Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2019, Vol. 23 ›› Issue (18): 2900-2908.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.1728
Previous Articles Next Articles
Preparation of agarose/gelatin/hyaluronic acid/extracellular matrix hydrogel and its property characterization
- 1School of Basic Sciences, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 2Shanxi Binda Stem Cell Technology Co., Ltd., Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; 3Shanxi Provincial Biomedical Health Graduate Education Innovation Center, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2019-02-19Online:2019-06-28Published:2019-06-28 -
Contact:Fu Songtao, Professor, School of Basic Sciences, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; Shanxi Binda Stem Cell Technology Co., Ltd., Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China; Shanxi Provincial Biomedical Health Graduate Education Innovation Center, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Li Jingjing, Master candidate, School of Basic Sciences, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030001, Shanxi Province, China
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Li Jingjing, Guo Xuan, Xie Jun, Huang Lei, Suo Jinrong, Fu Songtao. Preparation of agarose/gelatin/hyaluronic acid/extracellular matrix hydrogel and its property characterization[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2019, 23(18): 2900-2908.
share this article
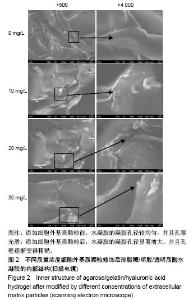
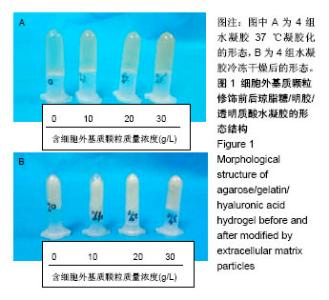
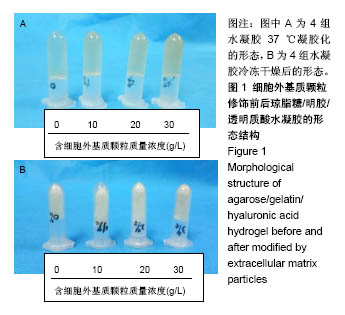
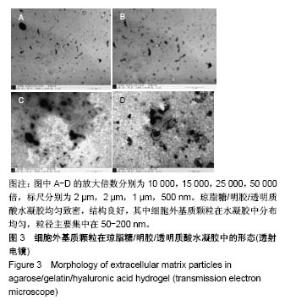
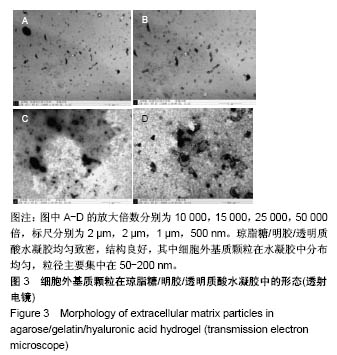
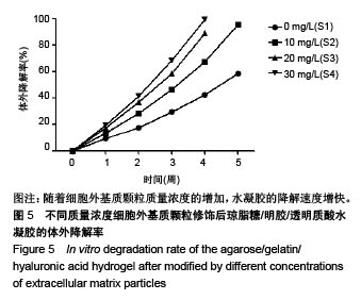
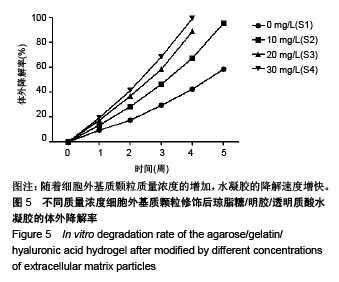
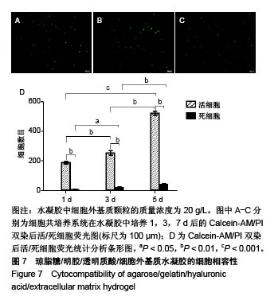
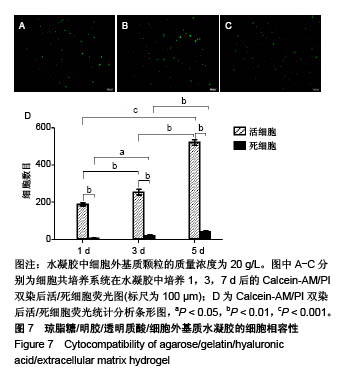
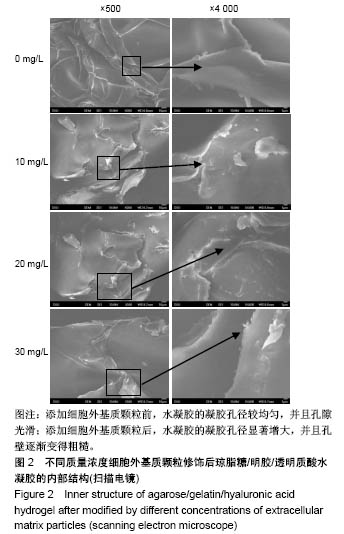
2.2 水凝胶支架及细胞外基质颗粒的超微结构 扫描电镜观察表明:4组样品均呈现高度互连且松散的不规则多孔网络结构,未添加细胞外基质颗粒水凝胶的凝胶孔径较均匀,并且孔隙光滑;添加细胞外基质颗粒后,通过光的透射情况可观察到水凝胶的凝胶孔径显著增大,并且孔壁逐渐变得粗糙,见图2,这可能是由于添加的细胞外基质颗粒本身是疏松多孔的结构,加入到水凝胶溶液后,部分水凝胶向细胞外基质颗粒内部多孔结构迁移,导致游离的水凝胶含量减少,即可形成水凝胶支架孔壁的含量减少,因而,水凝胶的凝胶孔径显著增大。孔壁变粗糙可能是较多的细胞外基质颗粒黏附在变薄的孔壁上造成的。以上结果说明细胞外基质颗粒的添加,会改变琼脂糖/明胶/透明质酸水凝胶的孔径大小和孔隙粗糙程度,改变其三维网络结构,故为确保水凝胶结构的稳定性,加入细胞外基质颗粒的量不能太高。"
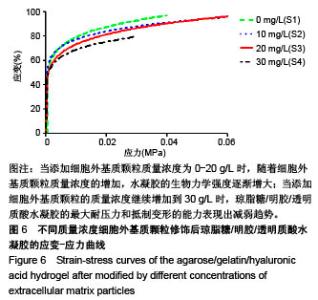
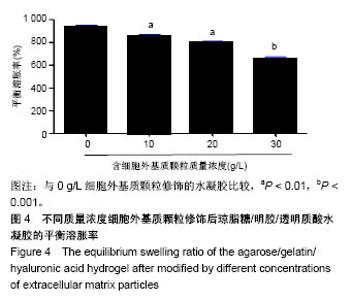
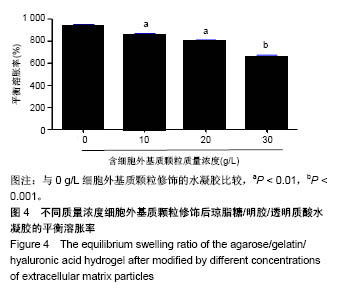
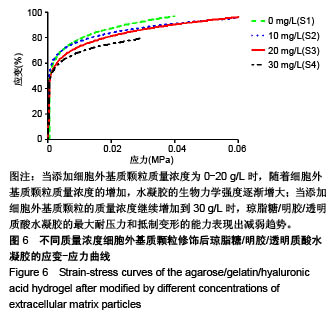
2.5 水凝胶的生物力学强度测试 加入适量细胞外基质颗粒,琼脂糖/明胶/透明质酸水凝胶的应力-应变行为明显得到了改善。当添加细胞外基质颗粒质量浓度为0-20 g/L时,随着细胞外基质颗粒质量浓度的增加,琼脂糖/明胶/透明质酸水凝胶的生物力学强度逐渐增大;当添加的细胞外基质颗粒质量浓度为20 g/L时,琼脂糖/明胶/透明质酸水凝胶拥有较大的耐压力(约为0.06 MPa)和较强的抵制变形能力;当添加细胞外基质颗粒的质量浓度继续增加到30 g/L时,琼脂糖/明胶/透明质酸水凝胶的最大耐压力和抵制变形的能力反而表现出减弱趋势,见图6。这可能是由于细胞外基质颗粒的添加,改变了琼脂糖/明胶/透明质酸水凝胶的交联度,造成其脆碎度增加,易产生碎裂现象。以上研究表明通过调控细胞外基质颗粒的添加量,可有效改善琼脂糖/明胶/透明质酸水凝胶的生物力学性能。"
| [1] Huckle J, Dootson G, Medcalf N, et al. Differentiated chondrocytes for cartilage tissue engineering. Novartis Found Symp.2003;249: 103-112. [2] 安勇,王丹亭,岳宏.基质诱导的自体软骨细胞移植治疗膝关节软骨损伤的研究进展[J].医学研究杂志,2017,46(7):177-180. [3] Min BH,Choi WH,Lee YS,et al.Effect of different bone marrow stimulation techniques (BSTs) on MSCs mobilization.J Orthop Res. 2013;31(11):1814-1819. [4] Bedi A,Feeley BT,Williams RJ 3rd.Management of articular cartilage defects of the knee. J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2010;92(4): 994-1009. [5] Chiang H,Liao CJ,Wang YH,et al.Comparison of articular cartilage repair by autologous chondrocytes with and without in vitro cultivation.Tissue Eng Part C Methods. 2010;16(2):291-300. [6] Langer R,Vacanti JP.Tissue Engineering.Science. 2000;260(5110): 920-926. [7] 神艳.骺板软骨组织工程支架的研究进展[J].中华小儿外科杂志, 2015, 36(5):397-400. [8] 张柏青,张仲文,孙磊.Ⅱ型胶原修饰脱细胞真皮基质胶原膜修复关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2017,21(6):871-876. [9] 陈维明.明胶/聚乳酸纳米纤维三维多孔支架的制备及应用于关节软骨组织再生[D].上海:东华大学,2017. [10] 李奇龙.一种光聚合PEGDA-HA水凝胶递送纳米粒药物用于非小细胞肺癌的治疗[D].上海:华东师范大学,2017. [11] 刘环宇,叶静仪,梁佩莹.水凝胶的制备[J].化工时刊, 2014,28(1):11-14. [12] 朱文,段世锋,丁建东.组织工程用水凝胶材料[J].功能高分子学报, 2004, 17(4):689-697. [13] Ninan N,Forget A,Shastri VP,et al.Antibacterial and Anti-Inflammatory pH-Responsive Tannic Acid-Carboxylated Agarose Composite Hydrogels for Wound Healing.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(42):28511-28521. [14] Singh YP,Bhardwaj N,Mandal BB.Potential of Agarose/Silk Fibroin Blended Hydrogel for in Vitro Cartilage Tissue Engineering.ACS Appl Mater Interfaces. 2016;8(33):21236-21249. [15] Zheng L,Sun J,Chen X,et al.In vivo cartilage engineering with collagen hydrogel and allogenous chondrocytes after diffusion chamber implantation in immunocompetent host.Tissue Eng Part A. 2009;15(8): 2145-2153. [16] Chao PH,Yodmuang S,Wang X,et al.Silk hydrogel for cartliage tissue enginee-ring.J Biomed Mater Res.2010;95(1):84-90. [17] Buwalda SJ,Boere KW,Dijkstra PJ,et al. Hydrogels in a historical perspective: from simple networks to smart materials.J Control Release.2014;190:254-273. [18] Smeets N,Bakaic E,Patenaude M,et al. Injectable poly(oligoethylene glycol methacrylate)-based hydrogels with tunable phase transition behaviours: physicochemical and biological responses. Acta Biomater. 2014;10(10):4143-4155. [19] Elias PZ,Liu GW,Wei H,et al.A functionalized, injectable hydrogel for localized drug delivery with tunable thermosensitivity:synthesis and characterization of physical and toxicological properties.J Control Release. 2015;208:76-84. [20] Lin C,Zhao P,Li F,et al.Thermosensitive in situ-forming dextran- pluronic hydrogels through Michael addition.Mater Sci Eng C. 2010;30(8):1236-1244. [21] Yu L,Ding J.Injectable hydrogels as unique biomedical materials. Chem Soc Rev. 2008;37(8):1473-1481. [22] Ni P, Ding Q, Fan M, et al.Injectable thermosensitive PEG-PCL- PEG hydrogel/acellular bone matrix composite for bone regeneration in cranial defects.Biomaterials. 2014;35(1):236-248. [23] Hudson SP, Langer R, Fink GR, et al. Injectable in situ cross-linking hydrogels for local antifungal therapy. Biomaterials. 2010;31(6): 1444-1452. [24] Li L, Wang N, Jin X, et al. Biodegradable and injectable in situ cross- linking chitosan-hyaluronic acid based hydrogels for postoperative adhesion prevention. Biomaterials. 2014;35(12): 3903-3917. [25] Xie B, Jin L, Luo Z, et al. An injectable thermosensitive polymeric hydrogel for sustained release of Avastin to treat posterior segment disease. Int J Pharm. 2015;490(1-2):375-383. [26] 倪培艳,罗静聪,钱志勇.可注射的温度敏感型水凝胶复合材料在骨组织工程中的应用研究[EB/OL]. 北京:中国科技论文在线[2012-02-22]. http://www.paper.edu.cn/releasepaper/content/201202-823. [27] 孙斌.可注射温敏壳聚糖/胶原/甘油磷酸钠水凝胶应用于骨组织工程的初步研究[D].北京:解放军军医进修学院,2011. [28] 赵守军,熊文化,许柯.细胞因子基因转染的骨骺干细胞复合明胶-硫酸软骨素-透明质酸钠支架修复大鼠骨骺生长板缺损的实验研究[J].中医正骨, 2018,30(2):10-15. [29] Tibbitt MW, Anseth KS. Hydrogels as extracellular matrix mimics for 3D cell culture. Biotechnol Bioeng. 2009;103:655–663. [30] Yin HY, Wang Y, Sun Z,et al.Induction of mesenchymal stem cell chondrogenic differentiation and functional cartilage microtissue formation for in vivo cartilage regeneration by cartilage extracellular matrix-derived particles. Acta Biomater.2016;33:96-109. [31] Buckley CT, Kelly DJ. Expansion in the presence of FGF-2 enhances the functional development of cartilaginous tissues engineered using infrapatellar fat pad derived MSCs. J Mech Behav Biomed Mater. 2012;11:102-111. [32] Pia M,Alexander T, Hagen Schmal,et al.Nanomechanics of Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells: Small GTPases Impact Chondrogenic Differentiation.Tissue Eng Part A. 2012;18(9-10): 1035-1044. [33] Diekman BO,Rowland CR,Lennon DP,et al.Chondrogenesis of adult stem cells from adipose tissue and bone marrow: induction by growth factors and cartilage-derived matrix.Tissue Eng Part A. 2010;16: 523-533. [34] Almeida HV,Eswaramoorthy R,Cunniffe GM,et al.Fibrin hydrogels functionalized with cartilage extracellular matrix and incorporating freshly isolated stromal cells as an injectable for cartilage regeneration. Acta Biomater. 2016;36:55-62. [35] Masaeli E,Karamali F,Loghmani S,et al.Bio-engineered electrospun nanofibrous membranes using cartilage extracellular matrix particles. Mater Chem B.2017;5:765-776. [36] 张莹莹,宫赫.骨支架材料性能的影响因素及其制备方法[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2015,32(2):480-484. [37] 刘威,于晓巍.天然来源可注射水凝胶修复软骨缺损的研究进展[J].国际骨科学杂志,2018,39(2):81-84. [38] 刘杰,周浩,黄郁芳,等.大豆分离蛋白/琼脂糖复合水凝胶[J].高等学校化学学报,2018,39(3):591-597. [39] 朱琳,贺健康,刘亚雄,等.琼脂糖/胶原复合水凝胶的制备及性能研究[J].西安交通大学学报,2013,47(10):121-126. [40] Karim A, Hall AC.Chondrocyte Morphology in Stiff and Soft Agarose Gels and the Influence of Fetal Calf Serum.J Cell Physiol. 2017;232(5): 1041-1052. [41] Li H,Fan J,Sun L,et al.Functional regeneration of ligament-bone interface using a triphasic silk-based graft.Biomaterials. 2016;106: 180-192. [42] Kundu B,Rajkhowa R,Kundu SC,et al. Silk fibroin biomaterials for tissue regenerations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2013;65(4):457-470. [43] Ng VW,Chan JM,Sardon H,et al.Antimicrobial hydrogels: A new weapon in the arsenal against multidrug-resistant infections. Adv Drug Deliv Rev.2014;78:46-62. [44] Ulrich TA,Jain A,Tanner K,et al.Probing cellular mechanobiology in three-dimensional culture with collagen-agarose matrices. Biomaterials. 2010;31(7):1875-1884. [45] 刘威,俞牧雨,于晓巍.可注射RGD功能化的透明质酸果胶水凝胶促进体外成软骨的研究[J].国际骨科学杂志, 2018,39(3):180-186. [46] Huang YX,Zhang XL, Wu AM,et al.An injectable nano-hydroxyapatite (n-HA)/glycol chitosan (G-CS)/hyaluronic acid (HyA) composite hydrogel for bone tissue engineering.RSC Adv. 2016;6:33529-33536. [47] Girotto D,Urbani S,Brun P,et al.Tissue specific gene expression in chondrocytes grown on three-dimensional hyaluronic acid scaffolds. Biomaterials. 2003;24(19):3265-3275. [48] Jakobsen RB,Shahdadfar A,Reinholt FP,et al. Chondrogenesis in a hyaluronic acid scaffold: comparison between chondrocytes and MSC from bone marrow and adipose tissue. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc. 2010;18:1407-1416. [49] Liu X,Yang Y,Niu X.An in situ photocrosslinkable platelet rich plasma - Complexed hydrogel glue with growth factor controlled release ability to promote cartilage defect repair. Acta Biomater. 2017; 62:179-187. [50] Mauck RL,Nicoll SB,Seyhan SL,et al.Synergistic action of growth factors and dynamic loading for articular cartilage tissue engineering. Tissue Eng.2003;9(4):597-611. [51] Barry F,Boynton RE,Liu B,et al.Chondrogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells from bone marrow:differentiation-dependent gene expression of matrix components.Exp Cell Res. 2001;268(2):189-200. [52] Li WJ,Tuli R,Okafor C,et al.A three-dimensional nanofibrous scaffold for cartilage tissue engineering using human mesenchymal stem cells.Biomaterials.2005;26(6):599-609. [53] Van Susante JL,Buma P,van Beuningen HM,et al. Responsiveness of bovine chondrocytes to growth factors in medium with different serum concentrations.J Orthop Res.2000;18(1):68-77. [54] Schalkwijk J,Joosten LA,van den Berg WB,et al.Insulin-like growth factor stimulation of chondrocyte proteoglycan synthesis by human synovial fluid. Arthritis Rheum. 1989;32(1):66-71. [55] Fortier LA,Nixon AJ,Lust G.Phenotypic expression of equine articular chondrocytes grown in three-dimensional cultures supplemented with supraphysiologic concentrations of insulin-like growth factor-1.Am J Vet Res. 2002;63(2):301-305. [56] Holden P,Meadows RS,Chapman KL,et al.Cartilage oligomeric matrix protein interacts with type IX collagen , and disruptions to these interactions identify a pathogenetic mechanism in a bone dysplasia family.J Biol Chem. 2001;276(8):6046-6055. [57] 毛艳,张西正.软骨组织工程中细胞外基质的研究[J].中国临床康复, 2006, 10(2):152-155. [58] Liu C, Liu D, Wang Y, et al.Glycol chitosan/oxidized hyaluronic acid hydrogels functionalized with cartilage extracellular matrix particles and incorporating BMSCs for cartilage repair. Artif Cells Nanomed Biotechnol. 2018;46(1):721-732. [59] Li H,Ghazanfari R,Zacharaki D,et al.Isolation and characterization of primary bone marrow mesenchymal stromal cells.Ann N Y Acad Sci.2016;1370(1):109-118. [60] 荣为为,韩明子,金世柱,等.骨髓间充质干细胞在组织工程研究中的应用新进展[J].现代生物医学进展,2017,17(5):982-992. [61] 方洪松,周建林,彭昊.组织工程支架材料修复关节软骨缺损[J].中国组织工程研究,2016,20(52):7891-7898. [62] Lv YM,Yu QS. Repair of articular osteochondral defects of the knee joint using a composite lamellar scaffold. Bone Joint Res.2015;4(4): 56-64. [63] Ma X,Sun Y,Cheng X,et al.Repair of osteochondral defects by mosaicplasty and allogeneic BMSCs transplantation.Int J Clin Exp Med. 2015;8(4):6053-6059. [64] Yamasaki S,Mera H,Itokazu M,et al.Cartilage Repair With Autologous Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell Transplantation: Review of Preclinical and Clinical Studies. Cartilage.2014;5(4):196-202. [65] Chen WH,Lai MT, Wu AT,et al.In vitro stage-specific chondrogenesis of mesenchymal stem cells committed to chondrocytes.Arthritis Rheum. 2009;60(2):450-459. [66] Dahlin RL,Ni M,Meretoja VV,et al.TGF-β3 induced chondrogenesis in co-cultures of chondrocytes and mesenchymal stem cells on biodegradable scaffolds. Biomaterials.2014;35(1):123-132. |
| [1] | Wang Hao, Chen Mingxue, Li Junkang, Luo Xujiang, Peng Liqing, Li Huo, Huang Bo, Tian Guangzhao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Guo Quanyi, Lu Xiaobo. Decellularized porcine skin matrix for tissue-engineered meniscus scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(22): 3473-3478. |
| [2] | Yang Tengyun, Li Yanlin, Liu Dejian, Wang Guoliang. Application prospects and problems of peripheral blood derived mesenchymal stem cells in cartilage repair of osteoarthritis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(19): 3071-3076. |
| [3] | Fu Liwei, Yang Zhen, Li Hao, Gao Cangjian, Sui Xiang, Liu Shuyun, Guo Quanyi . New strategies and problems of affinity peptide in cartilage tissue engineering [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(16): 2569-2574. |
| [4] | Liu Zhigang, Guo Qinggong, Chen Jingtao. Effect of Capparis spinosa total alkaloid on proliferation and apoptosis of nucleus pulposus cells in an intervertebral disc degeneration rat model [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1699-1704. |
| [5] | Luo Yaxin, Bi Haoran, Chen Xiaoxu, Yang Kun. Extracellular matrix and tissue engineering regeneration and repair [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(11): 1785-1790. |
| [6] | Li Junqi, Tian Guangzhao, Chen Mingxue, Wang Hao, Liu Shuyun, Sui Xiang, Huang Jingxiang, Li Ming, Guo Quanyi. Regulatory effect of acellular cartilage extracellular matrix on phenotype of mouse macrophage line [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1512-1516. |
| [7] | Guo Haoyu, Li Weiquan, Liu Kaiyuan, Xiao Ruifen, Sun Denglong, Xi Jiaoya. Recent research progress in construction of biomimetic engineered cardiac tissue based on extracellular matrix [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(10): 1577-1584. |
| [8] | Wu Ming, Zhang Yan. Related factors regulating osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 116-122. |
| [9] | Liu Chunyu, Han Xiaoyan, Wang Lin. Basic science related to tendinopathy: microbiomechanics and stress shielding [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(5): 766-772. |
| [10] | Qin Wenpin, Yang Yujie, Zhao Laihe, Shi Xiaowei, Lu Lei, Yang Hongxu, Huang Jinghui. Hemorrhage control of fluid gelatin SurgifloTM versus gelatin sponge in lumbar spine fusion surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(4): 561-565. |
| [11] | Wang Zhihao, Wu Cong, Wu Sihua, Shi Hongcan. Application and characteristics of decellularization technology in tissue engineered trachea [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5695-5700. |
| [12] | Yang Wenxiao, Yang Ning, Liu Yao. Immunomodulation of extracellular matrix and its role in tissue regeneration [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(35): 5701-5707. |
| [13] | He Jing, Ao Qiang. Research hotspots in tissue decellularization method for manufacturing extracellular matrices [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5413-5420. |
| [14] | Fang Yulu, Yi Bingcheng, Shen Yanbing, Tang Han, Zhang Yanzhong. Potential of corn husk fibers reinforced chitosan-based hydrogels in cartilage tissue engineering scaffold [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(34): 5493-5501. |
| [15] | Cheng Xue, Fang Hong, Zhang Yunke, Wu Yingen. Interventional mechanism of Feibi prescription on extracellular matrix transformation in a mouse model of pulmonary fibrosis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(31): 5038-5043. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||