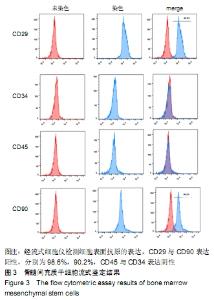
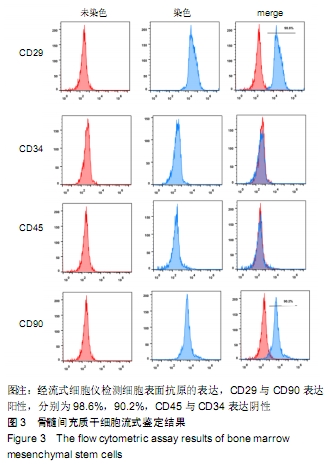
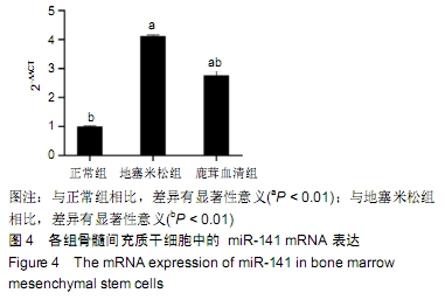
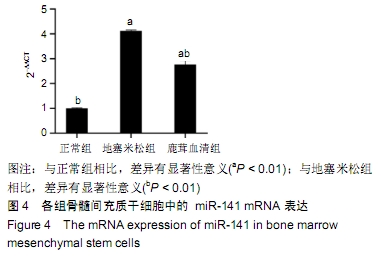
[1] SHIGEMURA T, NAKAMURA J, KISHIDA S, et al. Incidence of osteonecrosis associated with corticosteroid therapy among different underlying diseases: prospective MRI study. Rheumatology (Oxford). 2011;50(11):2023-2028.
[2] JONES JP JR. Fat embolism and osteonecrosis. Orthop Clin North Am. 1985;16(4):595-633.
[3] XU X, WEN H, HU Y, et al. STAT1-caspase 3 pathway in the apoptotic process associated with steroid-induced necrosis of the femoral head. J Mol Histol. 2014;45(4):473-485.
[4] PITTENGER MF, MACKAY AM, BECK SC, et al. Multilineage potential of adult human mesenchymal stem cells. Science. 1999;284(5411):143-147.
[5] MATSUYA H, KUSHIDA T, ASADA T, et al. Regenerative effects of transplanting autologous mesenchymal stem cells on corticosteroid-induced osteonecrosis in rabbits. Mod Rheumatol. 2008;18(2):132-139.
[6] LEE JS, LEE JS, ROH HL, et al. Alterations in the differentiation ability of mesenchymal stem cells in patients with nontraumatic osteonecrosis of the femoral head: comparative analysis according to the risk factor. J Orthop Res. 2006;24(4):604-609.
[7] FARAZI TA, SPITZER JI, MOROZOV P, et al. miRNAs in human cancer. J Pathol. 2011;223(2):102-115.
[8] SHI C, HUANG P, KANG H, et al. Glucocorticoid inhibits cell proliferation in differentiating osteoblasts by microRNA-199a targeting of WNT signaling. J Mol Endocrinol. 2015;54(3): 325-337.
[9] WEI ZJ, FAN BY, LIU Y, et al. MicroRNA changes of bone marrow-derived mesenchymal stem cells differentiated into neuronal-like cells by Schwann cell-conditioned medium. Neural Regen Res. 2019;14(8):1462-1469.
[10] WANG N, LI P, LIU W, et al. miR-141-3p suppresses proliferation and promotes apoptosis by targeting GLI2 in osteosarcoma cells. Oncol Rep. 2018;39(2):747-754.
[11] LONG ZH, BAI ZG, SONG JN, et al. miR-141 Inhibits Proliferation and Migration of Colorectal Cancer SW480 Cells. Anticancer Res. 2017;37(8):4345-4352.
[12] DE ALMEIDA DC, BASSI ÊJ, AZEVEDO H, et al. A Regulatory miRNA-mRNA Network Is Associated with Tissue Repair Induced by Mesenchymal Stromal Cells in Acute Kidney Injury. Front Immunol. 2017;7:645.
[13] SANGANI R, PERIYASAMY-THANDAVAN S, KOLHE R, et al. MicroRNAs-141 and 200a regulate the SVCT2 transporter in bone marrow stromal cells. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2015;410: 19-26.
[14] 蔡文君. 基于LIF因子探讨鹿茸多肽对骨髓间充质干细胞作用的实验研究[D].长春:长春中医药大学,2017.
[15] 张立岩,孙新,田丹,等.兔早期激素性股骨头缺血性坏死模型建立及其 MRI 与病理特征研究[J].中国修复重建外科杂志, 2015, 29(10):1240-1243.
[16] PROCKOP DJ. Marrow stromal cells as stem cells for nonhematopoietic tissues. Science. 1997;276(5309):71-74.
[17] LI Z, GE X, LU J, et al. MiR-141-3p regulates proliferation and senescence of stem cells from apical papilla by targeting YAP. Exp Cell Res. 2019;383(2):111562.
[18] 张文明. miR-141调控OP小鼠BMSCs 成骨分化机制及健骨颗粒干预作用研究[D].福州:福建中医药大学, 2016.
[19] 张洪长,张莹,刘明昕,等.鹿茸多肽对人骨髓间充质干细胞 BMP-2和Runx2表达的影响[J].吉林大学学报(医学版),2015, 41(3):491-495.
[20] 林建华,修忠标,吴朝阳,等.鹿茸多肽对兔骨髓间质干细胞体外增殖的影响[J].中华实验外科杂志,2005,22(7):827-828.
[21] 赵振群,张志峰,刘万林,等.激素性股骨头坏死过程中低氧诱导因子1α与骨细胞凋亡[J].中国组织工程研究,2015,19(51): 8201-8207.
[22] 孙庆鹏,皮红林,何继文,等.EZH2抑制剂GSK126对激素性股骨头坏死骨髓间充质干细胞增殖的影响[J].中国矫形外科杂志, 2018,26(23):2183-2188.
[23] LIU W, ZHAO Z, NA Y, et al. Dexamethasone-induced production of reactive oxygen species promotes apoptosis via endoplasmic reticulum stress and autophagy in MC3T3-E1 cells. Int J Mol Med. 2018;41(4):2028-2036.
|