Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2021, Vol. 25 ›› Issue (1): 116-122.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2158
Previous Articles Next Articles
Related factors regulating osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway
Wu Ming1, Zhang Yan2
- 1Postgraduate Training Base, Shanghai Pudong New Area Gongli Hospital, Ningxia Medical University, Shanghai 200120, China; 2Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong New Area Gongli Hospital, Shanghai 200120, China
-
Received:2020-03-12Revised:2020-03-18Accepted:2020-04-25Online:2021-01-08Published:2020-11-19 -
Contact:Zhang Yan, MD, Chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Shanghai Pudong New Area Gongli Hospital, Shanghai 200120, China -
About author:Wu Ming, Master candidate, Postgraduate Training Base, Shanghai Pudong New Area Gongli Hospital, Ningxia Medical University, Shanghai 200120, China -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China, No.81772383; the Outstanding Leaders Training Program of Pudong Health Bureau of Shanghai, No. PWRL2019-01; the Medical Discipline Construction Project of Pudong New Area, No. PWYts2018-03
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wu Ming, Zhang Yan. Related factors regulating osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells through Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(1): 116-122.
share this article
Add to citation manager EndNote|Reference Manager|ProCite|BibTeX|RefWorks
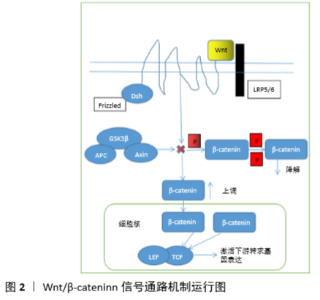
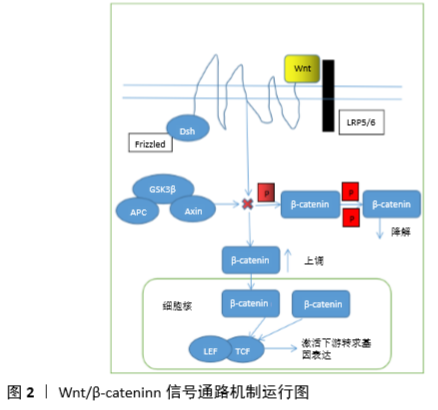
2.1 骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化及其作用 骨髓间充质干细胞是成骨前体细胞的主要来源,在一定的诱导条件下可以分化成骨细胞[4]。骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化能力受损是导致骨再生修复、骨塑建过程失衡的关键因素。目前大多研究都是各种因素对效果的影响,但其分化过程的具体分子调控机制鲜有报道,成为骨髓间充质干细胞临床应用促进骨修复和骨质疏松症防治的主要瓶颈。骨是一个动态的组织,不断地通过成骨细胞介导的骨形成和破骨细胞介导的骨吸收实现重建[5]。在正常生理条件下,骨形成和骨吸收紧密耦合,维持骨骼动态平衡并不断更新。在病理情况下,伴随着骨髓的脂肪化,成骨细胞的生成受到抑制,最终引起骨质流失[6]。 2.2 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的机制 Wnt/β-catenin信号通路参与调控多种生物学过程,在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化机制中起重要作用。Wnt胞内信号传递途径是一类重要的传导生长刺激信号的通路,其作用机制是细胞表面基质及其特异性受体的激活,通过下游一系列分子蛋白的磷酸化与去磷酸化来完成Wnt信号的传递,当胞外Wnt缺乏或者其受体被抑制时,降解复合体与β-catenin相互作用,APC和Axin做为支架使GSK3β与β-catenin结合,β-catenin能够被CK1和GSK3β持续性的磷酸化,然后被泛素化降解[7];当Wnt蛋白与Frizzled及LRP5/6结合后,通过Disheveled产生Axin和Frat-1抑制蛋白降解复合体的形成,并抑制GSK3β的活性,导致β-catenin不能被降解而在胞质中堆积转移入细胞核,作为转录共激活子与TCF和LEF相互作用,开启下游相关基因的表达调控,见图2。 2.3 不同类型影响因素通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的机制 从干细胞的发现到干细胞的分类研究越来越细化,单纯的单因素促进干细胞分化已经不能满足目前的研究和干细胞治疗的需要,只有更细化的研究,通过单因素分析了解他们的机制,从而了解单因素之间的联系,以及各种因素在同一种通道里产生的作用,甚至是激活单一信号通路后又自动启动另一通路的关系,理清这些机制通路的关系,有助于明确干细胞分化机制研究思路,为临床治疗提供更好的方案。 2.4 药物通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响骨髓间充质干细胞分化 2.4.1 中药对于骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响及其机制 传统中药治疗骨质疏松一直缺乏科学证据,随着科学研究的深入,中药治疗骨质疏松的科学证据逐渐增多,并证明Wnt/β-catenin信号通路是影响骨髓间充质干细胞成骨、成脂分化的关键信号通路。依香叫等[8]研究发现刺老苞根皮含药血清各剂量组可促进原代成骨细胞矿化形成,上调β-catenin、Frizzed-2的mRNA和蛋白表达,下调Axin的mRNA和蛋白表达,增强成骨细胞的分化和增殖。罗智等[9]研究发现葛根素对成骨细胞的体外增殖活性具有显著促进作用,葛根素能增加碱性磷酸酶(ALP)、RUNX2的表达量且呈剂量依赖性,同时通过激活Wnt/β-catenin通路来促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化及增殖。骨碎补活性成分骨碎补黄酮已被证实可上调关键物质Runx-2和碱性磷酸酶的表达水平,并在体外促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨方向的增殖和分化[10]。此外,陈云钢等[11]采用不同剂量的骨碎补含药血清干预骨髓间充质干细胞的生长过程,结果表明骨碎补含药血清促进了Wnt/β-catenin通路活性,使骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨方向分化。李晨睿等[12]研究显示原代鼠骨髓间充质干细胞分别经1,10,50 μmol/L黄芩苷处理3 d后,采用Western blot检测β-catenin和Runx2蛋白表达水平,结果显示黄芩苷仅在10 μmol/L浓度下能明显提高Runx2的表达,而在不同给药浓度时,黄芩苷均能提高β-catenin的蛋白表达。张哲等[13]研究显示老鹳草素实验组的Runx2、β-catenin、Axin2 mRNA及蛋白表达量较对照组明显上调,GSK-3β的蛋白和mRNA表达较对照组明显下调且呈剂量依赖性。添加DKK1后,碱性磷酸酶活性及OCN含量明显降低,同时Runx2、Axin2、β-catenin的mRNA和蛋白表达明显下调,GSK-3β的mRNA和蛋白表达明显上调。老鹳草素能够明显通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路促进骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖及向成骨方向分化。WEI等[14]研究显示淫羊藿苷在0.1 mmol/L浓度显著促进骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和成骨分化,通过雌激素受体和二十碳素激活Wnt/β-catenin途径可以促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。李新建[15]研究发现补肾活血汤对兔激素过多导致的股骨头坏死有治疗作用,促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨分化,而调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的主要机制是通过增强Wnt/β-catenin信号通路中成骨因子FZD6、Ror2和β-catenin的蛋白和基因表达及抑制sFRP4、DDK1的表达来实现的。 2.4.2 西药对于骨髓间充质干细胞成骨及成脂分化的影响及其机制 目前临床上治疗骨质疏松的西药比较少,效果也存在不足,通过对西药治疗骨质疏松症的机制研究,有助于进一步开发出更好的药物。马忠平等[16]研究显示在体外贝尼地平能通过增强Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的活性使骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化,这对高血压合并骨质疏松症患者而言是一个良好治疗药物,LRP5和β-catenin作为Wnt/β-catenin信号通路内关键正性调控蛋白,其表达水平的提高说明Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的活性显著增强。ZHAO等[17]研究显示6-溴代二异丁酸酯 3’-肟(6-Bromoindirubin-3’-oxime,BIO)上调GSK3β磷酸化并抑制其活性,从而激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,促进犬骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化, 1.0 μmol/L BIO对骨髓间充质干细胞分化的影响强于 0.5 μmol/L BIO。BIO上调GSK3β磷酸化并抑制其活性从而激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,促进犬骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。ZHU等[18]研究发现Catalpol可显著提高骨髓间充质干细胞中的成骨细胞特异性基因表达,增强碱性磷酸酶活性和钙沉积。由Catalpol 治疗而增强的成骨作用被Wnt/β-catenin拮抗剂部分逆转。Catalpol 提高了大鼠颅骨缺损模型中骨髓间充质干细胞的骨愈合能力,并在大鼠卵巢切除骨质疏松症模型中减轻了骨丢失。JIANG等[19]以成骨诱导2周的C57/BL6小鼠原代骨髓间充质干细胞为研究对象,给予远志皂苷干预后碱性磷酸酶活性、矿化结节和成骨标志物表达增加,Wnt/β-catenin信号转导增强;进一步制备卵巢切除小鼠模型,给予远志皂苷治疗3个月,发现小鼠骨小梁厚度、骨小梁数目、骨密度等骨参数均高于对照组,说明远志皂苷具有治疗绝经后骨质疏松症的潜力。RUSSO等[20]研究表明番茄红素通过激活WNT/β-catenin和ERK1/2通路,上调Saos-2细胞RUNX2、碱性磷酸酶、COL1A表达,下调RANKL表达,有助于防止绝经后妇女骨质流失。ZHANG等[21]研究发现CTLA4修饰骨髓间充质干细胞复合脱钙骨基质促进兔桡骨缺损的骨修复效果明显优于单纯脱钙骨基质或未经修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞复合脱钙骨基质,CTLA4修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞中骨膜蛋白表达明显高于未修饰的骨髓间充质干细胞,提示CTLA4通过靶向调控骨膜蛋白的表达激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路提高骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨作用。WANG等[22]研究发现瑞舒伐他汀组p-GSK-3β的蛋白表达水平明显低于对照组,瑞舒伐他汀组β-catenin和cyclin D1的蛋白表达水平明显高于对照组。MO等[23]研究显示骨质疏松患者骨髓间充质干细胞分化为成骨细胞的量明显少于正常骨髓间充质干细胞,而香叶素使这两种骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化和增殖能力增强,但骨质疏松性患者的骨髓间充质干细胞对香叶素的反应明显低于正常的骨髓间充质干细胞,另外β-catenin在骨质疏松骨髓间充质干细胞中的表达和核蓄积减少,香叶素增加了两种骨髓间充质干细胞的核转运和β-catenin的表达。YE等[24]研究显示GP-12通过改变G0/G1到S期以及从S到G2 /M期的细胞周期进程来增强成骨细胞增殖,实时定量PCR和Western blot结果表明GP-12通过以剂量依赖方式激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路诱导骨髓间充质干细胞分化和增殖。刘珊等[25]研究显示树豆内酯A通过经典的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路及Runx-2、Osterix转录因子促进人骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。农梦妮等[26]研究发现黄精多糖可促进小鼠骨髓间充干细胞向成骨细胞分化,提示具有潜在的抗骨质疏松作用。黄精多糖上调骨髓间充质干细胞中β-catenin的表达和促进β-catenin核定位,增强β-catenin/TCF的转录活性。因此,黄精多糖通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号传导通路促进体外诱导的骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化。 2.5 RNA通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路调控骨髓间充质干细胞分化 随着科学技术的发展,调控骨髓间充质干细胞分化的因素越来越精细化。LI等[27]研究发现miRNA-291a-3p可提高骨髓间充质干细胞的细胞活力、成骨分化和碱性磷酸酶活性,而地塞米松对其有抑制作用。当miRNA-291a-3p-mimics转染后,成骨基因Runx2、DMP1和ALP上调,而成脂基因C/EBPα和PPARγ下调。此外,还证明miRNA-291a-3p通过直接抑制DKK1 mRNA和蛋白表达,进而激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,促进骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。XU等[28]研究发现骨质疏松患者中miR-889的表达上调,然而miR-889在成骨分化过程中表达下调。与对照组相比,miR-889模拟物可降低碱性磷酸酶活性和钙沉积,而miR-889抑制剂则呈相反趋势。结果表明,miR-889通过结合WNT7A中的3’UTR来降低Wnt/β-catenin信号通路活性进而负调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。LI等[29]研究发现 miR-8485靶向GSK3β抑制GSK-3β的表达,并靶向DACT1诱导p-GSK-3β(Ser9),激活Wnt/β-catenin途径。DACT1是miR-8485的另一个靶标,通过调节GSK3β抑制ser9磷酸化,而没有影响总GSK3β。因此miR-8485也通过DACT1调节GSK3β的活性来调控骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。DAI等[30]研究发现骨质疏松大鼠胫骨组织miR-23a-3p表达显著增加,PGC-1α/WNT/β-catenin信号通路被抑制。此外,通过靶向PGC-1α/WNT/β-catenin信号通路,抑制miR-23a-3p的表达可提高细胞增殖活力,抑制细胞凋亡,促进碱性磷酸酶活性和钙结节的形成。LONG等[31]研究发现miR-139-5p表达随人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化程度的降低而降低。miR-139-5p通过阻断碱性磷酸酶活性、Runx2、OCN和Col-1的表达来抑制人骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。miR-139-5p可能通过Wnt/β-catenin途径直接靶向CTNNB1和FZD4在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨中发挥作用。WANG等[32]研究发现在人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中miR-101的表达增加。miR-101通过靶向EZH2激活人骨髓间充质干细胞中的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路。Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在miR-101成骨诱导分化中的作用是促进人骨髓间充质干细胞的分化速度,抑制剂ICG-001可以抑制β-catenin活性。WANG 等[33]研究发现miR-128在大鼠骨髓干细胞成骨分化过程中有不同程度的上调。miR-128模拟物干预后,碱性磷酸酶活性、基质矿化、成骨标志物的mRNA和蛋白水平升高,促进骨髓干细胞成骨分化,而miR-128抑制剂处理后则抑制体外成骨分化。在机制上,miR-128直接作用于Wnt信号通路拮抗剂DKK2,增强了Wnt/β-catenin的信号活性。此外,miR-128对成骨分化的积极作用明显被DKK2过度表达所阻断。总之,这些结果表明miR-128通过靶向DKK2促进大鼠骨髓干细胞成骨分化。SHEN等[34]研究发现抑制HOTAIR表达后碱性磷酸酶活性、成骨标志基因表达和钙化结节数量升高。然而,HOTAIR过表达却表现出相反的效果。HOTAIR抑制Wnt/β-catenin途径相关蛋白的表达。Wnt途径拮抗剂DKK1部分逆转了HOTAIR对Wnt/β-catenin的调节作用。实验证明HOTAIR通过抑制Wnt /β-catenin信号通路抑制了骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。WANG等[35]研究发现高糖可抑制骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化,显著升高miR-214-3p的表达。分子生物学研究表明miR-214-3p通过靶向β-catenin的3’-UTR抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。miR-214-3p是1型糖尿病小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的关键调控因子。ZHOU等[36]研究发现H19在绝经后骨质疏松症患者血清和卵巢切除小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞中的表达降低,H19的过表达促进了骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。此外,Foxc2可以与Wnt4启动子结合并促进其转录。H19与Foxc2结合,H19/Foxc2协同调控Wnt启动子的表达,H19/Foxc2通过Wnt/β-catenin途径调控骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。吴斯媛[37]研究发现miRNA-590-3p 对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨向分化有促进作用,这一作用与Wnt/β-catenin信号通路相关。miR-590-3p表达水平与成骨相关因子表达水平及矿化沉积呈正相关。miR-590-3p过表达细胞系中Wnt/β-catenin信号通路水平上调,双荧光素酶实验提示APC的3’UTR是miR-590-3p的特异性结合位点。周洁[38] 发现成骨分化过程中Runx2作为成骨特异性转录因子通过与Dicer启动子结合,直接调控Dicer转录表达。Dicer在细胞成骨分化中表达增高,并对细胞成骨分化起着正向调节作用。miR-21a-5p在成骨分化过程中表达增高,抑制其靶基因PTEN蛋白表达,使Akt和GSK3β磷酸化水平升高,GSK3β磷酸化后从Axin/APC复合体分离,使复合体对β-catenin的磷酸化作用失活,胞内β-catenin堆积增多,转运入核与转录因子结合共同调控成骨相关基因表达。 2.6 蛋白类通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响骨髓间充质干细胞分化 蛋白质是人体的重要组成物质之一,广泛参与人类各种生命活动,目前在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的研究中特别稀少,近几年才开始逐渐增多,尤其是TMEM18的发现证明了成骨分化可以负方向调节。SEN等[39]研究表明β-catenin可以与EZH2增强子启动子结合,EZH2是PRC2复合物的关键组分,它催化组蛋白甲基化。当EZH2被抑制,β-catenin的抗分化效应消失,说明调节EZH2活性是β-catenin对骨髓间充质干细胞保持多能性的关键因子。SHEN等[40]研究表明在卵巢切除小鼠骨组织中FOXF1表达增加,在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中FOXF1表达降低。在体外FOXF1基因敲低显著增加成骨细胞特异基因的表达、碱性磷酸酶活性和矿化能力。此外,siFoxf1激活了Wnt/β-catenin信号通路。Foxf1表达水平与绝经后骨质疏松患者骨组织中骨量减少和骨形成呈负相关,Foxf1基因敲除显著促进人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。彭杨茜子等[41]研究发现人Rspo1诱导的LRP6磷酸化可被LRP6的拮抗剂DKK1抑制。hRspo1与低浓度的Wnt3a 可协同增强β-catenin的稳定和LRP6磷酸化,而Rspo1缺失则严重影响Rspo1依赖的Wnt/β-catenin信号通路激活。Rspo1与 LGR4/5结合并通过其传递信号激活Wnt信号通路。GERLACH等[42]将单跨膜蛋白TMEM59鉴定为FZD、LRP6的相互作用体和Wnt信号的阳性调节因子。TMEM59通过膜内相互作用促进多聚Wnt-FZD组装体的形成,随后这些Wnt-FZD-TMEM59簇与LRP6融合形成成熟的Wnt信号体。Wnt信号体积聚在细胞质中并转移至细胞核内激活靶基因的表达。KIM等[43]研究表明Tmem64是通过SERCA2依赖性Ca2+信号传导介导破骨细胞分化的阳性调节因子,但其在成骨细胞中的确切作用尚未被证实。随后,JEONG 等[44]研究发现敲除Tmem64基因可显著促进骨髓基质细胞向成骨细胞分化且抑制向脂肪细胞分化。相反,Tmem64过表达抑制成骨和加速脂肪形成。Wnt关键信号分子β-catenin在Tmem64缺陷细胞中的表达显著增加,其核移位增强。在体外共转染实验和BAT-Gal报告基因小鼠体内实验中Tmem64的引入显著抑制了β-catenin介导的转录活性。这些结果表明,Tmem64通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路调节间充质细胞谱系分配中起重要作用。ZHANG等[45]研究发现大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨诱导后Tmem18表达显著下调。机制分析表明,TMEM18基因敲除增强了β-catenin的表达,促进了其核移位。TMEM18通过下调β-catenin表达在骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化中起到抑制作用。LIU等[46]首次报道了未羧化骨钙素通过Erk-Smad/β-catenin信号途径促进小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,强调了未羧化骨钙素作为一种激素促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的重要性,表明该激素可能有助于骨质疏松和骨折愈合的治疗。 2.7 生长因子通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响骨髓间充质干细胞分化 生长因子是促进人类生长发育的一个重要影响因素,促进人类各种组织的生长其中包括骨髓间充质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化,作用机制也是复杂多样化。ZHANG 等[47]研究发现IGFBP7的过表达增强了骨特异性基因和蛋白的表达,而IGFBP7的敲低则降低了成骨特异性基因和蛋白的表达。此外,β-catenin水平通过IGFBP7的过度表达或细胞外IGFBP7蛋白的加入而上调,通过IGFBP7的耗竭而降低。特异性Wnt/β-catenin信号抑制剂可部分抑制IGFBP7过表达引起成骨分化。通过影像学、生物力学和组织学分析证明,IGFBP7过表达的骨髓间充质干细胞能够促进骨愈合。这些发现表明IGFBP7通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路部分调控骨髓间充质干细胞的成骨分化。LIANG等[48]研究发现TIMP-1敲低上调了β-catenin和cyclin D1蛋白表达。在成骨分化过程中,TIMP-1敲低可增加碱性磷酸酶活性、钙结节沉积。TIMP-1通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在骨髓间充质干细胞增殖和成骨过程中至少部分发挥负调控作用。WU等[49]研究发现Ad-BMP2/EGFP转染兔骨髓间充质干细胞后碱性磷酸酶活性增加,促进钙结节形成和Ⅰ型胶原表达,β-catenin、cyclin D1、Runx2和c-myc的表达上调,GSK3β的表达明显降低。Ad-BMP2/EGFP过表达通过激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路增强兔骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化能力。LUO等[50]研究显示Runx1通过经典的Wnt/β-catenin途径促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化,同时抑制其脂肪生成,这为成骨细胞的发育提供了新的见解。陈杨[51]研究表明转染外源性Runx2质粒减弱了高糖对骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的抑制作用。高糖环境可通过PI3K/AKT通路使p-GSK3β降低,抑制Wnt通路中β-catenin表达,使骨髓间充质干细胞成骨能力下降,转染Runx2后可一定程度上逆转这种效应。ZHAO等[52]采用胫骨单皮质缺损模型,研究MSR1在体内膜内骨化过程中的作用。MSR1介导的PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin信号增强了共培养系统中骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的能力,还发现PGC1α是MSR1激活PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin途径的靶基因,该途径通过增强线粒体氧化磷酸化促进M2样细胞极化。因此,靶向MSR1可能是一种新的骨折修复治疗策略。SCHIAVONE 等[53]研究发现尿黑酸的沉积与Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的失调密切相关,为仍然缺乏已知治疗方法的黑尿症疾病提供可能的治疗策略。王潇丽等[54]研究表明尿酸可通过促进Wnt-3a/β-catenin信号通路进而促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞增殖和分化,具有浓度依赖性。岳辰等[55]研究表明DKK-1基因沉默通过特异性抑制DKK-1过表达而重新激活Wnt/β-catenin信号通路,减少成脂基因PPAR-γ2的表达、增加成骨基因RUNX2的表达,抑制骨髓间充质干细胞成脂分化,促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。任磊等[56]研究表明Wnt/ β-Catenin激活的骨细胞其自身的Jag1、Jag2、Dll4 mRNA表达较对照组显著升高,与骨髓间充质干细胞共培养后成骨转录因子Runx2、成骨分化特异标志物ALP、Osteocalcin mRNA的表达较野生型明显升高,加入DAPT后显著下降,骨细胞调控骨的代谢是通过激活Wnt/β-Catenin信号通路来增强Notch信号进而促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化。何鹏[57]研究表明降钙素基因相关肽能显著提高MC3T3-E1细胞成骨有关基因及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路相关基因的表达,Western blot结果提示降钙素基因相关肽可以显著促进β-catenin的表达及其核内聚集,而降钙素基因相关肽受体拮抗剂与DKK1显著抑制这一作用。陈坤[58]研究表明Vaspin通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路上调Runx2表达进而促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化且呈剂量依赖性。加入阻断剂DKK后β-catenin表达量明显下降。齐奇[59]研究表明组蛋白去甲基化酶KDM4A具有促进骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的能力。β-catenin靶向抑制Kdm4a的转录,KDM4A/Wnt/β-catenin形成调节环路共同调节骨髓间充质干细胞的分化。"
| [1] BATEMAN ME, STRONG AL, MCLACHLAN JA, et al. The Effects of Endocrine Disruptors on Adipogenesis and Osteogenesis in Mesenchymal Stem Cells: A Review. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2017;7:171. [2] BAGHERI L, PELLATI A, RIZZO P,et al. Notch pathway is active during osteogenic differentiation of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells induced by pulsed electromagnetic fields. J Tissue Eng Regen Med. 2018;12(2):304-315. [3] ZHAO C, LI Y, WANG X, et al. The Effect of Uniaxial Mechanical Stretch on Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway in Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells. J Craniofac Surg. 2017;28(1):113-117. [4] ZHANG S, CHEN X, HU Y, et al. All-trans retinoic acid modulates Wnt3A-induced osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via activating the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β signalling pathway. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2016;422:243-253. [5] SHAO J, ZHANG Y, YANG T, et al. HIF-1α disturbs osteoblasts and osteoclasts coupling in bone remodeling by up-regulating OPG expression. In Vitro Cell Dev Biol Anim. 2015;51(8):808-814. [6] CHEN Q, SHOU P, ZHENG C,et al. Fate decision of mesenchymal stem cells: adipocytes or osteoblasts? Cell Death Differ. 2016;23(7): 1128-1139. [7] NIZIOLEK PJ, MACDONALD BT, KEDLAYA R, et al. High Bone Mass-Causing Mutant LRP5 Receptors Are Resistant to Endogenous Inhibitors In Vivo. J Bone Miner Res. 2015;30(10):1822-1830. [8] 依香叫,李金诚,王松月,等.刺老苞根皮含药血清对原代成骨细胞Wnt/β-catenin信号通路的影响[J].中国中药杂志, 2017, 42(14): 2749-2753. [9] 罗智,史可测,田锋.葛根素对成骨细胞体外增殖及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路表达的影响[J].海南医学院学报,2017,23(10):1319-1321, 1325. [10] 齐鹏飞,尹文哲,孙奇峰,等.失重下骨碎补总黄酮抑制JNK通路促间充质干细胞增殖的研究[J].中医学报,2016,31(11):1742-1745. [11] 陈云刚,谭国庆,任维龙,等.骨碎补含药血清经wnt/β-catenin信号通路对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[J].中国药理学通报,2017,33(6):830-836. [12] 李晨睿,孟志远,牛银波,等.黄芩苷通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的促进作用[J].中国药理学通报,2015,31(7):919-924. [13] 张哲,徐秀娟,刘欣,等.老鹳草素通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路影响小鼠骨髓基质干细胞的增殖和成骨分化[J].中华中医药学刊, 2017,35(1):215-218. [14] WEI Q, ZHANG J, HONG G, et al. Icariin promotes osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow stromal cells by activating the ERα-Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Biomed Pharmacother. 2016;84: 931-939. [15] 李新建. 基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路探讨补肾活血汤调控激素性股骨头缺血坏死BMSCs成骨-成脂分化的机制[D].福州:福建中医药大学,2016. [16] 马忠平,黄健,张志峰,等.贝尼地平对小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化体外研究[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2016, 22(4):423-427. [17] ZHAO XE, YANG Z, GAO Z, et al. 6-Bromoindirubin-3’-oxime promotes osteogenic differentiation of canine BMSCs through inhibition of GSK3β activity and activation of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. An Acad Bras Cienc. 2019;91(1):e20180459. [18] ZHU Y, WANG Y, JIA Y,et al. Catalpol promotes the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells via the Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2019;10(1):37. [19] JIANG HJ, TIAN XG, HUANG SB, et al. Tenuigenin promotes the osteogenic differentiation of bone mesenchymal stem cells in vitro and in vivo. Cell Tissue Res. 2017;367(2):257-267. [20] RUSSO C, FERRO Y, MAUROTTI S, et al. Lycopene and bone: an in vitro investigation and a pilot prospective clinical study. J Transl Med. 2020;18(1):43. [21] ZHANG F, LUO K, RONG Z, et al. Periostin Upregulates Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling to Promote the Osteogenesis of CTLA4-Modified Human Bone Marrow-Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Sci Rep. 2017;7:41634. [22] WANG BX, LI KP, YU T, et al. Rosuvastatin promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells in the rat model of osteoporosis by the Wnt/β-catenin signal. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(22):10161-10168. [23] MO J, YANG R, LI F, et al. Geraniin promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (BMSCs) via activating β-catenin: a comparative study between BMSCs from normal and osteoporotic rats. J Nat Med. 2019;73(1):262-272. [24] YE M, ZHANG C, ZHU L, et al. Yak (Bos grunniens) bones collagen-derived peptides stimulate osteoblastic proliferation and differentiation via the activation of Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Sci Food Agric. 2020;100(6):2600-2609. [25] 刘珊.树豆内酯A调节Wnt/β-catenin/runx-2信号通路促进人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的作用研究[D].广州:广州中医药大学, 2016. [26] 农梦妮.基于Wnt/β-catenin信号通路研究黄精多糖促进骨髓间充质干细胞向成骨细胞分化及其作用机制[D].南宁:广西医科大学, 2016. [27] LI ZH, HU H, ZHANG XY, et al. MiR-291a-3p regulates the BMSCs differentiation via targeting DKK1 in dexamethasone-induced osteoporosis. Kaohsiung J Med Sci. 2020;36(1):35-42. [28] XU G, DING Z, SHI HF. The mechanism of miR-889 regulates osteogenesis in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells. J Orthop Surg Res. 2019;14(1):366. [29] LI Z, WANG Y, XIANG S, et al. Chondrocytes-derived exosomal miR-8485 regulated the Wnt/β-catenin pathways to promote chondrogenic differentiation of BMSCs. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2020;523(2):506-513. [30] DAI Y, ZHENG C, LI H. Inhibition of miR-23a-3p promotes osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. J Cell Biochem. 2019 Nov 6. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29497. Online ahead of print. [31] LONG H, SUN B, CHENG L, et al. miR-139-5p Represses BMSC Osteogenesis via Targeting Wnt/β-Catenin Signaling Pathway. DNA Cell Biol. 2017;36(8):715-724. [32] WANG H, MENG Y, CUI Q, et al. MiR-101 Targets the EZH2/Wnt/β-Catenin the Pathway to Promote the Osteogenic Differentiation of Human Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Sci Rep. 2016;6:36988. [33] WANG C, QIAO X, ZHANG Z, et al. MiR-128 promotes osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells in rat by targeting DKK2. Biosci Rep. 2020;40(2):BSR20182121. [34] SHEN JJ, ZHANG CH, CHEN ZW, et al. LncRNA HOTAIR inhibited osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by regulating Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2019;23(17):7232-7246. [35] WANG R, ZHANG Y, JIN F, et al. High-glucose-induced miR-214-3p inhibits BMSCs osteogenic differentiation in type 1 diabetes mellitus. Cell Death Discov. 2019;5:143. [36] ZHOU P, LI Y, DI R, et al. H19 and Foxc2 synergistically promotes osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs via Wnt-β-catenin pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2019;234(8):13799-13806. [37] 吴斯媛. MiR-590-3p在人间充质干细胞成骨向分化过程中的作用及机制研究[D].广州:南方医科大学, 2017. [38] 周洁.核酸内切酶Dicer1在成骨分化中的作用及其上游转录调控机制研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学,2017. [39] SEN B, PARADISE CR, XIE Z, et al. β-Catenin Preserves the Stem State of Murine Bone Marrow Stromal Cells Through Activation of EZH2. J Bone Miner Res. 2020 Feb 5. doi: 10.1002/jbmr.3975. Online ahead of print. [40] SHEN G, REN H, SHANG Q, et al. Foxf1 knockdown promotes BMSC osteogenesis in part by activating the Wnt/β-catenin signalling pathway and prevents ovariectomy-induced bone loss. EBioMedicine. 2020;52:102626. [41] 彭杨茜子,刘庆梅,马彦云,等. Rspo1通过Wnt/β-catenin信号通路调节成骨细胞分化的研究进展[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2015,21(4): 504-507. [42] GERLACH JP, JORDENS I, TAURIELLO DVF, et al. TMEM59 potentiates Wnt signaling by promoting signalosome formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115(17):E3996-E4005. [43] KIM H, KIM T, JEONG BC, et al. Tmem64 modulates calcium signaling during RANKL-mediated osteoclast differentiation. Cell Metab. 2013; 17(2):249-260. [44] JEONG BC, KIM TS, KIM HS, et al. Transmembrane protein 64 reciprocally regulates osteoblast and adipocyte differentiation by modulating Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Bone. 2015;78:165-173. [45] ZHANG Y, WANG H, YIN T,et al. TMEM18 inhibits osteogenic differentiation of rat bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by inactivating β-catenin. Exp Cell Res. 2019;383(1):111491. [46] LIU Z, YANG J. Uncarboxylated osteocalcin promotes osteogenic differentiation of mouse bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells by activating the Erk-Smad/β-catenin signalling pathways. Cell Biochem Funct. 2020;38(1):87-96. [47] ZHANG W, CHEN E, CHEN M, et al. IGFBP7 regulates the osteogenic differentiation of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells via Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. FASEB J. 2018;32(4):2280-2291. [48] LIANG T, GAO W, ZHU L, et al. TIMP-1 inhibits proliferation and osteogenic differentiation of hBMSCs through Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Biosci Rep. 2019;39(1):BSR20181290. [49] WU CC, WANG F, RONG S, et al. Enhancement of osteogenesis of rabbit bone marrow derived mesenchymal stem cells by transfection of human BMP-2 and EGFP recombinant adenovirus via Wnt signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med. 2018;16(5):4030-4036. [50] LUO Y, ZHANG Y, MIAO G,et al. Runx1 regulates osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by inhibiting adipogenesis through Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Arch Oral Biol. 2019;97:176-184. [51] 陈杨. Runx2对高糖环境下干细胞成骨分化作用和机制的初步研究[D].重庆:重庆医科大学, 2017. [52] ZHAO SJ, KONG FQ, JIE J, et al. Macrophage MSR1 promotes BMSC osteogenic differentiation and M2-like polarization by activating PI3K/AKT/GSK3β/β-catenin pathway. Theranostics. 2020;10(1):17-35. [53] SCHIAVONE ML, MILLUCCI L, BERNARDINI G, et al. Homogentisic acid affects human osteoblastic functionality by oxidative stress and alteration of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol. 2020 Jan 28. doi: 10.1002/jcp.29575. Online ahead of print. [54] 王潇丽,徐丽丽,杨乃龙.尿酸对人骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化过程中Wnt信号通路的影响[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(28): 4472-4477. [55] 岳辰,张雪,温阳阳,等. siRNA慢病毒载体介导DKK-1基因沉默对骨髓间充质干细胞分化影响的实验研究[J].中华骨与关节外科杂志,2018,11(2):137-142,150. [56] 任磊,代光明,林枭,等.骨细胞Wnt/β-Catenin通过Notch信号促进BMSCs成骨分化[J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2018,24(5): 600-605. [57] 何鹏. CGRP对MC3T3-E1细胞成骨分化的影响及Wnt/β-catenin信号通路在其中的作用[D].长沙:湖南师范大学,2016. [58] 陈坤. Wnt/β-catenin信号通路对vaspin介导的大鼠骨髓间充质干细胞成骨分化的影响[D].太原:山西医科大学, 2016. [59] 齐奇.组蛋白去甲基化酶KDM4A调控骨髓基质干细胞成脂/成骨分化的作用和机制研究[D].天津:天津医科大学, 2018. [60] LIU X, BAO C, XU HHK, et al. Osteoprotegerin gene-modified BMSCs with hydroxyapatite scaffold for treating critical-sized mandibular defects in ovariectomized osteoporotic rats. Acta Biomater. 2016;42: 378-388. [61] HASEGAWA A, YONEZAWA T, TANIGUCHI N, et al. Role of Fibulin 3 in Aging-Related Joint Changes and Osteoarthritis Pathogenesis in Human and Mouse Knee Cartilage. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2017;69(3):576-585. [62] CHEN K, ZHANG C, WANG L, et al. Progress on strategies to promote vascularization in bone tissue engineering. Zhongguo Gu Shang. 2015; 28(4):383-388. |
| [1] | Pu Rui, Chen Ziyang, Yuan Lingyan. Characteristics and effects of exosomes from different cell sources in cardioprotection [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 1-. |
| [2] | Lin Qingfan, Xie Yixin, Chen Wanqing, Ye Zhenzhong, Chen Youfang. Human placenta-derived mesenchymal stem cell conditioned medium can upregulate BeWo cell viability and zonula occludens expression under hypoxia [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(在线): 4970-4975. |
| [3] | Xu Feng, Kang Hui, Wei Tanjun, Xi Jintao. Biomechanical analysis of different fixation methods of pedicle screws for thoracolumbar fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1313-1317. |
| [4] | Jiang Yong, Luo Yi, Ding Yongli, Zhou Yong, Min Li, Tang Fan, Zhang Wenli, Duan Hong, Tu Chongqi. Von Mises stress on the influence of pelvic stability by precise sacral resection and clinical validation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1318-1323. |
| [5] | Zhang Tongtong, Wang Zhonghua, Wen Jie, Song Yuxin, Liu Lin. Application of three-dimensional printing model in surgical resection and reconstruction of cervical tumor [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [6] | Zhang Yu, Tian Shaoqi, Zeng Guobo, Hu Chuan. Risk factors for myocardial infarction following primary total joint arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1340-1345. |
| [7] | Wei Wei, Li Jian, Huang Linhai, Lan Mindong, Lu Xianwei, Huang Shaodong. Factors affecting fall fear in the first movement of elderly patients after total knee or hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1351-1355. |
| [8] | Wang Jinjun, Deng Zengfa, Liu Kang, He Zhiyong, Yu Xinping, Liang Jianji, Li Chen, Guo Zhouyang. Hemostatic effect and safety of intravenous drip of tranexamic acid combined with topical application of cocktail containing tranexamic acid in total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1356-1361. |
| [9] | Xiao Guoqing, Liu Xuanze, Yan Yuhao, Zhong Xihong. Influencing factors of knee flexion limitation after total knee arthroplasty with posterior stabilized prostheses [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1362-1367. |
| [10] | Peng Zhihao, Feng Zongquan, Zou Yonggen, Niu Guoqing, Wu Feng. Relationship of lower limb force line and the progression of lateral compartment arthritis after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty with mobile bearing [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1368-1374. |
| [11] | Huang Zexiao, Yang Mei, Lin Shiwei, He Heyu. Correlation between the level of serum n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids and quadriceps weakness in the early stage after total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1375-1380. |
| [12] | Zhang Chong, Liu Zhiang, Yao Shuaihui, Gao Junsheng, Jiang Yan, Zhang Lu. Safety and effectiveness of topical application of tranexamic acid to reduce drainage of elderly femoral neck fractures after total hip arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1381-1386. |
| [13] | Wang Haiying, Lü Bing, Li Hui, Wang Shunyi. Posterior lumbar interbody fusion for degenerative lumbar spondylolisthesis: prediction of functional prognosis of patients based on spinopelvic parameters [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1393-1397. |
| [14] | Lü Zhen, Bai Jinzhu. A prospective study on the application of staged lumbar motion chain rehabilitation based on McKenzie’s technique after lumbar percutaneous transforaminal endoscopic discectomy [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1398-1403. |
| [15] | Chen Xinmin, Li Wenbiao, Xiong Kaikai, Xiong Xiaoyan, Zheng Liqin, Li Musheng, Zheng Yongze, Lin Ziling. Type A3.3 femoral intertrochanteric fracture with augmented proximal femoral nail anti-rotation in the elderly: finite element analysis of the optimal amount of bone cement [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1404-1409. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||