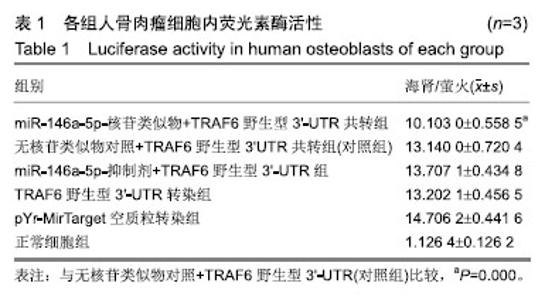
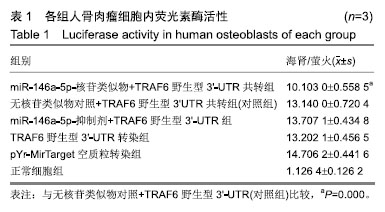
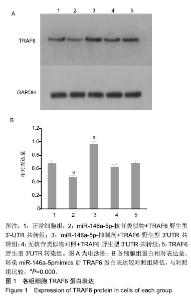
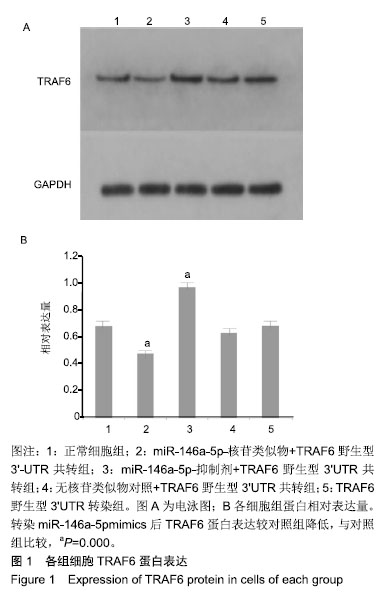
| [1]LiShiying, Qian Tianmei, Wang Xinghui,et al. Noncoding RNAs and Their Potential Therapeutic Applications in Tissue Engineering.Engineering.2017;3(1):3-15.[2]Toh WS, Lai RC, Zhang B,etal.MSC exosome works through a protein-based mechanism of action.BiochemSoc Trans. 2018;46(4):843-853[3]Zhong X, Zhang D, Xiong M, et al.Noncoding RNA for Cancer Gene Therapy. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2016;209:51-60.[4]Yao S. MicroRNA biogenesis and their functions in regulating stem cell potency and differentiation.BiolProced Online. 2016;18:1-10.[5]邓强,张亚楼,周杨俊杰,等. 氟化钠诱导人成骨细胞凋亡相关microRNA差异表达及分析[J].中国组织工程研究,2018,22(8): 1149-1154.[6]Min SK, Jung SY, Kang HK, et al.Functional diversity of miR-146a-5p and TRAF6 in normal and oral cancer cells. Int J Oncol.2017;51(5):1541-1552.[7]Peng S, Gao D, Gao C, et al. MicroRNAs regulate signaling pathways in osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Mol Med Rep.2016;14(1):623-9.[8]Wang W, Wang X, Chen L, et al.The microRNA miR-124 suppresses seizure activity and regulates CREB1 activity. Expert Rev Mol Med. 2016;18:e4.[9]Nicolas FE. Experimental validation of microRNA targets using a luciferase reporter system. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;732:139-52.[10]Huntley RP, Kramarz B, Sawford T, et al. Expanding the horizons of microRNA bioinformatics.RNA. 2018,24(8): 1005-1017.[11]马国福.氟骨症临床与影像学诊断[J]. 影像研究与医学应用, 2017,1(12): 55-56.[12]史睿亭,李维维,徐泽华. 地方性氟骨症治疗的研究进展[J].生物技术世界,2015,(5):81.[13]Lima VV, de Almeida Carrer FC, Gabriel M, et al. Knowledge of primary care professionals about fluoride topics. Minerva Stomatol.2016;67(5):196-201.[14]Liu L1, Zhang Y, GuH,et al. Fluorosis induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis in osteoblasts in vivo[J]. Biol Trace Elem Res.2015;164(1):64-71.[15]Li J, Zhao L, Zhao X ,et al. Foxo1 Attenuates NaF-Induced Apoptosis of LS8 Cells through the JNK and Mitochondrial Pathways. Biol Trace Elem Res.2018;181(1):104-111.[16]Suzuki M, Bandoski C, Bartlett JD. Fluoride induces oxidative damage and SIRT1/autophagy through ROS-mediated JNK signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2015,89:369-378.[17]陈荣,于燕妮,徐淋,等. mTOR自噬通路在染氟大鼠软骨关节损伤中的作用[J]. 中国地方病防治杂志2017,32(1):18-19.[18]Wang Y, Li Y. miR-146 promotes HBV replication and expression by targeting ZEB2. Biomed Pharmacother. 2018;99:576-582.[19]Testa U, Pelosi E, Castelli G, et al.miR-146 and miR-155: Two Key Modulators of Immune Response and Tumor Development. Noncoding RNA. 2017;3(3). pii: E22.[20]Wang H, Zhang Y, Wu X, et al. Regulation of Human Natural Killer Cell IFN-γ Production by MicroRNA-146a via Targeting the NF-κB Signaling Pathway.Front Immunol.2018;9:293.[21]Li P, Sun N, Zeng J, et al. Differential expression of miR-672-5p and miR-146a-5p in osteoblasts in rats after steroid intervention. Gene. 2016; 591(1):69-73.[22]Waki T, Lee SY, Niikura T, et al. Pro?ling microRNA expression in fracture nonunions: potential role of microRNAs in nonunion formation studied in a rat model. Bone Joint J.2015;97-B (8), 1144–1151.[23]Xi Y, Jiang T, Wang W, et al. Long non-coding HCG18 promotes intervertebral disc degeneration by sponging miR-146a-5p and regulating TRAF6 expression. Sci Rep.2017;7(1):13234[24]Xu B, Huang Y, Niu X, et al.Hsa-miR-146a-5p modulates androgen-independent prostate cancer cells apoptosis by targeting ROCK1.Prostate. 2015;75(16):1896-903.[25]Pan Q, Liu H, Zheng C, et al.Microvesicles Derived from Inflammation-Challenged Endothelial Cells Modulate Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Functions.Front Physiol.2017;7:692.[26]Li H, Xie S, Liu M, et al. The clinical signi?cance of downregulation of mir-1243p, mir-146a-5p, mir-155-5p and mir-335-5p in gastric cancer tumorigenesis. Int J Oncol. 2014;45 (1), 197–208.[27]Lu Y, Cao L, Jiang, B.C, et al., MicroRNA-146a-5p attenuates neuropathic pain via suppressing TRAF6 signaling in the spinal cord. Brain BehavImmun.2015;49, 119–129.[28]王珊,李晓霞,周杰,等.Nfic基因3’UTR双荧光素酶报告质粒的构建及其与miR-20a靶向关系的验证[J].天津医药,2016, 9(44): 1065-1068[29]Lee JY, Kim S, Hwang DW, et al.Development of a dual-luciferase reporter system for in vivo visualization of MicroRNA biogenesis and posttranscriptional regulation.J Nucl Med.2008;49(2):285-94.[30]Wu GQ, Wang X, Zhou HY, et al.Evidence for transcriptional interference in a dual-luciferase reporter system.Sci Rep. 2015;5:17675. |