hui3, Zhang Tianfeng1. Changes of kidney in rat models of type 2 diabetes mellitus after administering Lizhong Decoction [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(27): 4356-4362. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||