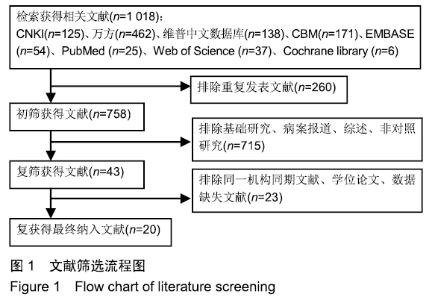
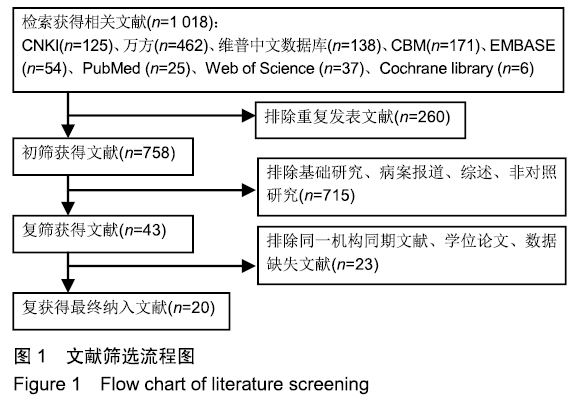
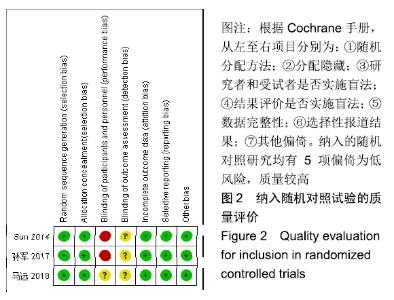
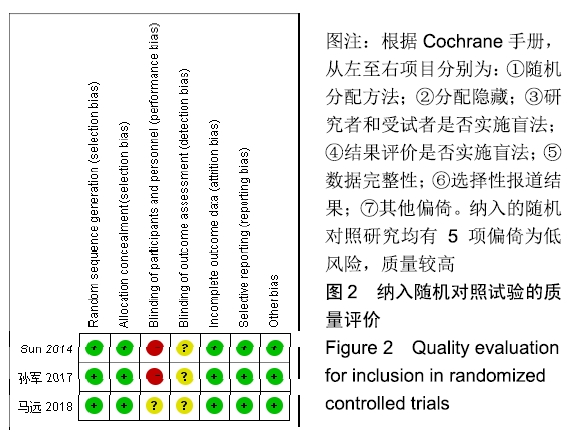
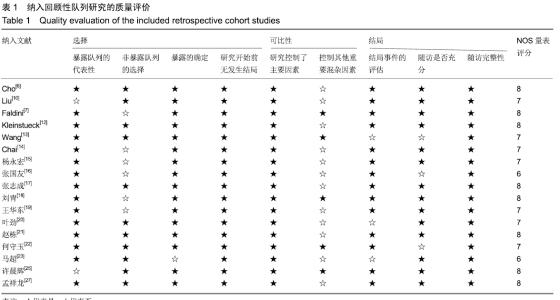
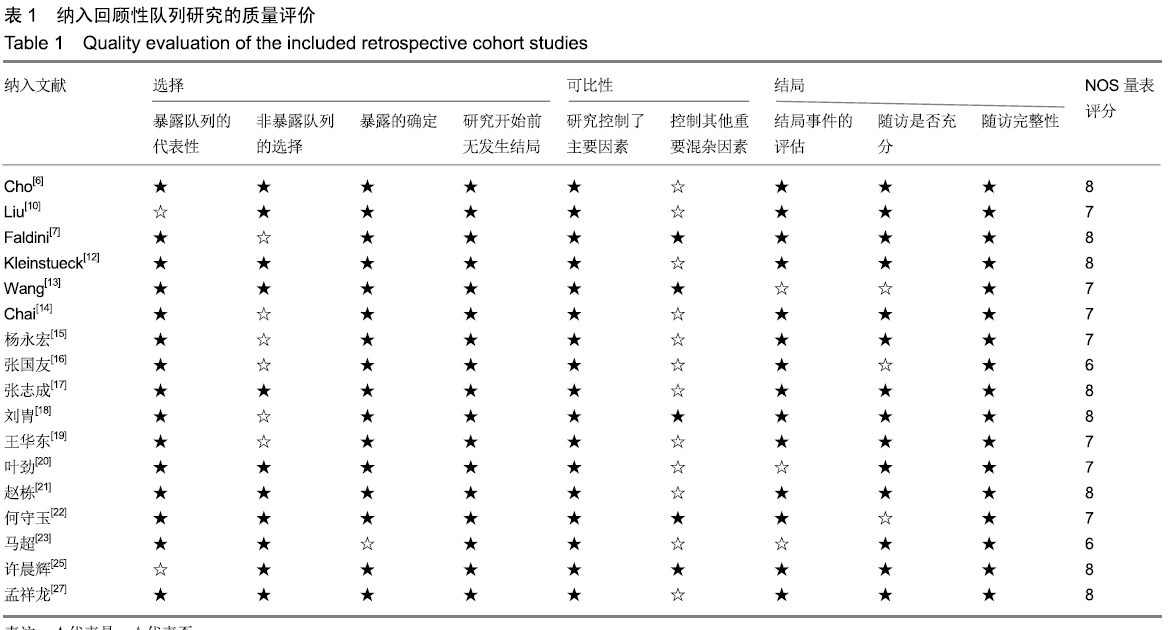
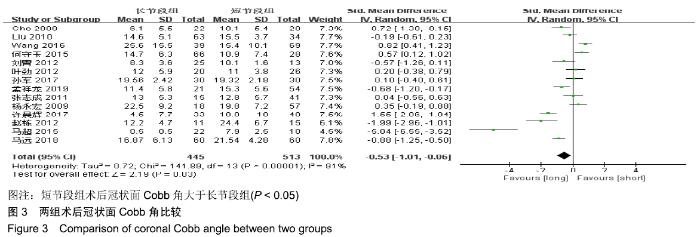
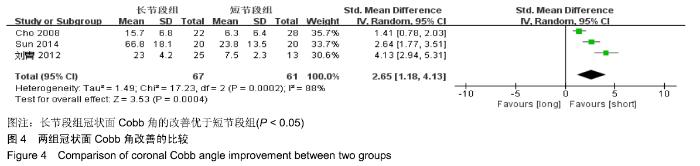
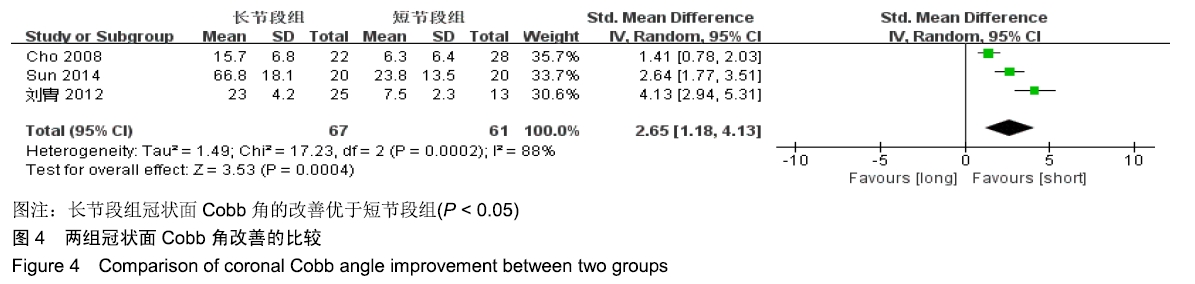
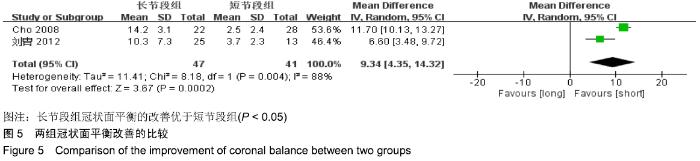
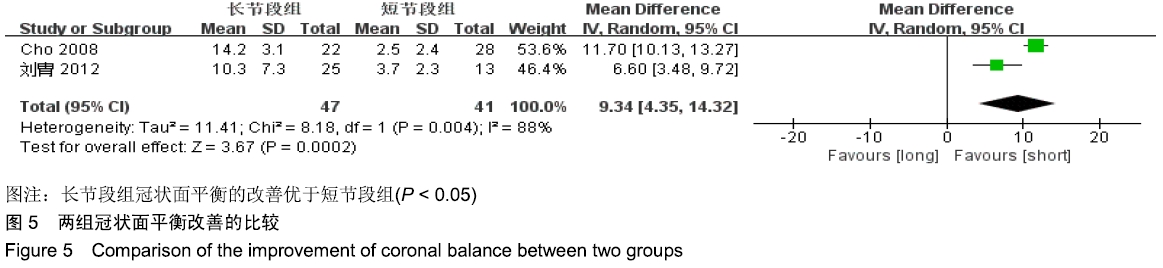Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (3): 438-445.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2418
Previous Articles Next Articles
Clinical efficacy and complications of short versus long segments of internal fixation for the treatment of degenerative scoliosis: a meta-analysis
Sun Jian1, Fang Chao1, Gao Fei2, Wei Laifu2, Qian Jun1, 2
- 1Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230601, Anhui Province, China; 2First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China
-
Received:2019-04-10Revised:2019-04-19Accepted:2019-06-12Online:2020-01-28Published:2019-12-27 -
Contact:Qian Jun, MD, Associate professor, Master’s supervisor, Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230601, Anhui Province, China; First Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230022, Anhui Province, China -
About author:Sun Jian, Master candidate, Second Affiliated Hospital of Anhui Medical University, Hefei 230601, Anhui Province, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81471273
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Sun Jian, Fang Chao, Gao Fei, Wei Laifu, Qian Jun. Clinical efficacy and complications of short versus long segments of internal fixation for the treatment of degenerative scoliosis: a meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(3): 438-445.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
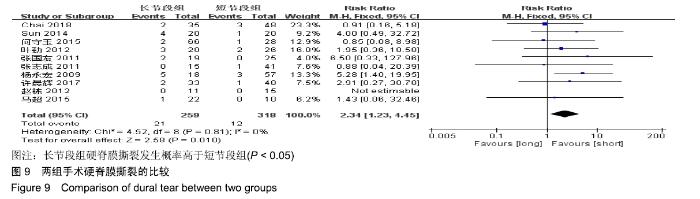
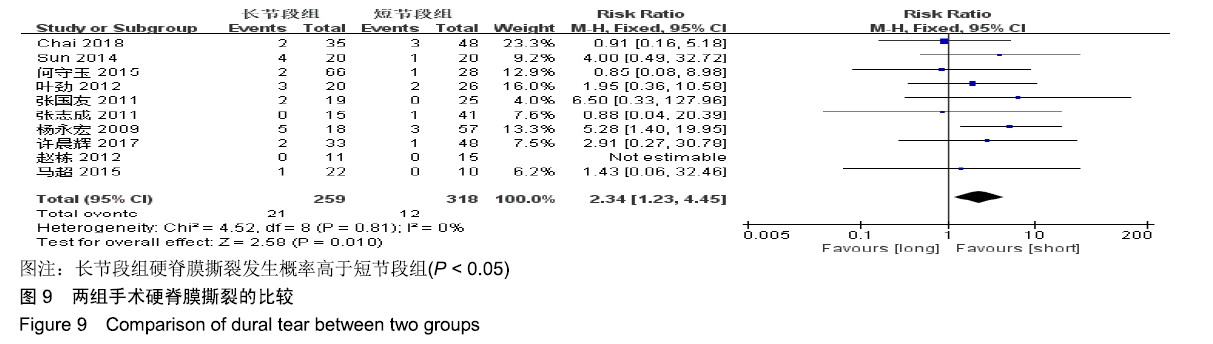
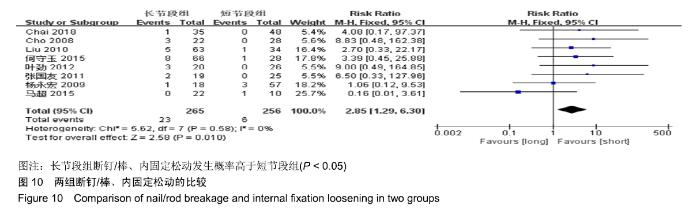
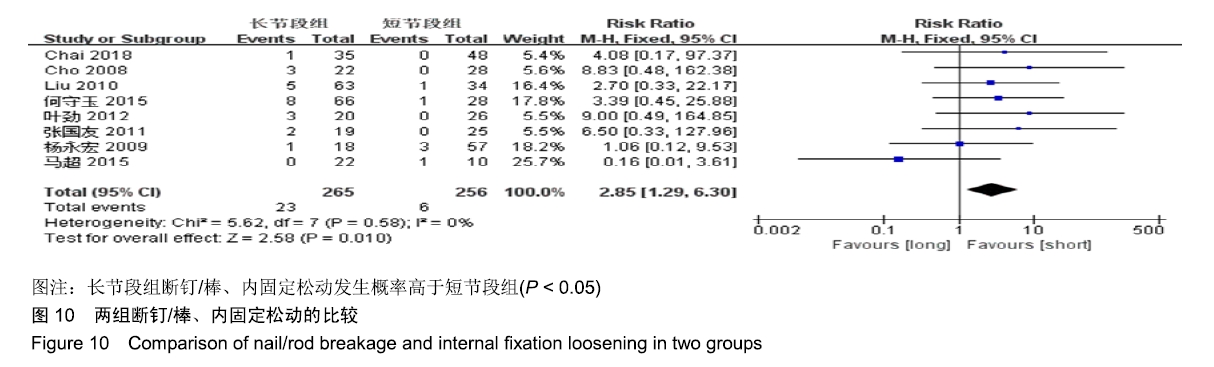
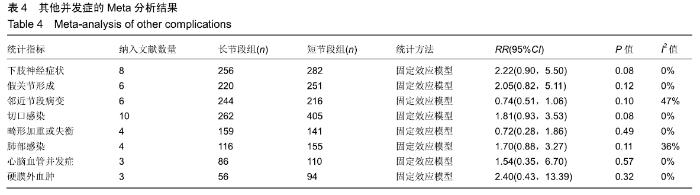
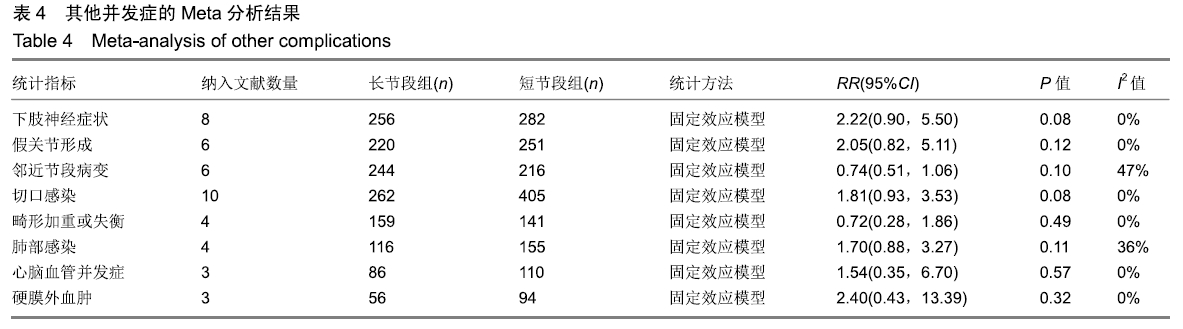
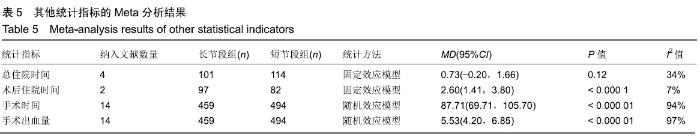
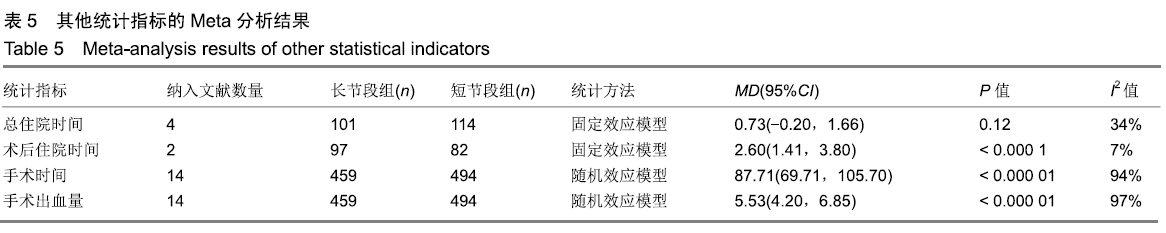
| [1] XIE D, ZHANG J, DING W, et al. Abnormal change of paravertebral muscle in adult degenerative scoliosis and its association with bony structural parameters. Eur Spine J. 2019. doi: 10.1007/s00586-019-05958-7. [2] EGUCHI Y, TOYOGUCHI T, INAGE K, et al. Analysis of skeletal muscle mass in women over 40 with degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2018. doi: 10.1007/s00586-018-5845-0. [3] BIRKNES JK, WHITE AP, ALBERT TJ, et al. Adult degenerative scoliosis: a review. Neurosurgery. 2008; 63(3 Suppl):94-103. [4] LIANG Y, ZHAO Y, WANG T, et al. Precision treatment of adult lumbar degenerative scoliosis complicated by lumbar stenosis with the use of selective nerve root block. World Neurosurg.2018;120: e970-e975. [5] PHAN K, XU J, MAHARAJ MM, et al. Outcomes of Short Fusion versus Long Fusion for Adult Degenerative Scoliosis: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Orthop Surg. 2017; 9(4): 342-349. [6] CHO K, SUK S, PARK S, et al. Short fusion versus long fusion for degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2008;17(5): 650-656. [7] FALDINI C, MARTINO A, BORGHI R, et al. Long vs. short fusions for adult lumbar degenerative scoliosis: does balance matters? Eur Spine J. 2015;24(7): 887-892. [8] 陆海涛,袁峰,杨宇明,等.短节段与长节段固定融合修复退变性脊柱侧凸的Meta分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,13(20): 1970-1976. [9] 罗益滨,王新伟,陈德玉.短节段与长节段内固定治疗退变性脊柱侧弯的Meta分析[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2017,32(1):44-48. [10] LIU W, CHEN XS, JIA LS, et al. The clinical features and surgical treatment of degenerative lumbar scoliosis: a review of 112 patients. Orthop Surg. 2010;1(3):176-183. [11] SUN Y, SHEN Y, DING W, et al. Comparison in Clinical Outcome of Two Surgical Treatments in Degenerative Scoliosis. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014; 70(1): 189-193. [12] KLEINSTUECK F, FEKETE T, JESZENSZKYD, et al. Adult degenerative scoliosis: comparison of patient-rated outcome after three different surgical treatments. Eur Spine J. 2016; 25(8): 2649-2656. [13] WANG G, CUI X, JIANG Z, et al. Evaluation and surgical management of adult degenerative scoliosis associated with lumbar stenosis. Medicine. 2016; 95(15): e3394. [14] CHAI Y, TIAN WM, LI Q, et al. Adult degenerative scoliosis: comparison of clinical outcome, reoperation rates and survivorship after three different surgical treatments. Int J Clin Exp Med. 2018;11(8): 8446-8452. [15] 杨永宏,郑杰,张冬生,等.长节段及短节段固定治疗退行性脊柱侧弯的比较[J].中国骨与关节损伤杂志,2009,24(7):613-615. [16] 张国友,李明,朱晓东,等.后路减压联合不同融合节段固定治疗退变性脊柱侧凸疗效分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2011,9(6):337-341. [17] 张志成,任大江,孙天胜,等.退变性腰椎侧凸合并椎管狭窄的阶梯性治疗策略[J].中国修复重建外科杂志,2011,25(8):951-955. [18] 刘胄,赵庆华,吴兴洲,等.短节段与长节段固定融合在退变性腰椎侧凸合并腰椎管狭窄症治疗的效果观察[J].中华医学杂志,2012, 92(25):1751-1755. [19] 王华东,侯树勋,史亚民,等.退变性腰椎侧凸两种手术方式的疗效观察[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2012,1(6):574-577. [20] 叶劲,龙厚清,陈应东,等.后路长、短节段固定结合有限减压治疗退变性腰椎侧凸的比较研究[J].中国临床解剖学杂志,2012, 30(5):568-572. [21] 赵栋,邓树才,孙志明,等.临床症状对退行性脊柱侧凸手术方案选择的影响[J].中华医学杂志,2012,92(17):1201-1205. [22] 何守玉,朱锋,邱勇,等. 长、短节段融合内固定治疗成人退变性脊柱侧凸并发症分析[J].中国骨与关节杂志,2015,4(3):176-181. [23] 马超,李利,史亚民,等.不同固定节段治疗中老年人退变性脊柱侧凸的疗效比较[J].中华老年医学杂志,2015,34(11):1186-1190. [24] 孙军,张亮.后路减压联合短节段或长节段固定融合治疗老年退变性脊柱侧凸疗效分析[J].川北医学院学报,2017,32(3):443-445. [25] 许晨辉,何阿祥,谢栋,等.长节段与短节段固定治疗退行性腰椎侧凸并椎管狭窄的短期临床疗效分析[J].脊柱外科杂志,2017, 16(6):321-325. [26] 马远.短节段和长节段固定融合术治疗脊柱退行性侧弯的疗效分析[J]. 河北医学,2018,24(9):1489-1494. [27] 孟祥龙,海涌,许刚,等.退变性脊柱侧凸固定节段选择不同的矢状位力线和疗效分析[J].中华医学杂志,2019,99(5):359-363. [28] ZHANG XN, SUN XY, HAI Y, et al. Incidence and risk factors for multiple medical complications in adult degenerative scoliosis long-level fusion. J Clin Neurosci. 2018;54:14-19. [29] HAI W, ZHANG Z, QIU G, et al. Risk factors of perioperative complications for posterior spinal fusion in degenerative scoliosis patients: a retrospective study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord. 2018;19(1): 242. [30] SILVA FE, LENKE LG. Adult degenerative scoliosis: evaluation and management. Neurosurg Focus. 2010;28(3): E1. [31] ZENG Y, WHITE AP, ALBERT TJ, et al. Surgical strategy in adult lumbar scoliosis: the utility of categorization into 2 groups based on primary symptom, each with 2-year minimum follow-up. Spine. 2012; 37(9): E556. [32] AEBI M. The adult scoliosis. Eur Spine J. 2005;14(10): 925-948. [33] DAFFNER SD, VACCARO AR. Adult degenerative lumbar scoliosis. Am J Orthop. 2003;32(2):77-82. [34] CHOI SW, AMES C, BERVEN S, et al. Contribution of lateral interbody fusion in staged correction of adult degenerative scoliosis. J Korean Neurosurg Soc.2018;61(6):716-722. [35] TEMPEL ZJ, GANDHOKE GS, BONFIELD CM, et al. Radiographic and clinical outcomes following combined lateral lumbar interbody fusion and posterior segmental stabilization in patients with adult degenerative scoliosis. Neurosurg Focus. 2014;36(5): E11. [36] KURRA S, LAVELLE WF, SILVERSTEIN MP, et al. Long-term outcomes of transforaminal lumbar interbody fusion in patients with spinal stenosis and degenerative scoliosis. Spine J. 2018; 18(6):1014-1021. [37] KIM DB, SHIN MH, KIM JT. Vertebral body rotation in patients with lumbar degenerative scoliosis: surgical implication for oblique lumbar interbody fusion. World Neurosurg. 2019. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu. 2018.12.073. [38] 赵兴,范顺武,方向前,等.斜外侧腰椎椎间融合术治疗成人退行性脊柱侧凸的近期疗效[J].中华骨科杂志,2017,37(16):989-996. [39] 孙浩林,李淳德,李绪文,等.多孔中空椎弓根螺钉骨水泥加强固定治疗合并骨质疏松症的腰椎退变性侧凸[J].北京大学学报(医学版), 2017,49(2):256-261. [40] 吴爱悯,陈栋,张凯,等. 长节段固定治疗成人退变性腰椎侧凸不同近端固定椎患者手术并发症和翻修情况的Meta分析[J].中国脊柱脊髓杂志,2018,28(11):995-1003. |
| [1] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [2] | Lu Dezhi, Mei Zhao, Li Xianglei, Wang Caiping, Sun Xin, Wang Xiaowen, Wang Jinwu. Digital design and effect evaluation of three-dimensional printing scoliosis orthosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1329-1334. |
| [3] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [4] | Du Xiupeng, Yang Zhaohui. Effect of degree of initial deformity of impacted femoral neck fractures under 65 years of age on femoral neck shortening [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1410-1416. |
| [5] | Zhang Shangpu, Ju Xiaodong, Song Hengyi, Dong Zhi, Wang Chen, Sun Guodong. Arthroscopic suture bridge technique with suture anchor in the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1417-1422. |
| [6] | Zhou Jihui, Li Xinzhi, Zhou You, Huang Wei, Chen Wenyao. Multiple problems in the selection of implants for patellar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1440-1445. |
| [7] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [8] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [9] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [10] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [11] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [12] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [13] | Xu Yulin, Shen Shi, Zhuo Naiqiang, Yang Huilin, Yang Chao, Li Yang, Zhao Heng, Zhao Lu. Biomechanical comparison of three different plate fixation methods for acetabular posterior column fractures in standing and sitting positions [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 826-830. |
| [14] | Hou Guangyuan, Zhang Jixue, Zhang Zhijun, Meng Xianghui, Duan Wen, Gao Weilu. Bone cement pedicle screw fixation and fusion in the treatment of degenerative spinal disease with osteoporosis: one-year follow-up [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 878-883. |
| [15] | He Li, Tian Wei, Xu Song, Zhao Xiaoyu, Miao Jun, Jia Jian. Factors influencing the efficacy of lumbopelvic internal fixation in the treatment of traumatic spinopelvic dissociation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 884-889. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||