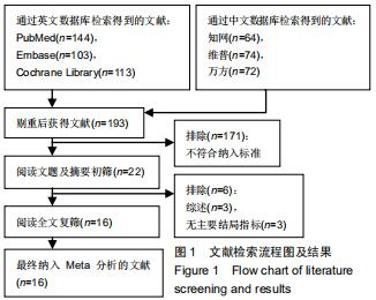
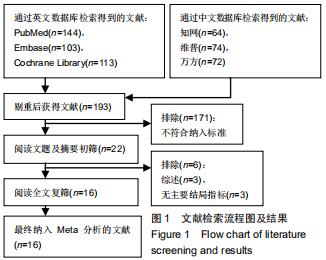
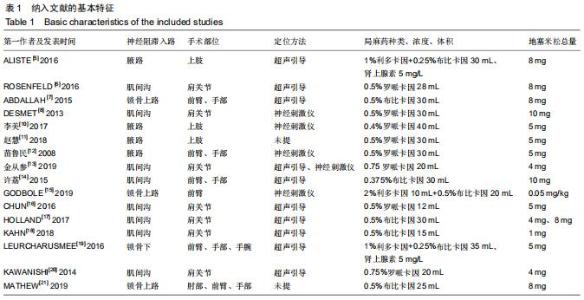
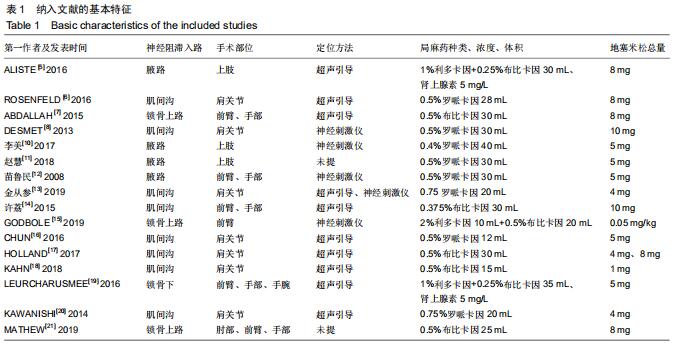
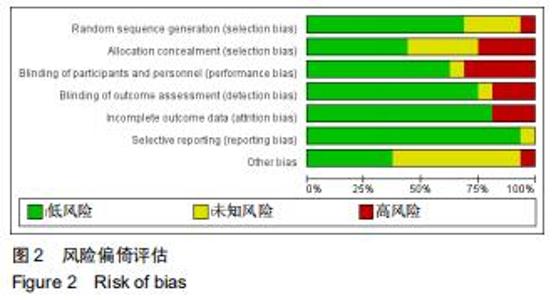
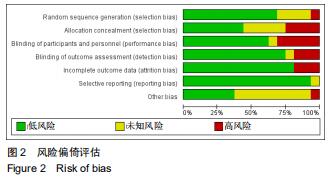
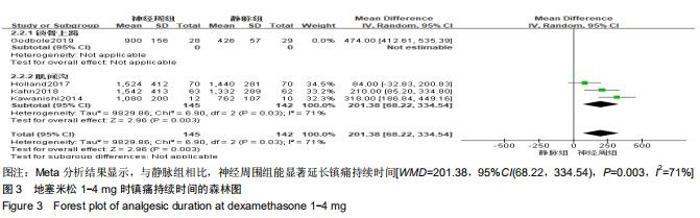
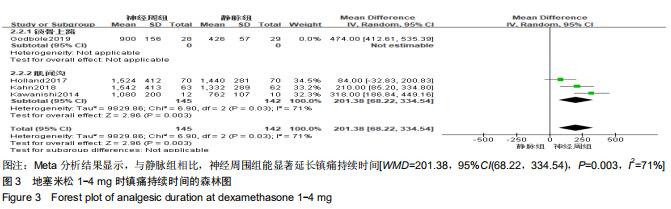
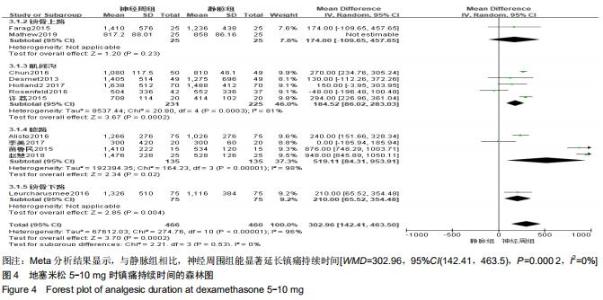
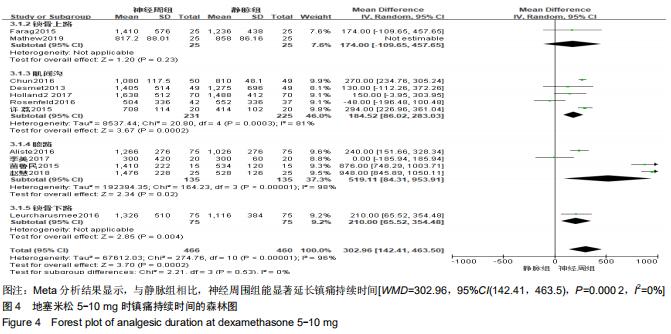
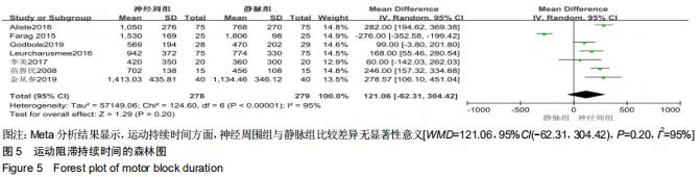
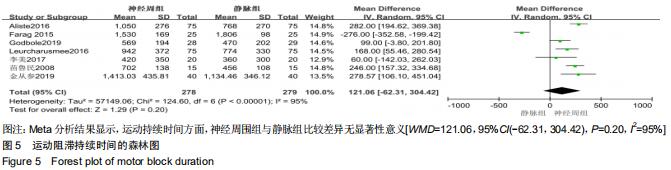
Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research ›› 2020, Vol. 24 ›› Issue (29): 4751-4756.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2787
The best route and dose of dexamethasone for brachial plexus block: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Zhang Qing1, Fan Junbai2, Zhao Xiaoyu1
1Department of Anesthesiology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China; 2Department of Anesthesiology, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China
-
Received:2019-11-13Revised:2019-11-16Accepted:2020-01-07Online:2020-10-18Published:2020-09-16 -
Contact:Fan Junbai, Professor, Department of Anesthesiology, Second Hospital of Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China -
About author:Zhang Qing, Master candidate, Department of Anesthesiology, Shanxi Medical University, Taiyuan 030000, Shanxi Province, China -
Supported by:the Innovation and Entrepreneurship Funding of Shanxi Medical University, No. 20160406
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhang Qing, Fan Junbai, Zhao Xiaoyu. The best route and dose of dexamethasone for brachial plexus block: a systematic review and meta-analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2020, 24(29): 4751-4756.
share this article
|
[1] SRUB B, SONDEREGGER J, CAMPE A, et al. What benefits does ultrasound-guided axillary block for brachial plexus anaesthesia offer over the conventional blind approach in hand surgery? J Hand Surg Eur. 2011;36(9):778-786.
[2] MARIANO ER, AFRA R, LOLAND VJ, et al. Continuous interscalene brachial plexus block via an ultrasound-guided posterior approach: a randomized, triple-masked, placebo-controlled study. Anesth Analg. 2009;108(5):1688-1694.
[3] GAN TJ. Poorly controlled postoperative pain: prevalence, consequences, and prevention. J Pain Res. 2017;28(10);2287-2298.
[4] MARHOFER P, HOPKINS PM. Dexamethasone in regional anaesthesia: travelling up a blind alley? Anaesthesia. 2019;74(8): 969-972.
[5] ALISTE J, LEURCHARUSMEE P, ENGSUSOPHON P, et al. A randomized comparison between intravenous and perineural dexamethasone for ultrasound-guided axillary block. Can J Anaesth. 2017;64(1):29-36.
[6] ROSENFELD DM, IVANCIC MG, HATTRUP SJ, et al.Perineural versus intravenous dexamethasone as adjuncts to local anaesthetic brachial plexus block for shoulder surgery.Anaesthesia. 2016;71(4): 380-388.
[7] ABDALLAH FW, JOHNSON J, CHAN V, et al. Intravenous dexamethasone and perineural dexamethasone similarly prolong the duration of analgesia after supraclavicular brachial plexus block: a randomized, triple-arm, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2015;40(2):125-132.
[8] DESMET M, BRAEMS H, REYNVOET M, et al. I.V. and perineural dexamethasone are equivalent in increasing the analgesic duration of a single-shot interscalene block with ropivacaine for shoulder surgery: a prospective, randomized, placebo-controlled study. Br J Anaesth. 2013;111(3):445-452.
[9] RAHANGDALE R, KENDALL MC, MCCARTHY RJ, et al.The effects of perineural versus intravenous dexamethasone on sciatic nerve blockade outcomes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Anesth Analg. 2014;118(5):1113-1119.
[10] 李美,于泳浩,李平.不同剂量地塞米松对罗哌卡因臂丛神经阻滞效果的影响[J].中国中西医结合外科杂志. 2017, 23(6):621-625.
[11] 赵慧.地塞米松对罗哌卡因臂丛神经阻滞效果的影响分析[J].中国实用医药,2018,13(29):140-141.
[12] 苗鲁民,周国强,于泳浩,等.地塞米松对罗哌卡因臂丛神经阻滞效果的影响[J].天津医药,2008,36(9):682-684.
[13] 金从参,吴君斐.地塞米松复合罗哌卡因在超声引导下肌间沟臂丛神经阻滞中的临床应用[J].浙江创伤外科,2019,24(2):396-398.
[14] 许荔,查本俊,邓莎,等.超声引导下左旋布比卡因联合地塞米松对臂丛神经阻滞的效果观察[J].临床军医杂志,2015,43(11):856-857.
[15] GODBOLE MR, KARHADE SS, PARIHAR PP, et al. A prospective study of comparison of analgesic efficacy of dexamethasone as an adjuvant in supraclavicular block with intravenous dexamethasone after supraclavicular block in patients undergoing forearm surgeries. Anesth Essays Res. 2019;13(1):31-35.
[16] CHUN EH, KIM YJ, WOO JH. Which is your choice for prolonging the analgesic duration of single-shot interscalene brachial blocks for arthroscopic shoulder surgery? intravenous dexamethasone 5 mg vs. perineural dexamethasone 5 mg randomized, controlled, clinical trial. Medicine (Baltimore). 2016;95(23):e3828.
[17] HOLLAND D, AMADEO RJJ, WOLFE S, et al. Effect of dexamethasone dose and route on the duration of interscalene brachial plexus block for outpatient arthroscopic shoulder surgery: a randomized controlled trial. Can J Anaesth. 2018;65(1):34-45.
[18] KAHN RL, CHENG J, GADULOV Y,et al. Perineural low-dose dexamethasone prolongs interscalene block analgesia with bupivacaine compared with systemic dexamethasone: a randomized trial. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2018;43(6):572-579.
[19] LEURCHARUSMEE P, ALISTE J, VAN ZUNDERT TC, et al. A multicenter randomized comparison between intravenous and perineural dexamethasone for ultrasound-guided infraclavicular block. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2016;41(3):328-333.
[20] KAWANISHI R, YAMAMOTO K, TOBETTO Y, et al. Perineural but not systemic low-dose dexamethasone prolongs the duration of interscalene block with ropivacaine: a prospective randomized trial. Local Reg Anesthesia.2014;7(1):5-9.
[21] MATHEW R, RADHA KR, HEMA VR, et al. Effect of perineural and intravenous dexamethasone on duration of analgesia in supraclavicular brachial plexus block with bupivacaine: a comparative study. Anesth Essays Res. 2019 ;13(2):280-283.
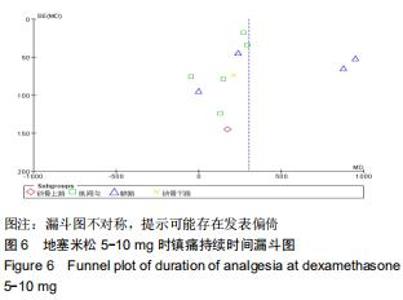
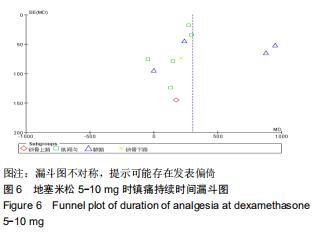
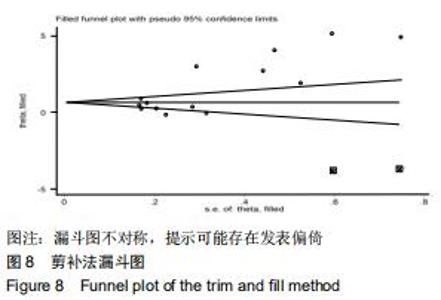
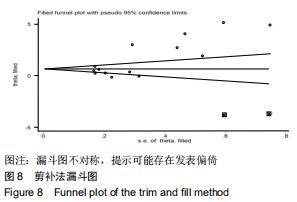
[22] 王丹,牟振云,翟俊霞,等.Stata软件在Meta分析发表性偏倚识别中的探讨[J].现代预防医学,2008,35(15):2819-2822.
[23] SHRESTHA BR, MAHARJAN SK, TABEDAR S. Supraclavicular brachial plexus block with and without dexamethasone-a comparative study.Kathmandu Univ Med J(KUMJ). 2003;1(3):158-160.
[24] FREDRICKSON FANZCA MJ, DANESH-CLOUGH TK, WHITE R. Adjuvant dexamethasone for bupivacaine sciatic and ankle blocks: results from 2 randomized placebo-controlled trials. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2013;38(4):300-307.
[25] SARITAS A, SABUNCU C. Comparison of clinical effects of prilocaine, dexamethasone added to prilocaine and levobupivacaine on brachial plexus block. J Pak Med Assoc. 2014;64(4):433-436.
[26] WILLIAMS BA, HOUGH KA, TSUI BY, et al. Neurotoxicity of adjuvants used in perineural anesthesia and analgesia in comparison with ropivacaine. Reg Anesth Pain Med. 2011;36(3):225-230.
[27] MA R, WANG X, LU C, et al. Dexamethasone attenuated bupivacaine- induced neuron injury in vitro through a threonine-serine protein kinase B-dependent mechanism. Send Neurosci. 2010;167(2):329-342.
[28] WANG PH, TSAI CL, LEE JS, et al. Effects of topical corticosteroids on the sciatic nerve: an experimental study to adduce the safety in treating carpal tunnel syndrome. J Hand Surg Eur. 2011;36(3):236-243.
[29] MOVAFEGH A, RAZAZIAN M, HAJIMAOHAMADI F, et al. Dexamethasone added to lidocaine prolongs axillary brachial plexus blockade.Anesth Analg. 2006; 102(1) :263-267.
[30] KIRKHAM KR, JACOT-GUILLARMOD A, ALBRECHT E. Optimal dose of perineural dexamethasone to prolong analgesia after brachial plexus blockade: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Anesth Analg. 2018;126(1):270-279.
[31] VYVEY M. Steroids as pain relief adjuvants. Can Fam Physician. 2010; 56(12):1295-1297, e415.
[32] JOHANSSON A, HAO J, SJÖLUND B. Local corticosteroid application blocks transmission in normal nociceptive C-fibres. Acta Anaesthesiol Scand. 1990;34(5):335-338. |
| [1] | Chen Junming, Yue Chen, He Peilin, Zhang Juntao, Sun Moyuan, Liu Youwen. Hip arthroplasty versus proximal femoral nail antirotation for intertrochanteric fractures in older adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1452-1457. |
| [2] | Chen Jinping, Li Kui, Chen Qian, Guo Haoran, Zhang Yingbo, Wei Peng. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of tranexamic acid in open spinal surgery [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1458-1464. |
| [3] | Hu Kai, Qiao Xiaohong, Zhang Yonghong, Wang Dong, Qin Sihe. Treatment of displaced intra-articular calcaneal fractures with cannulated screws and plates: a meta-analysis of 15 randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1465-1470. |
| [4] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Comparison of the short-term efficacy of extracorporeal shock wave therapy for middle-aged and elderly knee osteoarthritis: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(9): 1471-1476. |
| [5] | Wang Yongsheng, Wu Yang, Li Yanchun. Effect of acute high-intensity exercise on appetite hormones in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(8): 1305-1312. |
| [6] | Kong Desheng, He Jingjing, Feng Baofeng, Guo Ruiyun, Asiamah Ernest Amponsah, Lü Fei, Zhang Shuhan, Zhang Xiaolin, Ma Jun, Cui Huixian. Efficacy of mesenchymal stem cells in the spinal cord injury of large animal models: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(7): 1142-1148. |
| [7] | Zhang Nianjun, Chen Ru. Analgesic effect of cocktail therapy combined with femoral nerve block on total knee arthroplasty [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 866-872. |
| [8] | Huang Dengcheng, Wang Zhike, Cao Xuewei. Intravenous, topical tranexamic acid alone or their combination in total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 948-956. |
| [9] | Li Yan, Wang Pei, Deng Donghuan, Yan Wei, Li Lei, Jiang Hongjiang. Electroacupuncture for pain control after total knee arthroplasty: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 957-963. |
| [10] | He Xiangzhong, Chen Haiyun, Liu Jun, Lü Yang, Pan Jianke, Yang Wenbin, He Jingwen, Huang Junhan. Platelet-rich plasma combined with microfracture versus microfracture in the treatment of knee cartilage lesions: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 964-969. |
| [11] | Hua Haotian, Zhao Wenyu, Zhang Lei, Bai Wenbo, Wang Xinwei. Meta-analysis of clinical efficacy and safety of antibiotic artificial bone in the treatment of chronic osteomyelitis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 970-976. |
| [12] | Zhan Fangbiao, Cheng Jun, Zou Xinsen, Long Jie, Xie Lizhong, Deng Qianrong. Intraoperative intravenous application of tranexamic acid reduces perioperative bleeding in multilevel posterior spinal surgery: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(6): 977-984. |
| [13] | Zhong Yuanming, Wan Tong, Zhong Xifeng, Wu Zhuotan, He Bingkun, Wu Sixian. Meta-analysis of the efficacy and safety of percutaneous curved vertebroplasty and unilateral pedicle approach percutaneous vertebroplasty in the treatment of osteoporotic vertebral compression fracture [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 456-462. |
| [14] | Li Yang, Zhang Mingyong. Meta-analysis of the effect of double Endobutton and clavicular hook plate on the treatment of acromioclavicular dislocation [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 463-470. |
| [15] | Li Yanle, Yue Xiaohua, Wang Pei, Nie Weizhi, Zhang Junwei, Tan Yonghai, Jiang Hongjiang. Intramedullary nail fixation versus plate fixation in the treatment of displaced midshaft clavicular fractures in adults: a meta-analysis [J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2021, 25(3): 471-476. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||