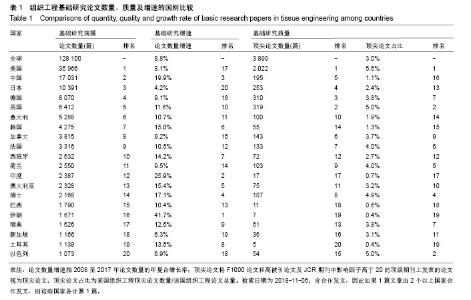
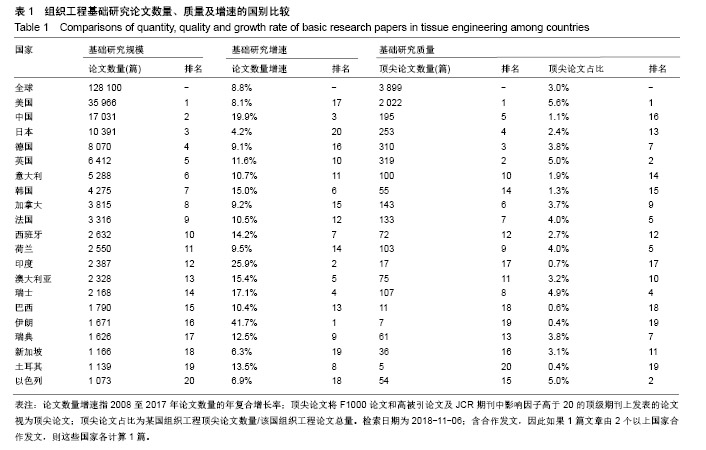
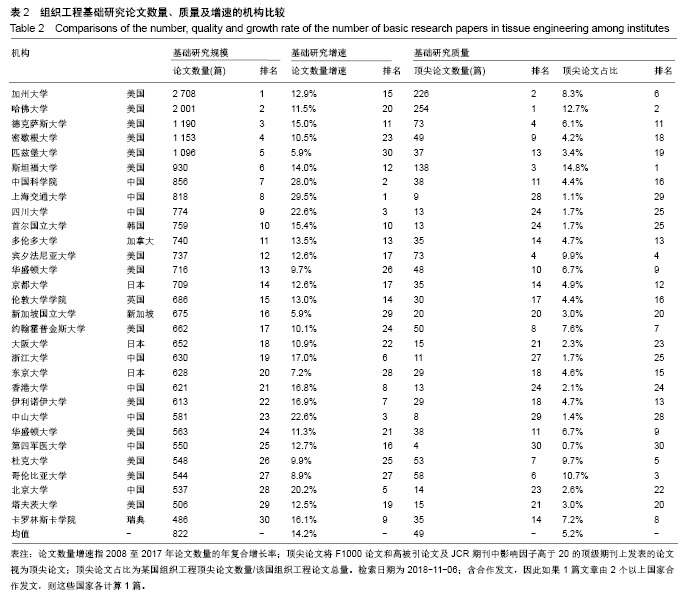
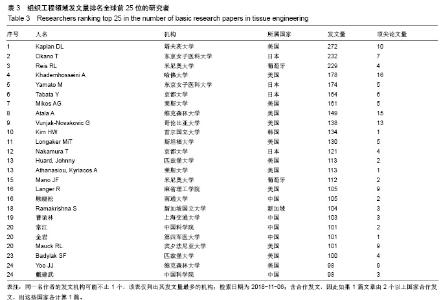
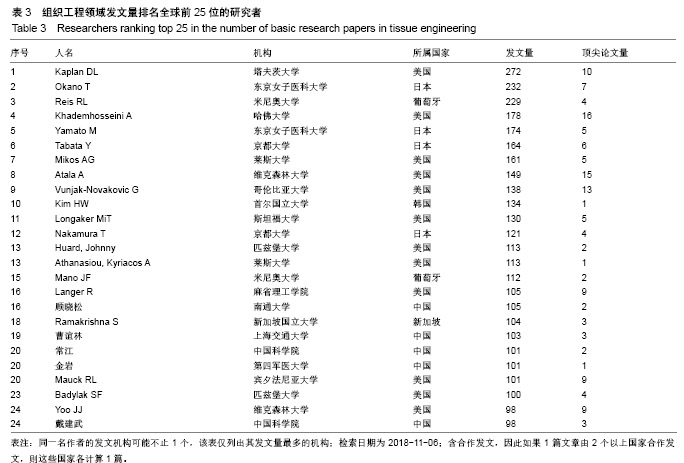
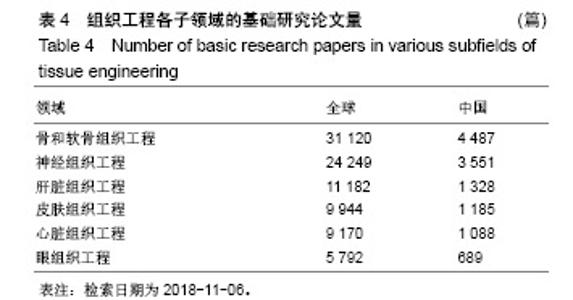
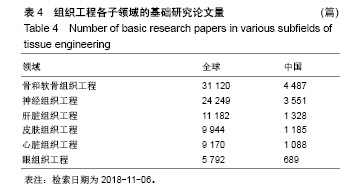
| [1]冯刚.生物材料和再生医学的进展[J].现代经济信息, 2017,38(17): 377-379.[2]王莉莎,贾红春.对临床康复、组织工程、再生医学学科定义以及相关内涵的认识与理解[J].中国组织工程研究与临床康复, 2007, 11(5):801-806.[3]Langer R.Perspectives and challenges in tissue engineering and regenerative medicine. Adv Mater. 2009;21(32-33): 3235-3236.[4]Atala A.Organ preservation, organ and cell transplantation, tissue engineering, and regenerative medicine: the terms may change, but the goals remain the same.Tissue Eng Part A. 2014; 20(3-4):445-446.[5]Atala A.Tissue engineering and regenerative medicine: concepts for clinical application. Rejuvenation Res. 2004; 7(1):15-31.[6]Liu W,Cao Y.Translational Research of Tissue Engineering in China.Tissue Eng Part A.2019;25(7-8):518-521.[7]Caplan AI.Tissue Engineering: Then, Now and the Future. Tissue Eng Part A.2019;25(7-8):515-517.[8]Milne CP,Kaitin KI.Challenge and Change at the Forefront of Regenerative Medicine. Clin Ther. 2018;40(7):1056-1059.[9]Trommelmans L.The challenge of regenerative medicine. Hastings Cent Rep.2010;40(6):24-26.[10]王正国.中国再生医学研究现状及展望[J].中国实用内科杂志, 2012,32(8):561-564.[11]谭谦.再生医学与组织工程[J].医学研究生学报, 2011,24(2): 113-116.[12]石颖.从国际顶级期刊的论文发表看广东省基础研究的水平与影响力[J].现代情报,2014,34(1):69-73.[13]吴国雄,赵庚新.基于SCI论文的海峡两岸基础研究领域合作状况研究[J].中国基础科学,2013,15(2):36-41.[14]李国栋.基于SCI论文产出的我国基础研究比较分析[J].北华航天工业学院学报,2010,20(4):21-23.[15]陈娟,贾晓峰.我国医学基础理论研究水平、学科分布及趋势分析[J].中华医学科研管理杂志,2015,28(6): 453-456,460.[16]Bornmann L,Daniel HD.Selecting scientific excellence through committee peer review - A citation analysis of publications previously published to approval or rejection of post-doctoral research fellowship applicants. Scientometrics. 2006;68(3):427-440.[17]刘雪立.基于Web of Science和ESI数据库高被引论文的界定方法[J].中国科技期刊研究,2012,23(6): 975-978.[18]池慧,欧阳昭连.中国医疗器械创新力发展报告[M].北京:科学出版社,2018.[19]陈娟,张婷,欧阳昭连.我国医疗器械领域基础研究态势分析[J].医疗卫生装备,2019,40(1):69-72.[20]孙晓北.组织工程及其我国发展问题对策研究[D].北京:中国协和医科大学,2009.[21]陈兆莹.关于科技评价和科技评价改革的讨论[J].科学通报, 2018, 63(7):611-617.[22]王海燕,张昕妍.我国科技评价体系改革的困境与对策[J].中国软科学,2018,33(4):10-17.[23]Gu X, Ding F, Yang Y, et al. Construction of tissue engineered nerve grafts and their application in peripheral nerve regeneration. Prog Neurobiol.2011;93(2):204-230.[24]曹谊林.“耳郭软骨组织工程的研究进展”点评[J].中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志,2018,18(4):238-239.[25]刘宁华,张天宇.耳郭软骨组织工程的研究进展[J].中国眼耳鼻喉科杂志,2018,18(4):234-237.[26]Wu C,Zhou Y,Xu M,et al.Copper-containing mesoporous bioactive glass scaffolds with multifunctional properties of angiogenesis capacity, osteostimulation and antibacterial activity. Biomaterials.2013;34(2):422-433. [27]郝文丽,张平,吴训伟.组织工程皮肤的现状和展望[J].北京生物医学工程,2016,35(1):94-99. |