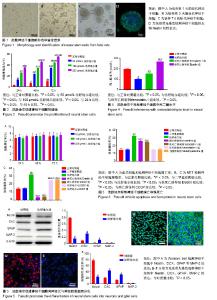
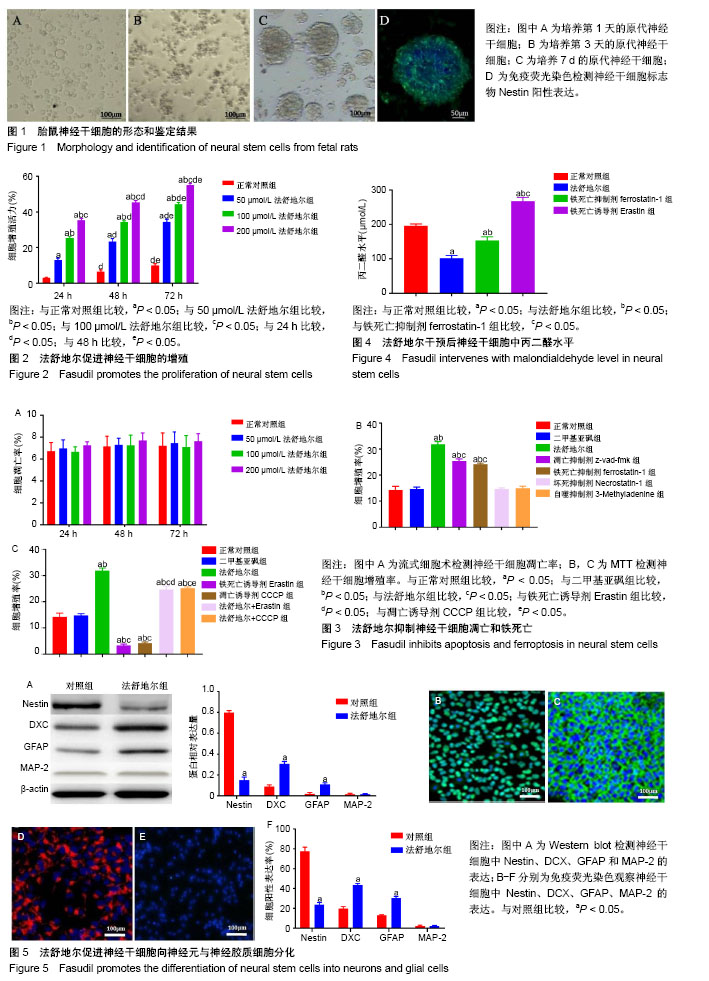
| [1] 黄志,张良明,陈瑞强,等.Purmorphamine对神经干细胞分化的影响及其机制[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(29):4675-4680.[2] Matsuda S, Nakagawa Y, Amano K, et al. By using either endogenous or transplanted stem cells, which could you prefer for neural regeneration. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(10):1731-1732.[3] Kashem MA, Sultana N, Balcar VJ. Exposure of Rat Neural Stem Cells to Ethanol Affects Cell Numbers and Alters Expression of 28 Proteins. Neurochem Res. 2018;43(9):1841-1854.[4] Zheng PD, Mungur R, Zhou HJ, et al. Ginkgolide B promotes the proliferation and differentiation of neural stem cells following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury, both in vivo and in vitro. Neural Regen Res. 2018;13(7):1204-1211.[5] Wang Y, Pan J, Wang D, et al. The Use of Stem Cells in Neural Regeneration: A Review of Current Opinion. Curr Stem Cell Res Ther. 2018;13(7):608-617.[6] Henzi R, Guerra M, Vío K, et al. Neurospheres from neural stem/neural progenitor cells (NSPCs) of non-hydrocephalic HTx rats produce neurons, astrocytes and multiciliated ependyma: the cerebrospinal fluid of normal and hydrocephalic rats supports such a differentiation. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;373(2):421-438.[7] Abdanipour A, Jafari Anarkooli I, Shokri S, et al. Neuroprotective effects of selegiline on rat neural stem cells treated with hydrogen peroxide. Biomed Rep. 2018;8(1):41-46.[8] Toyoda T, Kimura A, Tanaka H, et al. Rho-Associated Kinases and Non-muscle Myosin IIs Inhibit the Differentiation of Human iPSCs to Pancreatic Endoderm. Stem Cell Reports. 2017;9(2):419-428.[9] 李超,付红杰,张建军,等.亚低温干预下神经干细胞的RhoA/ROCK通路[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2017,21(13):2094-2099.[10] Lai AY, McLaurin J. Rho-associated protein kinases as therapeutic targets for both vascular and parenchymal pathologies in Alzheimer's disease. J Neurochem. 2018;144(5):659-668.[11] Pireddu R, Forinash KD, Sun NN, et al. Pyridylthiazole-based ureas as inhibitors of Rho associated protein kinases (ROCK1 and 2). Medchemcomm. 2012;3(6):699-709.[12] Ding J, Li QY, Yu JZ, et al. Fasudil, a Rho kinase inhibitor, drives mobilization of adult neural stem cells after hypoxia/reoxygenation injury in mice. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2010;43(2):201-208.[13] Nizamudeen ZA, Chakrabarti L, Sottile V. Exposure to the ROCK inhibitor fasudil promotes gliogenesis of neural stem cells in vitro. Stem Cell Res. 2018;28:75-86.[14] Li YH, Yu JW, Xi JY, et al. Fasudil Enhances Therapeutic Efficacy of Neural Stem Cells in the Mouse Model of MPTP-Induced Parkinson's Disease. Mol Neurobiol. 2017;54(7):5400-5413.[15] Yu JW, Li YH, Song GB, et al. Synergistic and Superimposed Effect of Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Combined with Fasudil in Experimental Autoimmune Encephalomyelitis. J Mol Neurosci. 2016; 60(4):486-497.[16] Chen S, Luo M, Zhao Y, et al. Fasudil Stimulates Neurite Outgrowth and Promotes Differentiation in C17.2 Neural Stem Cells by Modulating Notch Signalling but not Autophagy. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(2):531-541.[17] Ji YT, Chen DY, Jiang SL, et al. Effect of fasudil hydrochloride on the post-thaw viability of cryopreserved porcine adipose-derived stem cells. Cryo Letters. 2014;35(5):356-360.[18] Satoh S, Ikegaki I, Kawasaki K, et al. Pleiotropic effects of the rho-kinase inhibitor fasudil after subarachnoid hemorrhage: a review of preclinical and clinical studies. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 2014;12(5):758-765.[19] Shi J, Wei L. Rho kinases in cardiovascular physiology and pathophysiology: the effect of fasudil. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2013; 62(4):341-354.[20] Chen M, Liu A, Ouyang Y, et al. Fasudil and its analogs: a new powerful weapon in the long war against central nervous system disorders. Expert Opin Investig Drugs. 2013;22(4):537-550.[21] Gao H, Dou L, Shan L, et al. Proliferation and committed differentiation into dopamine neurons of neural stem cells induced by the active ingredients of radix astragali. Neuroreport. 2018;29(7):577-582.[22] Hu YD, Zhao Q, Zhang XR, et al. Comparison of the properties of neural stem cells of the hippocampus in the tree shrew and rat in vitro. Mol Med Rep. 2018;17(4):5676-5683.[23] Karimzadeh S, Hosseinkhani S, Fathi A, et al. Insufficient Apaf-1 expression in early stages of neural differentiation of human embryonic stem cells might protect them from apoptosis. Eur J Cell Biol. 2018;97(2): 126-135.[24] Wang C, Lu CF, Peng J, et al. Roles of neural stem cells in the repair of peripheral nerve injury. Neural Regen Res. 2017;12(12):2106-2112.[25] Pakvasa M, Alverdy A, Mostafa S, et al. Neural EGF-like protein 1 (NELL-1): Signaling crosstalk in mesenchymal stem cells and applications in regenerative medicine. Genes Dis. 2017;4(3):127-137.[26] Zhang F, Duan X, Lu L, et al. In Vivo Long-Term Tracking of Neural Stem Cells Transplanted into an Acute Ischemic Stroke model with Reporter Gene-Based Bimodal MR and Optical Imaging. Cell Transplant. 2017; 26(10):1648-1662.[27] Dong H, Lin X, Li Y, et al. Genetic deletion of Rnd3 in neural stem cells promotes proliferation via upregulation of Notch signaling. Oncotarget. 2017;8(53):91112.[28] Rajan TS, Scionti D, Diomede F, et al. Prolonged Expansion Induces Spontaneous Neural Progenitor Differentiation from Human Gingiva- Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cell Reprogram. 2017;19(6):389-401.[29] 宋国斌,席国萍,尉杰忠,等.Fasudil促进体外培养骨髓源神经干细胞的增殖与存活[J].细胞与分子免疫学杂志, 2015,31(11):1488-1496.[30] Fearnhead HO, Vandenabeele P, Vanden Berghe T. How do we fit ferroptosis in the family of regulated cell death. Cell Death Differ. 2017; 24(12):1991-1998.[31] Latunde-Dada GO. Ferroptosis: Role of lipid peroxidation, iron and ferritinophagy. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017;1861(8):1893-1900.[32] Dixon SJ. Ferroptosis: bug or feature. Immunol Rev. 2017;277(1):150-157.[33] Angeli JPF, Shah R, Pratt DA, et al. Ferroptosis Inhibition: Mechanisms and Opportunities. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 2017;38(5):489-498.[34] Chen S, Luo M, Zhao Y, et al. Fasudil Stimulates Neurite Outgrowth and Promotes Differentiation in C17.2 Neural Stem Cells by Modulating Notch Signalling but not Autophagy. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;36(2): 531-541.[35] 沈雷,张博爱,贾延劼,等.盐酸法舒地尔对体外培养大鼠神经干细胞分化的影响[J].山东医药,2010,50(9):28-29. |